Thomas Leonard
Stochastic Domain Wall-Magnetic Tunnel Junction Artificial Neurons for Noise-Resilient Spiking Neural Networks
Apr 10, 2023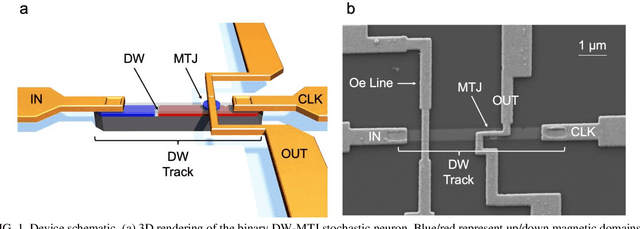
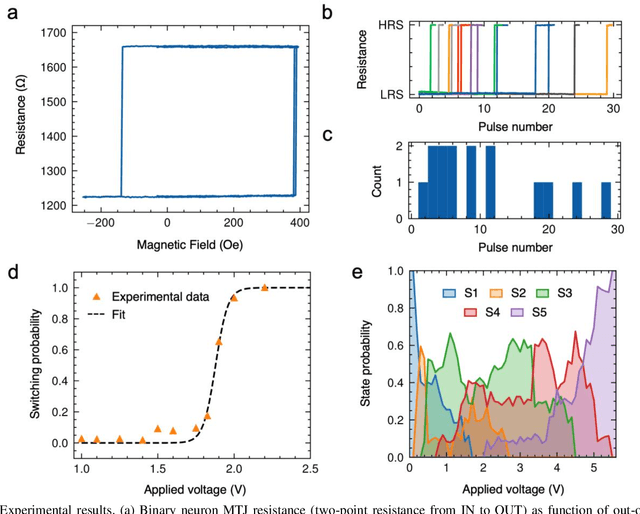
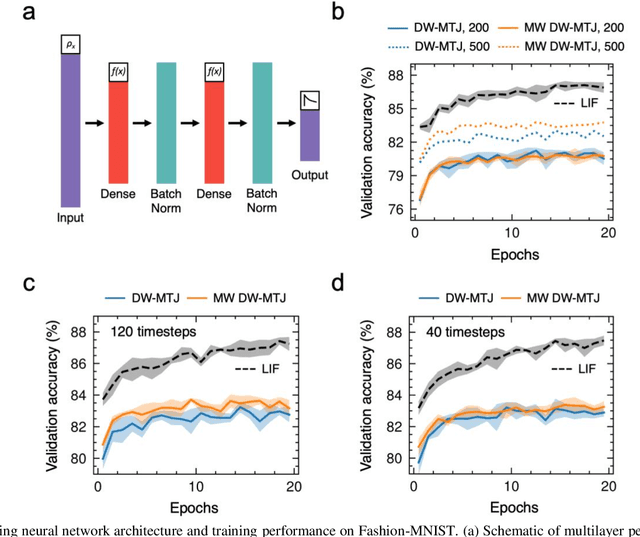
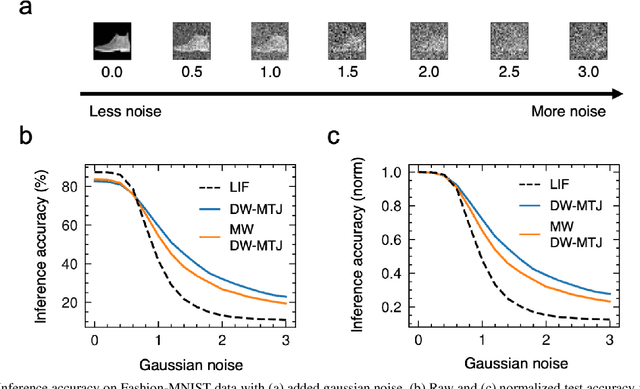
Abstract:The spatiotemporal nature of neuronal behavior in spiking neural networks (SNNs) make SNNs promising for edge applications that require high energy efficiency. To realize SNNs in hardware, spintronic neuron implementations can bring advantages of scalability and energy efficiency. Domain wall (DW) based magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) devices are well suited for probabilistic neural networks given their intrinsic integrate-and-fire behavior with tunable stochasticity. Here, we present a scaled DW-MTJ neuron with voltage-dependent firing probability. The measured behavior was used to simulate a SNN that attains accuracy during learning compared to an equivalent, but more complicated, multi-weight (MW) DW-MTJ device. The validation accuracy during training was also shown to be comparable to an ideal leaky integrate and fire (LIF) device. However, during inference, the binary DW-MTJ neuron outperformed the other devices after gaussian noise was introduced to the Fashion-MNIST classification task. This work shows that DW-MTJ devices can be used to construct noise-resilient networks suitable for neuromorphic computing on the edge.
Shape-Dependent Multi-Weight Magnetic Artificial Synapses for Neuromorphic Computing
Nov 22, 2021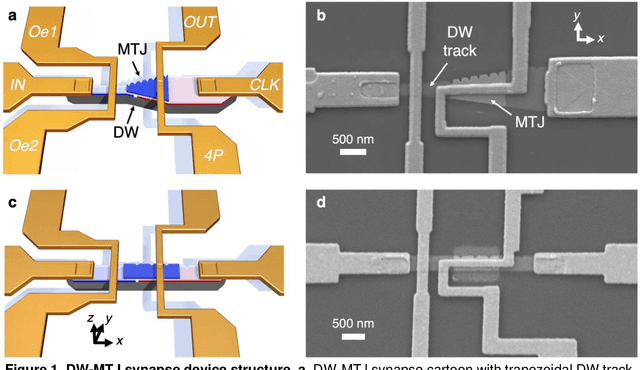
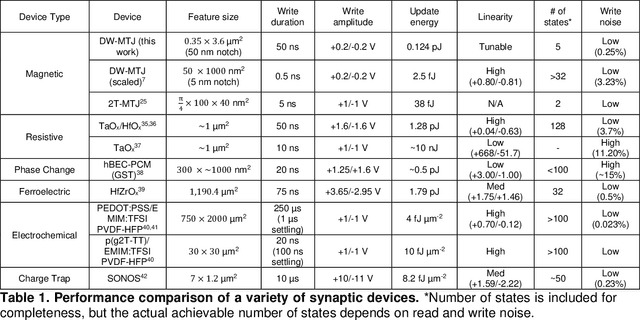
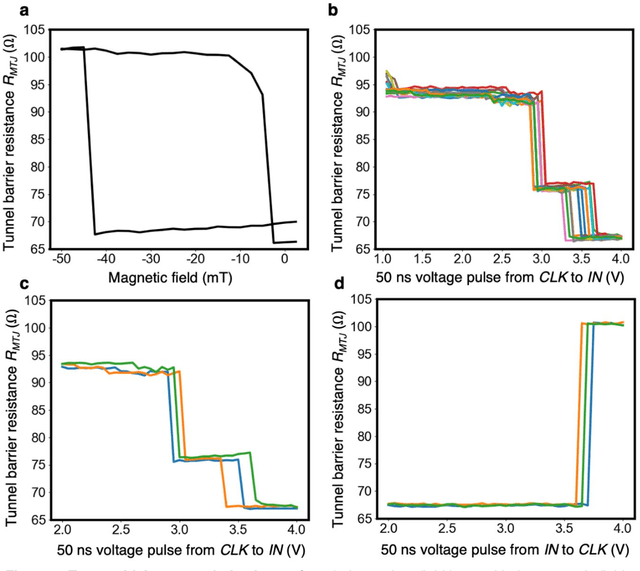
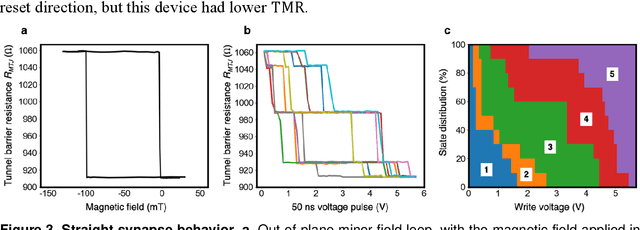
Abstract:In neuromorphic computing, artificial synapses provide a multi-weight conductance state that is set based on inputs from neurons, analogous to the brain. Additional properties of the synapse beyond multiple weights can be needed, and can depend on the application, requiring the need for generating different synapse behaviors from the same materials. Here, we measure artificial synapses based on magnetic materials that use a magnetic tunnel junction and a magnetic domain wall. By fabricating lithographic notches in a domain wall track underneath a single magnetic tunnel junction, we achieve 4-5 stable resistance states that can be repeatably controlled electrically using spin orbit torque. We analyze the effect of geometry on the synapse behavior, showing that a trapezoidal device has asymmetric weight updates with high controllability, while a straight device has higher stochasticity, but with stable resistance levels. The device data is input into neuromorphic computing simulators to show the usefulness of application-specific synaptic functions. Implementing an artificial neural network applied on streamed Fashion-MNIST data, we show that the trapezoidal magnetic synapse can be used as a metaplastic function for efficient online learning. Implementing a convolutional neural network for CIFAR-100 image recognition, we show that the straight magnetic synapse achieves near-ideal inference accuracy, due to the stability of its resistance levels. This work shows multi-weight magnetic synapses are a feasible technology for neuromorphic computing and provides design guidelines for emerging artificial synapse technologies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge