Terry M. Peters
Virtual Fluoroscopy for Interventional Guidance using Magnetic Tracking
May 20, 2025Abstract:Purpose: In conventional fluoroscopy-guided interventions, the 2D projective nature of X-ray imaging limits depth perception and leads to prolonged radiation exposure. Virtual fluoroscopy, combined with spatially tracked surgical instruments, is a promising strategy to mitigate these limitations. While magnetic tracking shows unique advantages, particularly in tracking flexible instruments, it remains under-explored due to interference from ferromagnetic materials in the C-arm room. This work proposes a virtual fluoroscopy workflow by effectively integrating magnetic tracking, and demonstrates its clinical efficacy. Methods: An automatic virtual fluoroscopy workflow was developed using a radiolucent tabletop field generator prototype. Specifically, we developed a fluoro-CT registration approach with automatic 2D-3D shared landmark correspondence to establish the C-arm-patient relationship, along with a general C-arm modelling approach to calculate desired poses and generate corresponding virtual fluoroscopic images. Results: Testing on a dataset with views ranging from RAO 90 degrees to LAO 90 degrees, simulated fluoroscopic images showed visually imperceptible differences from the real ones, achieving a mean target projection distance error of 1.55 mm. An endoleak phantom insertion experiment highlighted the effectiveness of simulating multiplanar views with real-time instrument overlays, achieving a mean needle tip error of 3.42 mm. Conclusions: Results demonstrated the efficacy of virtual fluoroscopy integrated with magnetic tracking, improving depth perception during navigation. The broad capture range of virtual fluoroscopy showed promise in improving the users understanding of X-ray imaging principles, facilitating more efficient image acquisition.
Towards Seamless Integration of Magnetic Tracking into Fluoroscopy-guided Interventions
Nov 12, 2024



Abstract:The 2D projective nature of X-ray radiography presents significant limitations in fluoroscopy-guided interventions, particularly the loss of depth perception and prolonged radiation exposure. Integrating magnetic trackers into these workflows is promising; however, it remains challenging and under-explored in current research and practice. To address this, we employed a radiolucent magnetic field generator (FG) prototype as a foundational step towards seamless magnetic tracking (MT) integration. A two-layer FG mounting frame was designed for compatibility with various C-arm X-ray systems, ensuring smooth installation and optimal tracking accuracy. To overcome technical challenges, including accurate C-arm pose estimation, robust fluoro-CT registration, and 3D navigation, we proposed the incorporation of external aluminum fiducials without disrupting conventional workflows. Experimental evaluation showed no clinically significant impact of the aluminum fiducials and the C-arm on MT accuracy. Our fluoro-CT registration demonstrated high accuracy (mean projection distance approxiamtely 0.7 mm, robustness (wide capture range), and generalizability across local and public datasets. In a phantom targeting experiment, needle insertion error was between 2 mm and 3 mm, with real-time guidance using enhanced 2D and 3D navigation. Overall, our results demonstrated the efficacy and clinical applicability of the MT-assisted approach. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to integrate a radiolucent FG into a fluoroscopy-guided workflow.
Deep Regression 2D-3D Ultrasound Registration for Liver Motion Correction in Focal Tumor Thermal Ablation
Oct 03, 2024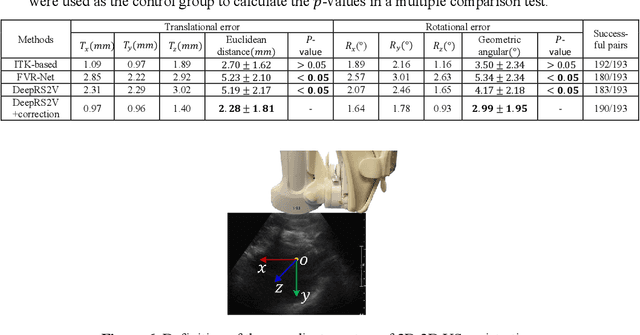
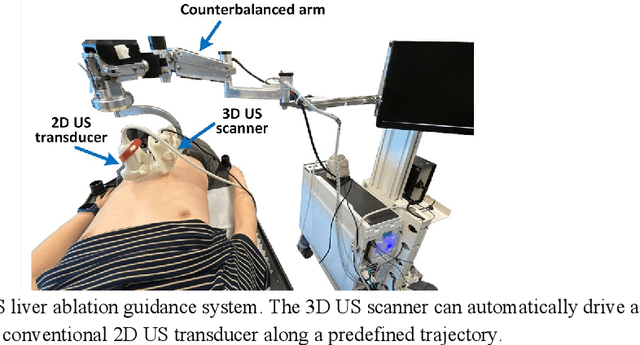
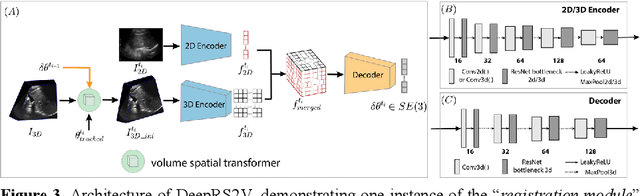
Abstract:Liver tumor ablation procedures require accurate placement of the needle applicator at the tumor centroid. The lower-cost and real-time nature of ultrasound (US) has advantages over computed tomography (CT) for applicator guidance, however, in some patients, liver tumors may be occult on US and tumor mimics can make lesion identification challenging. Image registration techniques can aid in interpreting anatomical details and identifying tumors, but their clinical application has been hindered by the tradeoff between alignment accuracy and runtime performance, particularly when compensating for liver motion due to patient breathing or movement. Therefore, we propose a 2D-3D US registration approach to enable intra-procedural alignment that mitigates errors caused by liver motion. Specifically, our approach can correlate imbalanced 2D and 3D US image features and use continuous 6D rotation representations to enhance the model's training stability. The dataset was divided into 2388, 196 and 193 image pairs for training, validation and testing, respectively. Our approach achieved a mean Euclidean distance error of 2.28 mm $\pm$ 1.81 mm and a mean geodesic angular error of 2.99$^{\circ}$ $\pm$ 1.95$^{\circ}$, with a runtime of 0.22 seconds per 2D-3D US image pair. These results demonstrate that our approach can achieve accurate alignment and clinically acceptable runtime, indicating potential for clinical translation.
A Continuous Max-Flow Approach to Cyclic Field Reconstruction
Nov 11, 2015
Abstract:Reconstruction of an image from noisy data using Markov Random Field theory has been explored by both the graph-cuts and continuous max-flow community in the form of the Potts and Ishikawa models. However, neither model takes into account the particular cyclic topology of specific intensity types such as the hue in natural colour images, or the phase in complex valued MRI. This paper presents \textit{cyclic continuous max-flow} image reconstruction which models the intensity being reconstructed as having a fundamentally cyclic topology. This model complements the Ishikawa model in that it is designed with image reconstruction in mind, having the topology of the intensity space inherent in the model while being readily extendable to an arbitrary intensity resolution.
Shape Complexes in Continuous Max-Flow Hierarchical Multi-Labeling Problems
Oct 15, 2015
Abstract:Although topological considerations amongst multiple labels have been previously investigated in the context of continuous max-flow image segmentation, similar investigations have yet to be made about shape considerations in a general and extendable manner. This paper presents shape complexes for segmentation, which capture more complex shapes by combining multiple labels and super-labels constrained by geodesic star convexity. Shape complexes combine geodesic star convexity constraints with hierarchical label organization, which together allow for more complex shapes to be represented. This framework avoids the use of co-ordinate system warping techniques to convert shape constraints into topological constraints, which may be ambiguous or ill-defined for certain segmentation problems.
A Proximal Bregman Projection Approach to Continuous Max-Flow Problems Using Entropic Distances
Jan 30, 2015Abstract:One issue limiting the adaption of large-scale multi-region segmentation is the sometimes prohibitive memory requirements. This is especially troubling considering advances in massively parallel computing and commercial graphics processing units because of their already limited memory compared to the current random access memory used in more traditional computation. To address this issue in the field of continuous max-flow segmentation, we have developed a \textit{pseudo-flow} framework using the theory of Bregman proximal projections and entropic distances which implicitly represents flow variables between labels and designated source and sink nodes. This reduces the memory requirements for max-flow segmentation by approximately 20\% for Potts models and approximately 30\% for hierarchical max-flow (HMF) and directed acyclic graph max-flow (DAGMF) models. This represents a great improvement in the state-of-the-art in max-flow segmentation, allowing for much larger problems to be addressed and accelerated using commercially available graphics processing hardware.
A Continuous Max-Flow Approach to Multi-Labeling Problems under Arbitrary Region Regularization
Jun 05, 2014


Abstract:The incorporation of region regularization into max-flow segmentation has traditionally focused on ordering and part-whole relationships. A side effect of the development of such models is that it constrained regularization only to those cases, rather than allowing for arbitrary region regularization. Directed Acyclic Graphical Max-Flow (DAGMF) segmentation overcomes these limitations by allowing for the algorithm designer to specify an arbitrary directed acyclic graph to structure a max-flow segmentation. This allows for individual 'parts' to be a member of multiple distinct 'wholes.'
A Continuous Max-Flow Approach to General Hierarchical Multi-Labeling Problems
Jun 05, 2014
Abstract:Multi-region segmentation algorithms often have the onus of incorporating complex anatomical knowledge representing spatial or geometric relationships between objects, and general-purpose methods of addressing this knowledge in an optimization-based manner have thus been lacking. This paper presents Generalized Hierarchical Max-Flow (GHMF) segmentation, which captures simple anatomical part-whole relationships in the form of an unconstrained hierarchy. Regularization can then be applied to both parts and wholes independently, allowing for spatial grouping and clustering of labels in a globally optimal convex optimization framework. For the purposes of ready integration into a variety of segmentation tasks, the hierarchies can be presented in run-time, allowing for the segmentation problem to be readily specified and alternatives explored without undue programming effort or recompilation.
RANCOR: Non-Linear Image Registration with Total Variation Regularization
Apr 09, 2014
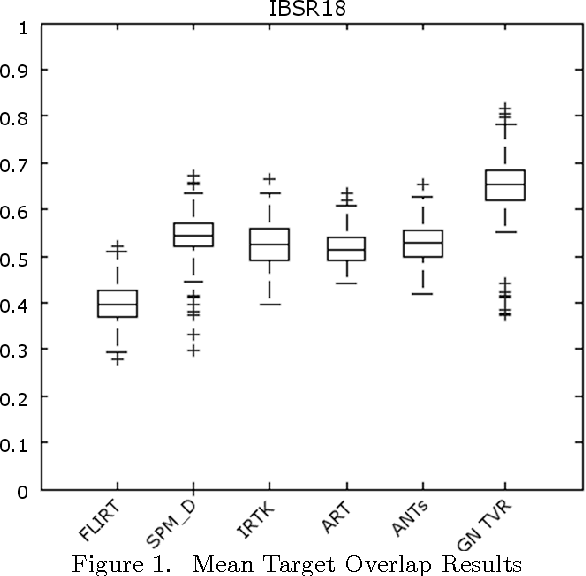
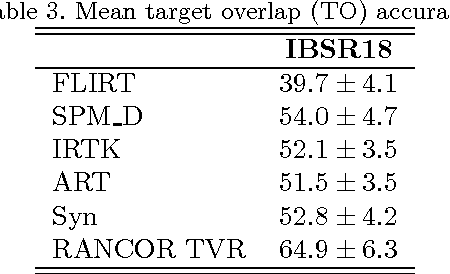
Abstract:Optimization techniques have been widely used in deformable registration, allowing for the incorporation of similarity metrics with regularization mechanisms. These regularization mechanisms are designed to mitigate the effects of trivial solutions to ill-posed registration problems and to otherwise ensure the resulting deformation fields are well-behaved. This paper introduces a novel deformable registration algorithm, RANCOR, which uses iterative convexification to address deformable registration problems under total-variation regularization. Initial comparative results against four state-of-the-art registration algorithms are presented using the Internet Brain Segmentation Repository (IBSR) database.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge