Tiancheng He
RareAlert: Aligning heterogeneous large language model reasoning for early rare disease risk screening
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Missed and delayed diagnosis remains a major challenge in rare disease care. At the initial clinical encounters, physicians assess rare disease risk using only limited information under high uncertainty. When high-risk patients are not recognised at this stage, targeted diagnostic testing is often not initiated, resulting in missed diagnosis. Existing primary care triage processes are structurally insufficient to reliably identify patients with rare diseases at initial clinical presentation and universal screening is needed to reduce diagnostic delay. Here we present RareAlert, an early screening system which predict patient-level rare disease risk from routinely available primary-visit information. RareAlert integrates reasoning generated by ten LLMs, calibrates and weights these signals using machine learning, and distils the aligned reasoning into a single locally deployable model. To develop and evaluate RareAlert, we curated RareBench, a real-world dataset of 158,666 cases covering 33 Orphanet disease categories and more than 7,000 rare conditions, including both rare and non-rare presentations. The results showed that rare disease identification can be reconceptualised as a universal uncertainty resolution process applied to the general patient population. On an independent test set, RareAlert, a Qwen3-4B based model trained with calibrated reasoning signals, achieved an AUC of 0.917, outperforming the best machine learning ensemble and all evaluated LLMs, including GPT-5, DeepSeek-R1, Claude-3.7-Sonnet, o3-mini, Gemini-2.5-Pro, and Qwen3-235B. These findings demonstrate the diversity in LLM medical reasoning and the effectiveness of aligning such reasoning in highly uncertain clinical tasks. By incorporating calibrated reasoning into a single model, RareAlert enables accurate, privacy-preserving, and scalable rare disease risk screening suitable for large-scale local deployment.
Multimodal Breast Lesion Classification Using Cross-Attention Deep Networks
Aug 21, 2021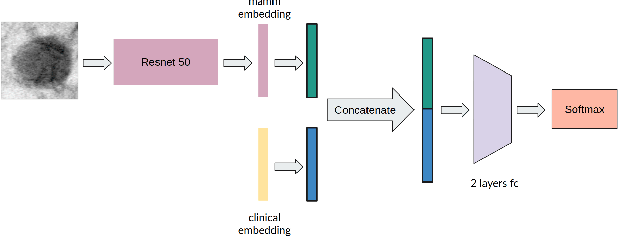
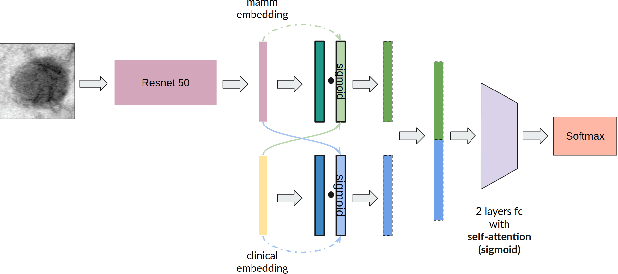
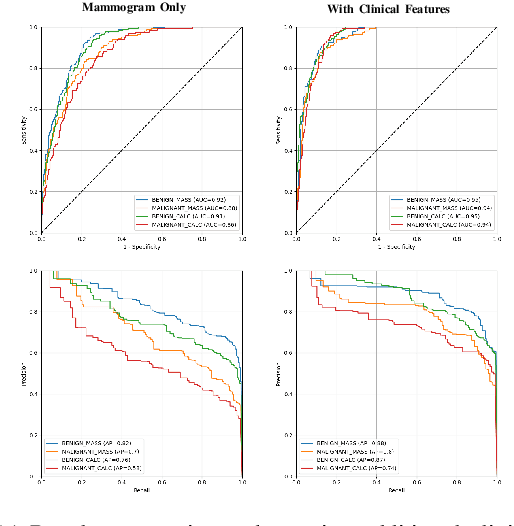
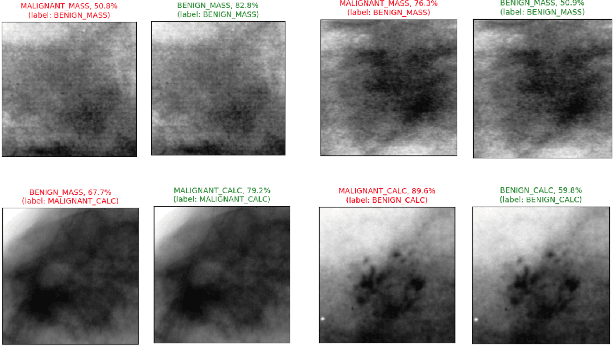
Abstract:Accurate breast lesion risk estimation can significantly reduce unnecessary biopsies and help doctors decide optimal treatment plans. Most existing computer-aided systems rely solely on mammogram features to classify breast lesions. While this approach is convenient, it does not fully exploit useful information in clinical reports to achieve the optimal performance. Would clinical features significantly improve breast lesion classification compared to using mammograms alone? How to handle missing clinical information caused by variation in medical practice? What is the best way to combine mammograms and clinical features? There is a compelling need for a systematic study to address these fundamental questions. This paper investigates several multimodal deep networks based on feature concatenation, cross-attention, and co-attention to combine mammograms and categorical clinical variables. We show that the proposed architectures significantly increase the lesion classification performance (average area under ROC curves from 0.89 to 0.94). We also evaluate the model when clinical variables are missing.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge