Tiago Fonseca
Control of Renewable Energy Communities using AI and Real-World Data
May 22, 2025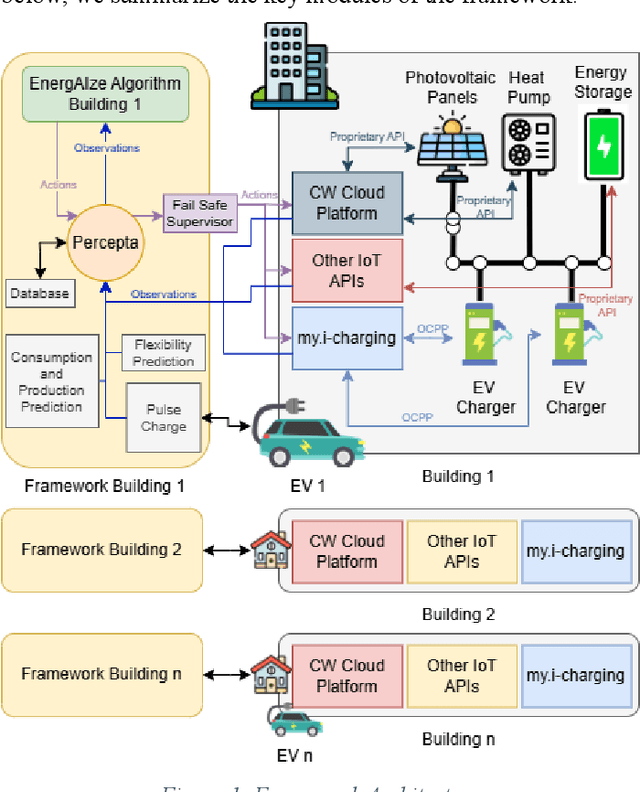
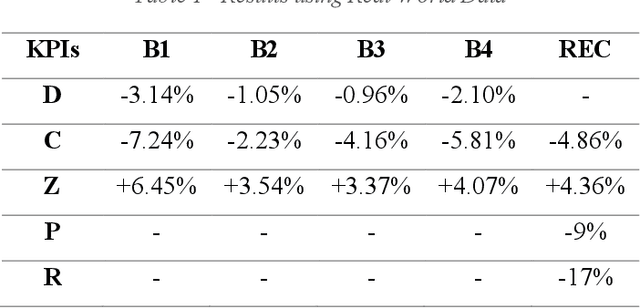
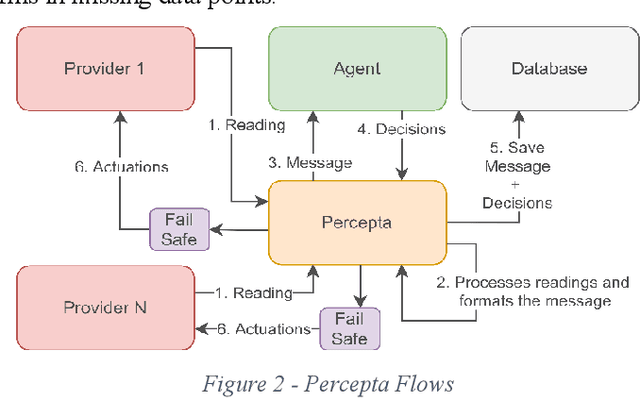
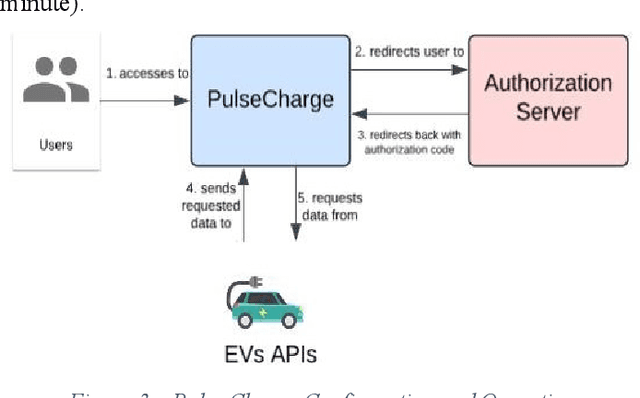
Abstract:The electrification of transportation and the increased adoption of decentralized renewable energy generation have added complexity to managing Renewable Energy Communities (RECs). Integrating Electric Vehicle (EV) charging with building energy systems like heating, ventilation, air conditioning (HVAC), photovoltaic (PV) generation, and battery storage presents significant opportunities but also practical challenges. Reinforcement learning (RL), particularly MultiAgent Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (MADDPG) algorithms, have shown promising results in simulation, outperforming heuristic control strategies. However, translating these successes into real-world deployments faces substantial challenges, including incomplete and noisy data, integration of heterogeneous subsystems, synchronization issues, unpredictable occupant behavior, and missing critical EV state-of-charge (SoC) information. This paper introduces a framework designed explicitly to handle these complexities and bridge the simulation to-reality gap. The framework incorporates EnergAIze, a MADDPG-based multi-agent control strategy, and specifically addresses challenges related to real-world data collection, system integration, and user behavior modeling. Preliminary results collected from a real-world operational REC with four residential buildings demonstrate the practical feasibility of our approach, achieving an average 9% reduction in daily peak demand and a 5% decrease in energy costs through optimized load scheduling and EV charging behaviors. These outcomes underscore the framework's effectiveness, advancing the practical deployment of intelligent energy management solutions in RECs.
CityLearn v2: Energy-flexible, resilient, occupant-centric, and carbon-aware management of grid-interactive communities
May 02, 2024Abstract:As more distributed energy resources become part of the demand-side infrastructure, it is important to quantify the energy flexibility they provide on a community scale, particularly to understand the impact of geographic, climatic, and occupant behavioral differences on their effectiveness, as well as identify the best control strategies to accelerate their real-world adoption. CityLearn provides an environment for benchmarking simple and advanced distributed energy resource control algorithms including rule-based, model-predictive, and reinforcement learning control. CityLearn v2 presented here extends CityLearn v1 by providing a simulation environment that leverages the End-Use Load Profiles for the U.S. Building Stock dataset to create virtual grid-interactive communities for resilient, multi-agent distributed energy resources and objective control with dynamic occupant feedback. This work details the v2 environment design and provides application examples that utilize reinforcement learning to manage battery energy storage system charging/discharging cycles, vehicle-to-grid control, and thermal comfort during heat pump power modulation.
EnergAIze: Multi Agent Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient for Vehicle to Grid Energy Management
Apr 09, 2024Abstract:This paper investigates the increasing roles of Renewable Energy Sources (RES) and Electric Vehicles (EVs). While indicating a new era of sustainable energy, these also introduce complex challenges, including the need to balance supply and demand and smooth peak consumptions amidst rising EV adoption rates. Addressing these challenges requires innovative solutions such as Demand Response (DR), energy flexibility management, Renewable Energy Communities (RECs), and more specifically for EVs, Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G). However, existing V2G approaches often fall short in real-world adaptability, global REC optimization with other flexible assets, scalability, and user engagement. To bridge this gap, this paper introduces EnergAIze, a Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL) energy management framework, leveraging the Multi-Agent Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (MADDPG) algorithm. EnergAIze enables user-centric and multi-objective energy management by allowing each prosumer to select from a range of personal management objectives, thus encouraging engagement. Additionally, it architects' data protection and ownership through decentralized computing, where each prosumer can situate an energy management optimization node directly at their own dwelling. The local node not only manages local energy assets but also fosters REC wide optimization. The efficacy of EnergAIze was evaluated through case studies employing the CityLearn simulation framework. These simulations were instrumental in demonstrating EnergAIze's adeptness at implementing V2G technology within a REC and other energy assets. The results show reduction in peak loads, ramping, carbon emissions, and electricity costs at the REC level while optimizing for individual prosumers objectives.
From Data to Action: Exploring AI and IoT-driven Solutions for Smarter Cities
Jun 06, 2023Abstract:The emergence of smart cities demands harnessing advanced technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) and promises to unlock cities' potential to become more sustainable, efficient, and ultimately livable for their inhabitants. This work introduces an intelligent city management system that provides a data-driven approach to three use cases: (i) analyze traffic information to reduce the risk of traffic collisions and improve driver and pedestrian safety, (ii) identify when and where energy consumption can be reduced to improve cost savings, and (iii) detect maintenance issues like potholes in the city's roads and sidewalks, as well as the beginning of hazards like floods and fires. A case study in Aveiro City demonstrates the system's effectiveness in generating actionable insights that enhance security, energy efficiency, and sustainability, while highlighting the potential of AI and IoT-driven solutions for smart city development.
Constrained Adversarial Learning and its applicability to Automated Software Testing: a systematic review
Mar 14, 2023Abstract:Every novel technology adds hidden vulnerabilities ready to be exploited by a growing number of cyber-attacks. Automated software testing can be a promising solution to quickly analyze thousands of lines of code by generating and slightly modifying function-specific testing data to encounter a multitude of vulnerabilities and attack vectors. This process draws similarities to the constrained adversarial examples generated by adversarial learning methods, so there could be significant benefits to the integration of these methods in automated testing tools. Therefore, this systematic review is focused on the current state-of-the-art of constrained data generation methods applied for adversarial learning and software testing, aiming to guide researchers and developers to enhance testing tools with adversarial learning methods and improve the resilience and robustness of their digital systems. The found constrained data generation applications for adversarial machine learning were systematized, and the advantages and limitations of approaches specific for software testing were thoroughly analyzed, identifying research gaps and opportunities to improve testing tools with adversarial attack methods.
An IoT Cloud and Big Data Architecture for the Maintenance of Home Appliances
Oct 25, 2022



Abstract:Billions of interconnected Internet of Things (IoT) sensors and devices collect tremendous amounts of data from real-world scenarios. Big data is generating increasing interest in a wide range of industries. Once data is analyzed through compute-intensive Machine Learning (ML) methods, it can derive critical business value for organizations. Powerfulplatforms are essential to handle and process such massive collections of information cost-effectively and conveniently. This work introduces a distributed and scalable platform architecture that can be deployed for efficient real-world big data collection and analytics. The proposed system was tested with a case study for Predictive Maintenance of Home Appliances, where current and vibration sensors with high acquisition frequency were connected to washing machines and refrigerators. The introduced platform was used to collect, store, and analyze the data. The experimental results demonstrated that the presented system could be advantageous for tackling real-world IoT scenarios in a cost-effective and local approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge