Taichi Murayama
Data-driven Methods of Extracting Text Structure and Information Transfer
Sep 16, 2025Abstract:The Anna Karenina Principle (AKP) holds that success requires satisfying a small set of essential conditions, whereas failure takes diverse forms. We test AKP, its reverse, and two further patterns described as ordered and noisy across novels, online encyclopedias, research papers, and movies. Texts are represented as sequences of functional blocks, and convergence is assessed in transition order and position. Results show that structural principles vary by medium: novels follow reverse AKP in order, Wikipedia combines AKP with ordered patterns, academic papers display reverse AKP in order but remain noisy in position, and movies diverge by genre. Success therefore depends on structural constraints that are specific to each medium, while failure assumes different shapes across domains.
D-Tracker: Modeling Interest Diffusion in Social Activity Tensor Data Streams
May 01, 2025Abstract:Large quantities of social activity data, such as weekly web search volumes and the number of new infections with infectious diseases, reflect peoples' interests and activities. It is important to discover temporal patterns from such data and to forecast future activities accurately. However, modeling and forecasting social activity data streams is difficult because they are high-dimensional and composed of multiple time-varying dynamics such as trends, seasonality, and interest diffusion. In this paper, we propose D-Tracker, a method for continuously capturing time-varying temporal patterns within social activity tensor data streams and forecasting future activities. Our proposed method has the following properties: (a) Interpretable: it incorporates the partial differential equation into a tensor decomposition framework and captures time-varying temporal patterns such as trends, seasonality, and interest diffusion between locations in an interpretable manner; (b) Automatic: it has no hyperparameters and continuously models tensor data streams fully automatically; (c) Scalable: the computation time of D-Tracker is independent of the time series length. Experiments using web search volume data obtained from GoogleTrends, and COVID-19 infection data obtained from COVID-19 Open Data Repository show that our method can achieve higher forecasting accuracy in less computation time than existing methods while extracting the interest diffusion between locations. Our source code and datasets are available at {https://github.com/Higashiguchi-Shingo/D-Tracker.
Fredformer: Frequency Debiased Transformer for Time Series Forecasting
Jun 14, 2024

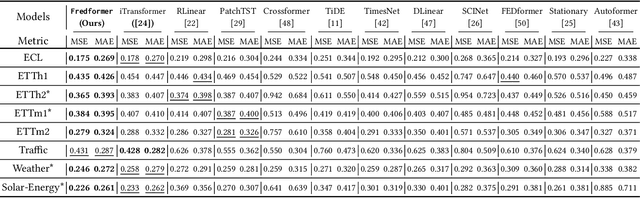

Abstract:The Transformer model has shown leading performance in time series forecasting. Nevertheless, in some complex scenarios, it tends to learn low-frequency features in the data and overlook high-frequency features, showing a frequency bias. This bias prevents the model from accurately capturing important high-frequency data features. In this paper, we undertook empirical analyses to understand this bias and discovered that frequency bias results from the model disproportionately focusing on frequency features with higher energy. Based on our analysis, we formulate this bias and propose Fredformer, a Transformer-based framework designed to mitigate frequency bias by learning features equally across different frequency bands. This approach prevents the model from overlooking lower amplitude features important for accurate forecasting. Extensive experiments show the effectiveness of our proposed approach, which can outperform other baselines in different real-world time-series datasets. Furthermore, we introduce a lightweight variant of the Fredformer with an attention matrix approximation, which achieves comparable performance but with much fewer parameters and lower computation costs. The code is available at: https://github.com/chenzRG/Fredformer
Mining Reaction and Diffusion Dynamics in Social Activities
Aug 07, 2022



Abstract:Large quantifies of online user activity data, such as weekly web search volumes, which co-evolve with the mutual influence of several queries and locations, serve as an important social sensor. It is an important task to accurately forecast the future activity by discovering latent interactions from such data, i.e., the ecosystems between each query and the flow of influences between each area. However, this is a difficult problem in terms of data quantity and complex patterns covering the dynamics. To tackle the problem, we propose FluxCube, which is an effective mining method that forecasts large collections of co-evolving online user activity and provides good interpretability. Our model is the expansion of a combination of two mathematical models: a reaction-diffusion system provides a framework for modeling the flow of influences between local area groups and an ecological system models the latent interactions between each query. Also, by leveraging the concept of physics-informed neural networks, FluxCube achieves high interpretability obtained from the parameters and high forecasting performance, together. Extensive experiments on real datasets showed that FluxCube outperforms comparable models in terms of the forecasting accuracy, and each component in FluxCube contributes to the enhanced performance. We then show some case studies that FluxCube can extract useful latent interactions between queries and area groups.
Annotation-Scheme Reconstruction for "Fake News" and Japanese Fake News Dataset
Apr 06, 2022


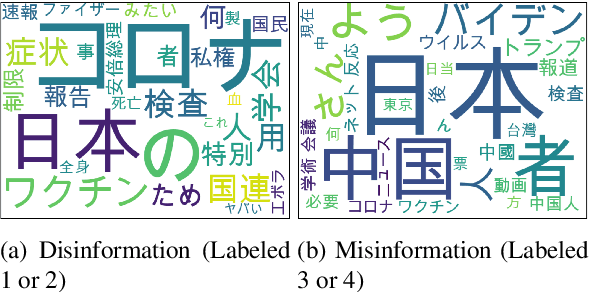
Abstract:Fake news provokes many societal problems; therefore, there has been extensive research on fake news detection tasks to counter it. Many fake news datasets were constructed as resources to facilitate this task. Contemporary research focuses almost exclusively on the factuality aspect of the news. However, this aspect alone is insufficient to explain "fake news," which is a complex phenomenon that involves a wide range of issues. To fully understand the nature of each instance of fake news, it is important to observe it from various perspectives, such as the intention of the false news disseminator, the harmfulness of the news to our society, and the target of the news. We propose a novel annotation scheme with fine-grained labeling based on detailed investigations of existing fake news datasets to capture these various aspects of fake news. Using the annotation scheme, we construct and publish the first Japanese fake news dataset. The annotation scheme is expected to provide an in-depth understanding of fake news. We plan to build datasets for both Japanese and other languages using our scheme. Our Japanese dataset is published at https://hkefka385.github.io/dataset/fakenews-japanese/.
Dataset of Fake News Detection and Fact Verification: A Survey
Nov 05, 2021



Abstract:The rapid increase in fake news, which causes significant damage to society, triggers many fake news related studies, including the development of fake news detection and fact verification techniques. The resources for these studies are mainly available as public datasets taken from Web data. We surveyed 118 datasets related to fake news research on a large scale from three perspectives: (1) fake news detection, (2) fact verification, and (3) other tasks; for example, the analysis of fake news and satire detection. We also describe in detail their utilization tasks and their characteristics. Finally, we highlight the challenges in the fake news dataset construction and some research opportunities that address these challenges. Our survey facilitates fake news research by helping researchers find suitable datasets without reinventing the wheel, and thereby, improves fake news studies in depth.
Mitigation of Diachronic Bias in Fake News Detection Dataset
Aug 28, 2021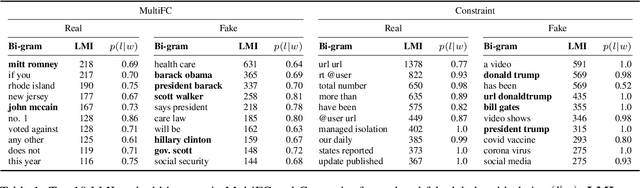
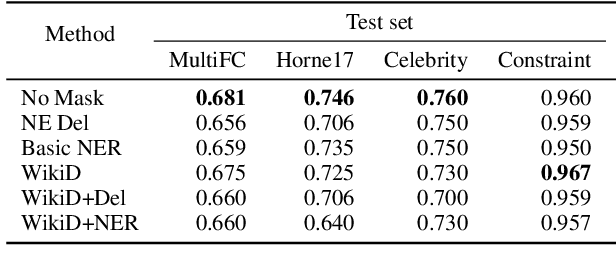
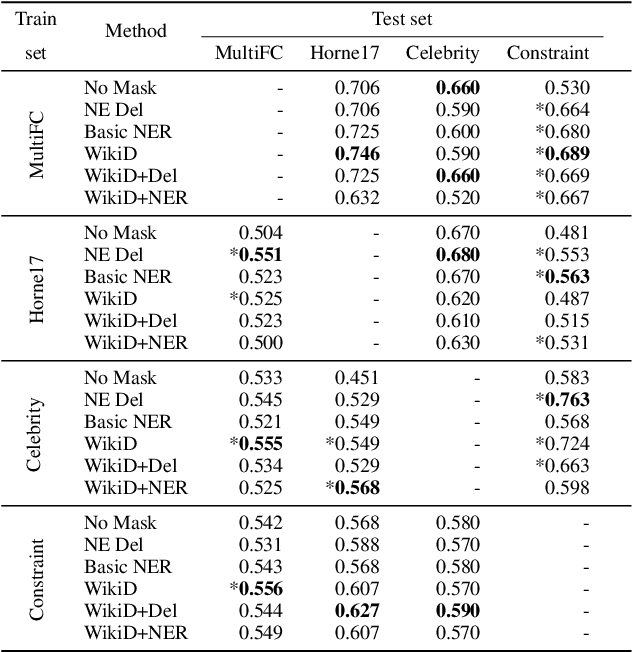
Abstract:Fake news causes significant damage to society.To deal with these fake news, several studies on building detection models and arranging datasets have been conducted. Most of the fake news datasets depend on a specific time period. Consequently, the detection models trained on such a dataset have difficulty detecting novel fake news generated by political changes and social changes; they may possibly result in biased output from the input, including specific person names and organizational names. We refer to this problem as \textbf{Diachronic Bias} because it is caused by the creation date of news in each dataset. In this study, we confirm the bias, especially proper nouns including person names, from the deviation of phrase appearances in each dataset. Based on these findings, we propose masking methods using Wikidata to mitigate the influence of person names and validate whether they make fake news detection models robust through experiments with in-domain and out-of-domain data.
Single Model for Influenza Forecasting of Multiple Countries by Multi-task Learning
Jul 07, 2021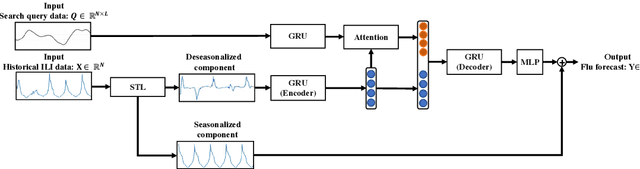
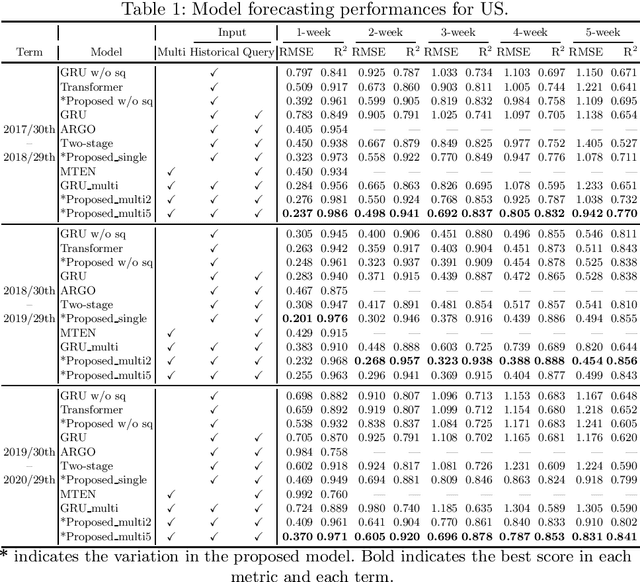
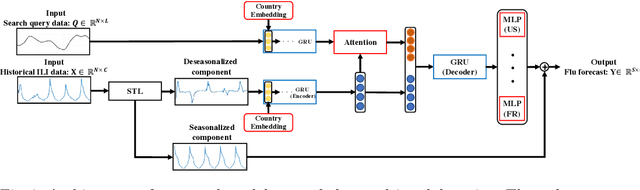
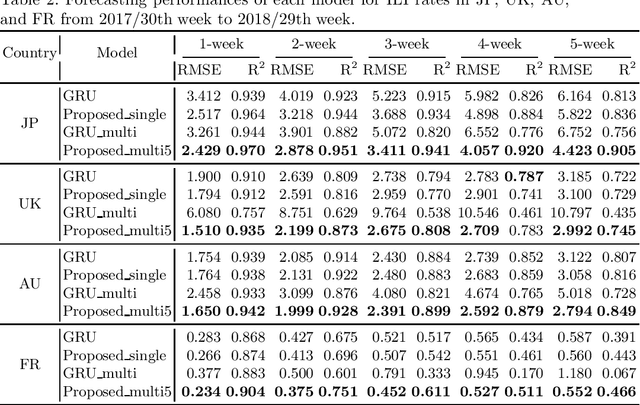
Abstract:The accurate forecasting of infectious epidemic diseases such as influenza is a crucial task undertaken by medical institutions. Although numerous flu forecasting methods and models based mainly on historical flu activity data and online user-generated contents have been proposed in previous studies, no flu forecasting model targeting multiple countries using two types of data exists at present. Our paper leverages multi-task learning to tackle the challenge of building one flu forecasting model targeting multiple countries; each country as each task. Also, to develop the flu prediction model with higher performance, we solved two issues; finding suitable search queries, which are part of the user-generated contents, and how to leverage search queries efficiently in the model creation. For the first issue, we propose the transfer approaches from English to other languages. For the second issue, we propose a novel flu forecasting model that takes advantage of search queries using an attention mechanism and extend the model to a multi-task model for multiple countries' flu forecasts. Experiments on forecasting flu epidemics in five countries demonstrate that our model significantly improved the performance by leveraging the search queries and multi-task learning compared to the baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge