Te Pi
Mark
Emotion Eliciting Machine: Emotion Eliciting Conversation Generation based on Dual Generator
May 18, 2021



Abstract:Recent years have witnessed great progress on building emotional chatbots. Tremendous methods have been proposed for chatbots to generate responses with given emotions. However, the emotion changes of the user during the conversation has not been fully explored. In this work, we study the problem of positive emotion elicitation, which aims to generate responses that can elicit positive emotion of the user, in human-machine conversation. We propose a weakly supervised Emotion Eliciting Machine (EEM) to address this problem. Specifically, we first collect weak labels of user emotion status changes in a conversion based on a pre-trained emotion classifier. Then we propose a dual encoder-decoder structure to model the generation of responses in both positive and negative side based on the changes of the user's emotion status in the conversation. An emotion eliciting factor is introduced on top of the dual structure to balance the positive and negative emotional impacts on the generated response during emotion elicitation. The factor also provides a fine-grained controlling manner for emotion elicitation. Experimental results on a large real-world dataset show that EEM outperforms the existing models in generating responses with positive emotion elicitation.
Boosted Zero-Shot Learning with Semantic Correlation Regularization
Jul 25, 2017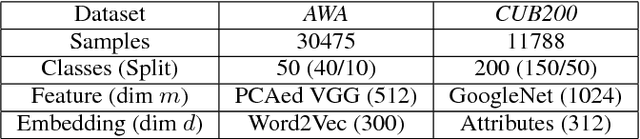

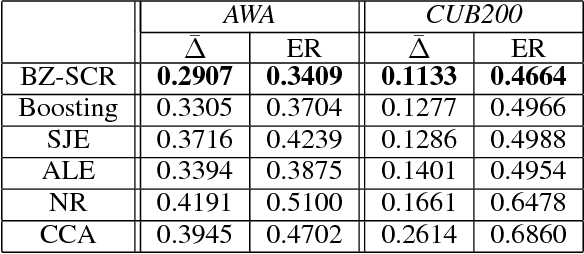
Abstract:We study zero-shot learning (ZSL) as a transfer learning problem, and focus on the two key aspects of ZSL, model effectiveness and model adaptation. For effective modeling, we adopt the boosting strategy to learn a zero-shot classifier from weak models to a strong model. For adaptable knowledge transfer, we devise a Semantic Correlation Regularization (SCR) approach to regularize the boosted model to be consistent with the inter-class semantic correlations. With SCR embedded in the boosting objective, and with a self-controlled sample selection for learning robustness, we propose a unified framework, Boosted Zero-shot classification with Semantic Correlation Regularization (BZ-SCR). By balancing the SCR-regularized boosted model selection and the self-controlled sample selection, BZ-SCR is capable of capturing both discriminative and adaptable feature-to-class semantic alignments, while ensuring the reliability and adaptability of the learned samples. The experiments on two ZSL datasets show the superiority of BZ-SCR over the state-of-the-arts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge