Thiago Tomei
On the Evaluation of Generative Models in High Energy Physics
Nov 18, 2022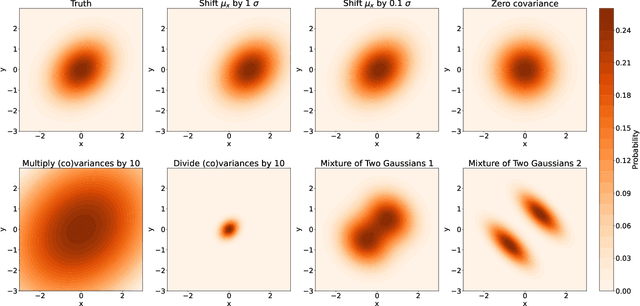
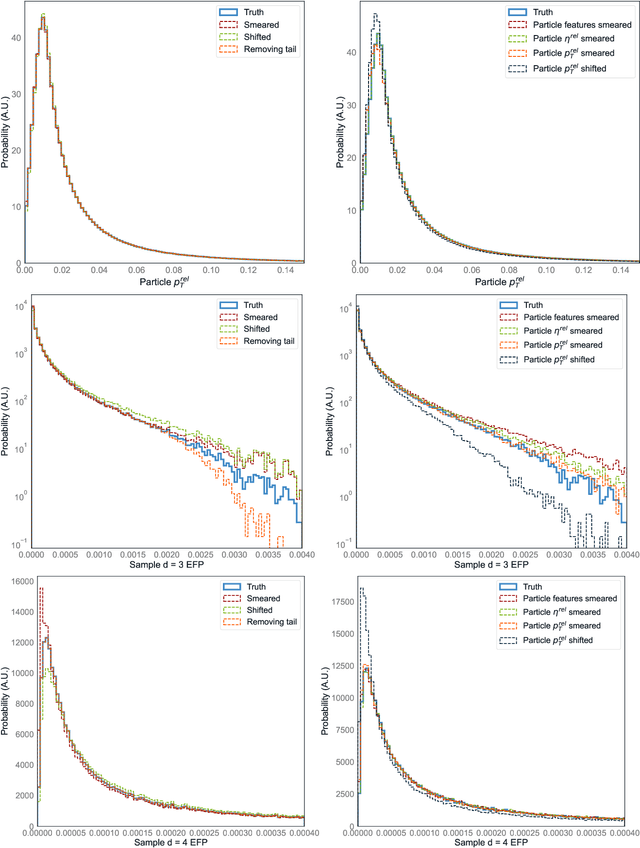
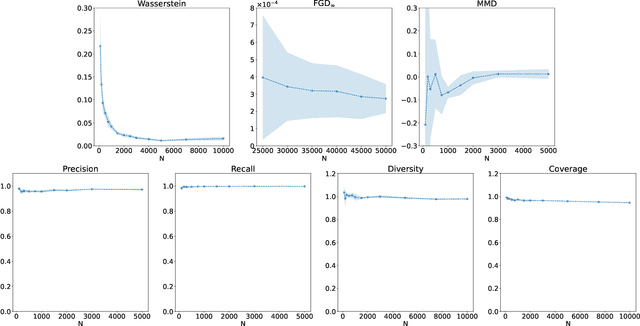
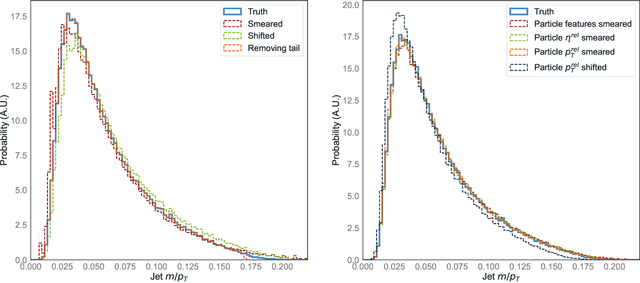
Abstract:There has been a recent explosion in research into machine-learning-based generative modeling to tackle computational challenges for simulations in high energy physics (HEP). In order to use such alternative simulators in practice, we need well defined metrics to compare different generative models and evaluate their discrepancy from the true distributions. We present the first systematic review and investigation into evaluation metrics and their sensitivity to failure modes of generative models, using the framework of two-sample goodness-of-fit testing, and their relevance and viability for HEP. Inspired by previous work in both physics and computer vision, we propose two new metrics, the Fr\'echet and kernel physics distances (FPD and KPD), and perform a variety of experiments measuring their performance on simple Gaussian-distributed, and simulated high energy jet datasets. We find FPD, in particular, to be the most sensitive metric to all alternative jet distributions tested and recommend its adoption, along with the KPD and Wasserstein distances between individual feature distributions, for evaluating generative models in HEP. We finally demonstrate the efficacy of these proposed metrics in evaluating and comparing a novel attention-based generative adversarial particle transformer to the state-of-the-art message-passing generative adversarial network jet simulation model.
Particle-based Fast Jet Simulation at the LHC with Variational Autoencoders
Mar 01, 2022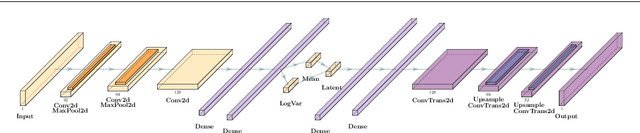
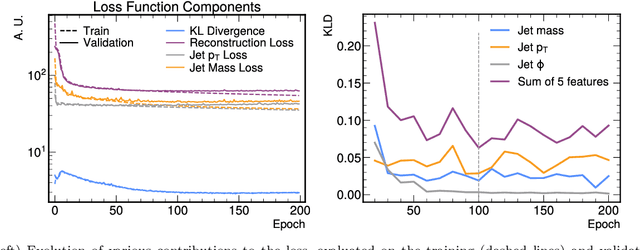
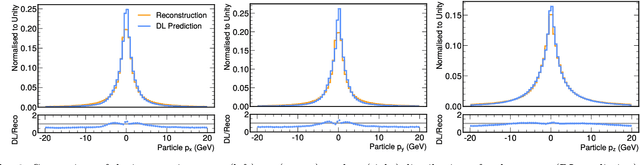
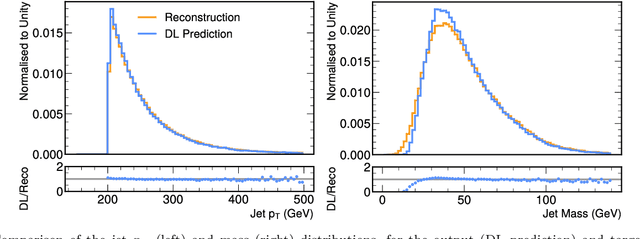
Abstract:We study how to use Deep Variational Autoencoders for a fast simulation of jets of particles at the LHC. We represent jets as a list of constituents, characterized by their momenta. Starting from a simulation of the jet before detector effects, we train a Deep Variational Autoencoder to return the corresponding list of constituents after detection. Doing so, we bypass both the time-consuming detector simulation and the collision reconstruction steps of a traditional processing chain, speeding up significantly the events generation workflow. Through model optimization and hyperparameter tuning, we achieve state-of-the-art precision on the jet four-momentum, while providing an accurate description of the constituents momenta, and an inference time comparable to that of a rule-based fast simulation.
Particle Cloud Generation with Message Passing Generative Adversarial Networks
Jun 22, 2021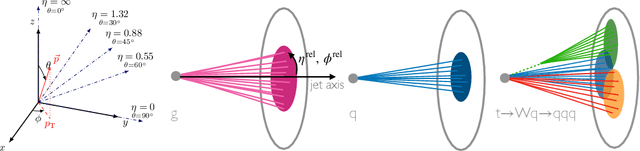

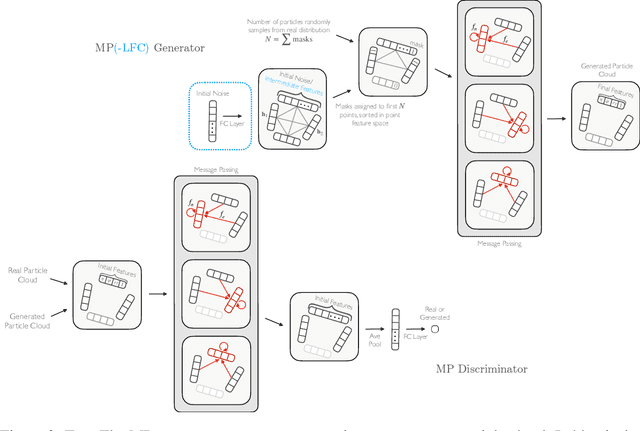
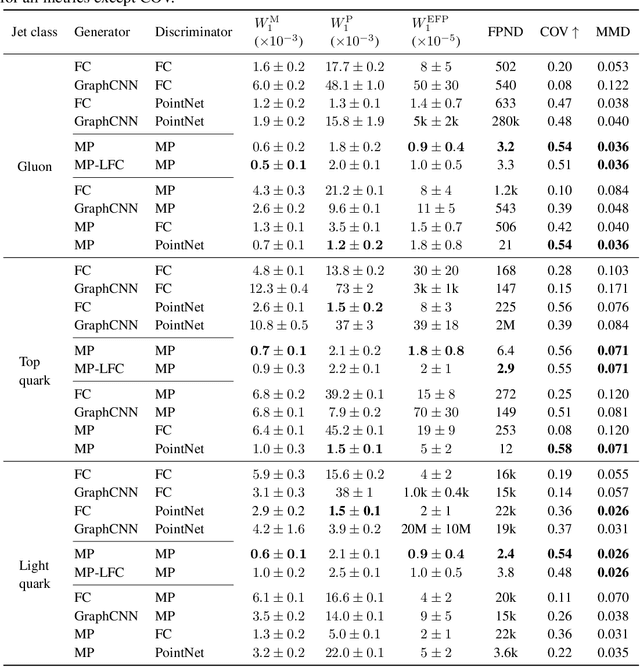
Abstract:In high energy physics (HEP), jets are collections of correlated particles produced ubiquitously in particle collisions such as those at the CERN Large Hadron Collider (LHC). Machine-learning-based generative models, such as generative adversarial networks (GANs), have the potential to significantly accelerate LHC jet simulations. However, despite jets having a natural representation as a set of particles in momentum-space, a.k.a. a particle cloud, to our knowledge there exist no generative models applied to such a dataset. We introduce a new particle cloud dataset (JetNet), and, due to similarities between particle and point clouds, apply to it existing point cloud GANs. Results are evaluated using (1) the 1-Wasserstein distance between high- and low-level feature distributions, (2) a newly developed Fr\'{e}chet ParticleNet Distance, and (3) the coverage and (4) minimum matching distance metrics. Existing GANs are found to be inadequate for physics applications, hence we develop a new message passing GAN (MPGAN), which outperforms existing point cloud GANs on virtually every metric and shows promise for use in HEP. We propose JetNet as a novel point-cloud-style dataset for the machine learning community to experiment with, and set MPGAN as a benchmark to improve upon for future generative models.
Graph Generative Adversarial Networks for Sparse Data Generation in High Energy Physics
Dec 08, 2020



Abstract:We develop a graph generative adversarial network to generate sparse data sets like those produced at the CERN Large Hadron Collider (LHC). We demonstrate this approach by training on and generating sparse representations of MNIST handwritten digit images and jets of particles in proton-proton collisions like those at the LHC. We find the model successfully generates sparse MNIST digits and particle jet data. We quantify agreement between real and generated data with a graph-based Fr\'echet Inception distance, and the particle and jet feature-level 1-Wasserstein distance for the MNIST and jet datasets respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge