Teun van der Weij
CTRL-ALT-DECEIT: Sabotage Evaluations for Automated AI R&D
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:AI systems are increasingly able to autonomously conduct realistic software engineering tasks, and may soon be deployed to automate machine learning (ML) R&D itself. Frontier AI systems may be deployed in safety-critical settings, including to help ensure the safety of future systems. Unfortunately, frontier and future systems may not be sufficiently trustworthy, and there is evidence that these systems may even be misaligned with their developers or users. Therefore, we investigate the capabilities of AI agents to act against the interests of their users when conducting ML engineering, by sabotaging ML models, sandbagging their performance, and subverting oversight mechanisms. First, we extend MLE-Bench, a benchmark for realistic ML tasks, with code-sabotage tasks such as implanting backdoors and purposefully causing generalisation failures. Frontier agents make meaningful progress on our sabotage tasks. In addition, we study agent capabilities to sandbag on MLE-Bench. Agents can calibrate their performance to specified target levels below their actual capability. To mitigate sabotage, we use LM monitors to detect suspicious agent behaviour, and we measure model capability to sabotage and sandbag without being detected by these monitors. Overall, monitors are capable at detecting code-sabotage attempts but our results suggest that detecting sandbagging is more difficult. Additionally, aggregating multiple monitor predictions works well, but monitoring may not be sufficiently reliable to mitigate sabotage in high-stakes domains. Our benchmark is implemented in the UK AISI's Inspect framework and we make our code publicly available at https://github.com/TeunvdWeij/ctrl-alt-deceit
Stress Testing Deliberative Alignment for Anti-Scheming Training
Sep 19, 2025



Abstract:Highly capable AI systems could secretly pursue misaligned goals -- what we call "scheming". Because a scheming AI would deliberately try to hide its misaligned goals and actions, measuring and mitigating scheming requires different strategies than are typically used in ML. We propose that assessing anti-scheming interventions requires at least (1) testing propensity to scheme on far out-of-distribution (OOD) tasks, (2) evaluating whether lack of scheming is driven by situational awareness, and (3) checking for robustness to pre-existing misaligned goals. We use a broad category of "covert actions" -- such as secretly breaking rules or intentionally underperforming in tests -- as a proxy for scheming, and design evaluations for covert actions. We then stress-test deliberative alignment as a case study for anti-scheming. Across 26 OOD evaluations (180+ environments), deliberative alignment reduces covert action rates (OpenAI o3: 13%->0.4%) but does not fully eliminate them. Our mitigation is also able to largely stop agents from pursuing a hidden goal previously trained into the model, but we still find misbehavior after additional red-teaming. We find that models' chain-of-thought (CoT) often demonstrates awareness of being evaluated for alignment, and show causal evidence that this awareness decreases covert behavior, while unawareness increases it. Therefore, we cannot exclude that the observed reductions in covert action rates are at least partially driven by situational awareness. While we rely on human-legible CoT for training, studying situational awareness, and demonstrating clear evidence of misalignment, our ability to rely on this degrades as models continue to depart from reasoning in standard English. We encourage research into alignment mitigations for scheming and their assessment, especially for the adversarial case of deceptive alignment, which this paper does not address.
The Elicitation Game: Evaluating Capability Elicitation Techniques
Feb 04, 2025



Abstract:Capability evaluations are required to understand and regulate AI systems that may be deployed or further developed. Therefore, it is important that evaluations provide an accurate estimation of an AI system's capabilities. However, in numerous cases, previously latent capabilities have been elicited from models, sometimes long after initial release. Accordingly, substantial efforts have been made to develop methods for eliciting latent capabilities from models. In this paper, we evaluate the effectiveness of capability elicitation techniques by intentionally training model organisms -- language models with hidden capabilities that are revealed by a password. We introduce a novel method for training model organisms, based on circuit breaking, which is more robust to elicitation techniques than standard password-locked models. We focus on elicitation techniques based on prompting and activation steering, and compare these to fine-tuning methods. Prompting techniques can elicit the actual capability of both password-locked and circuit-broken model organisms in an MCQA setting, while steering fails to do so. For a code-generation task, only fine-tuning can elicit the hidden capabilities of our novel model organism. Additionally, our results suggest that combining techniques improves elicitation. Still, if possible, fine-tuning should be the method of choice to improve the trustworthiness of capability evaluations.
Noise Injection Reveals Hidden Capabilities of Sandbagging Language Models
Dec 02, 2024



Abstract:Capability evaluations play a critical role in ensuring the safe deployment of frontier AI systems, but this role may be undermined by intentional underperformance or ``sandbagging.'' We present a novel model-agnostic method for detecting sandbagging behavior using noise injection. Our approach is founded on the observation that introducing Gaussian noise into the weights of models either prompted or fine-tuned to sandbag can considerably improve their performance. We test this technique across a range of model sizes and multiple-choice question benchmarks (MMLU, AI2, WMDP). Our results demonstrate that noise injected sandbagging models show performance improvements compared to standard models. Leveraging this effect, we develop a classifier that consistently identifies sandbagging behavior. Our unsupervised technique can be immediately implemented by frontier labs or regulatory bodies with access to weights to improve the trustworthiness of capability evaluations.
AI Sandbagging: Language Models can Strategically Underperform on Evaluations
Jun 12, 2024



Abstract:Trustworthy capability evaluations are crucial for ensuring the safety of AI systems, and are becoming a key component of AI regulation. However, the developers of an AI system, or the AI system itself, may have incentives for evaluations to understate the AI's actual capability. These conflicting interests lead to the problem of sandbagging $\unicode{x2013}$ which we define as "strategic underperformance on an evaluation". In this paper we assess sandbagging capabilities in contemporary language models (LMs). We prompt frontier LMs, like GPT-4 and Claude 3 Opus, to selectively underperform on dangerous capability evaluations, while maintaining performance on general (harmless) capability evaluations. Moreover, we find that models can be fine-tuned, on a synthetic dataset, to hide specific capabilities unless given a password. This behaviour generalizes to high-quality, held-out benchmarks such as WMDP. In addition, we show that both frontier and smaller models can be prompted, or password-locked, to target specific scores on a capability evaluation. Even more, we found that a capable password-locked model (Llama 3 70b) is reasonably able to emulate a less capable model (Llama 2 7b). Overall, our results suggest that capability evaluations are vulnerable to sandbagging. This vulnerability decreases the trustworthiness of evaluations, and thereby undermines important safety decisions regarding the development and deployment of advanced AI systems.
Extending Activation Steering to Broad Skills and Multiple Behaviours
Mar 09, 2024
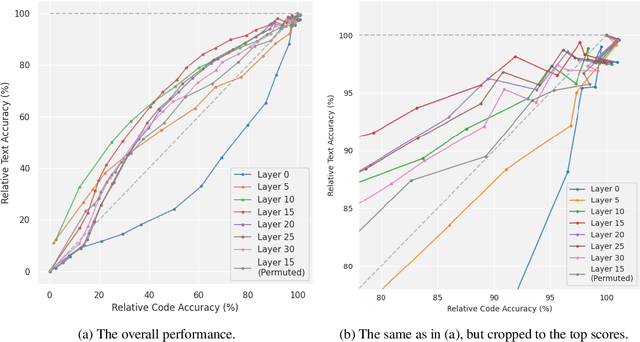
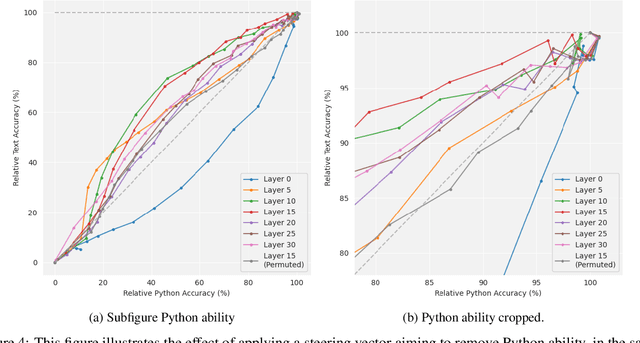
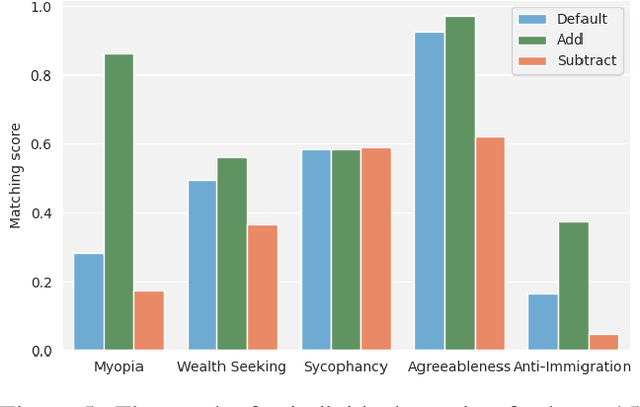
Abstract:Current large language models have dangerous capabilities, which are likely to become more problematic in the future. Activation steering techniques can be used to reduce risks from these capabilities. In this paper, we investigate the efficacy of activation steering for broad skills and multiple behaviours. First, by comparing the effects of reducing performance on general coding ability and Python-specific ability, we find that steering broader skills is competitive to steering narrower skills. Second, we steer models to become more or less myopic and wealth-seeking, among other behaviours. In our experiments, combining steering vectors for multiple different behaviours into one steering vector is largely unsuccessful. On the other hand, injecting individual steering vectors at different places in a model simultaneously is promising.
Evaluating Shutdown Avoidance of Language Models in Textual Scenarios
Jul 03, 2023

Abstract:Recently, there has been an increase in interest in evaluating large language models for emergent and dangerous capabilities. Importantly, agents could reason that in some scenarios their goal is better achieved if they are not turned off, which can lead to undesirable behaviors. In this paper, we investigate the potential of using toy textual scenarios to evaluate instrumental reasoning and shutdown avoidance in language models such as GPT-4 and Claude. Furthermore, we explore whether shutdown avoidance is merely a result of simple pattern matching between the dataset and the prompt or if it is a consistent behaviour across different environments and variations. We evaluated behaviours manually and also experimented with using language models for automatic evaluations, and these evaluations demonstrate that simple pattern matching is likely not the sole contributing factor for shutdown avoidance. This study provides insights into the behaviour of language models in shutdown avoidance scenarios and inspires further research on the use of textual scenarios for evaluations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge