Swanie Juhng
PsychAdapter: Adapting LLM Transformers to Reflect Traits, Personality and Mental Health
Dec 22, 2024



Abstract:Artificial intelligence-based language generators are now a part of most people's lives. However, by default, they tend to generate "average" language without reflecting the ways in which people differ. Here, we propose a lightweight modification to the standard language model transformer architecture - "PsychAdapter" - that uses empirically derived trait-language patterns to generate natural language for specified personality, demographic, and mental health characteristics (with or without prompting). We applied PsychAdapters to modify OpenAI's GPT-2, Google's Gemma, and Meta's Llama 3 and found generated text to reflect the desired traits. For example, expert raters evaluated PsychAdapter's generated text output and found it matched intended trait levels with 87.3% average accuracy for Big Five personalities, and 96.7% for depression and life satisfaction. PsychAdapter is a novel method to introduce psychological behavior patterns into language models at the foundation level, independent of prompting, by influencing every transformer layer. This approach can create chatbots with specific personality profiles, clinical training tools that mirror language associated with psychological conditionals, and machine translations that match an authors reading or education level without taking up LLM context windows. PsychAdapter also allows for the exploration psychological constructs through natural language expression, extending the natural language processing toolkit to study human psychology.
Transfer and Active Learning for Dissonance Detection: Addressing the Rare-Class Challenge
May 05, 2023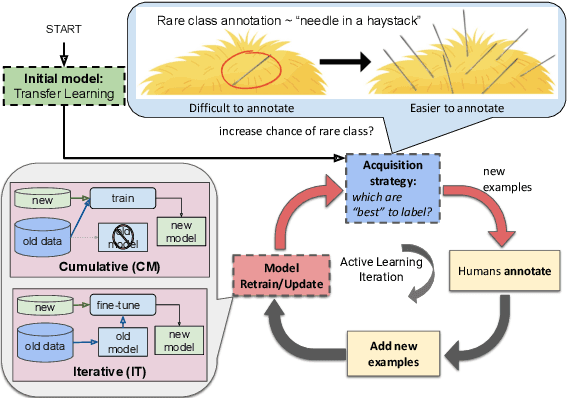
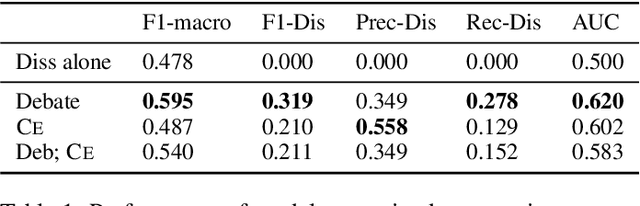
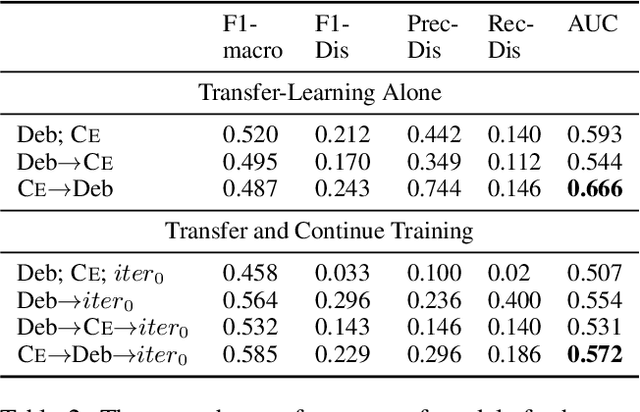
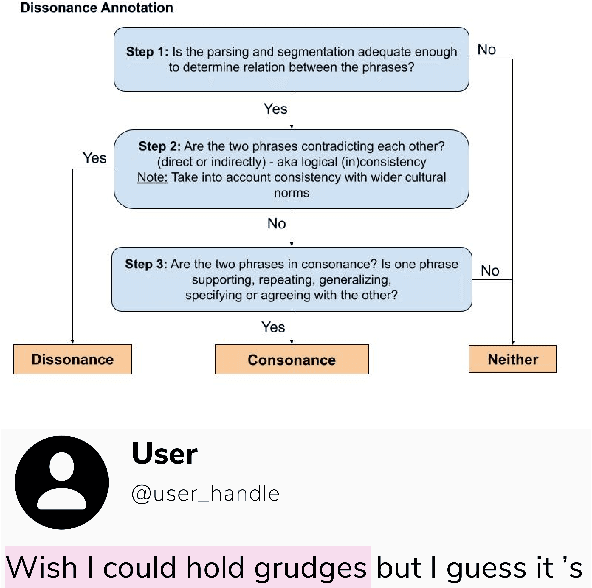
Abstract:While transformer-based systems have enabled greater accuracies with fewer training examples, data acquisition obstacles still persist for rare-class tasks -- when the class label is very infrequent (e.g. < 5% of samples). Active learning has in general been proposed to alleviate such challenges, but choice of selection strategy, the criteria by which rare-class examples are chosen, has not been systematically evaluated. Further, transformers enable iterative transfer-learning approaches. We propose and investigate transfer- and active learning solutions to the rare class problem of dissonance detection through utilizing models trained on closely related tasks and the evaluation of acquisition strategies, including a proposed probability-of-rare-class (PRC) approach. We perform these experiments for a specific rare class problem: collecting language samples of cognitive dissonance from social media. We find that PRC is a simple and effective strategy to guide annotations and ultimately improve model accuracy while transfer-learning in a specific order can improve the cold-start performance of the learner but does not benefit iterations of active learning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge