Sujeong Im
LabTOP: A Unified Model for Lab Test Outcome Prediction on Electronic Health Records
Feb 20, 2025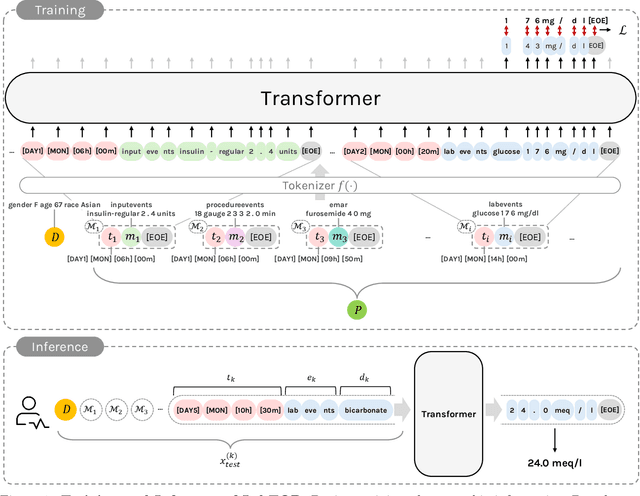
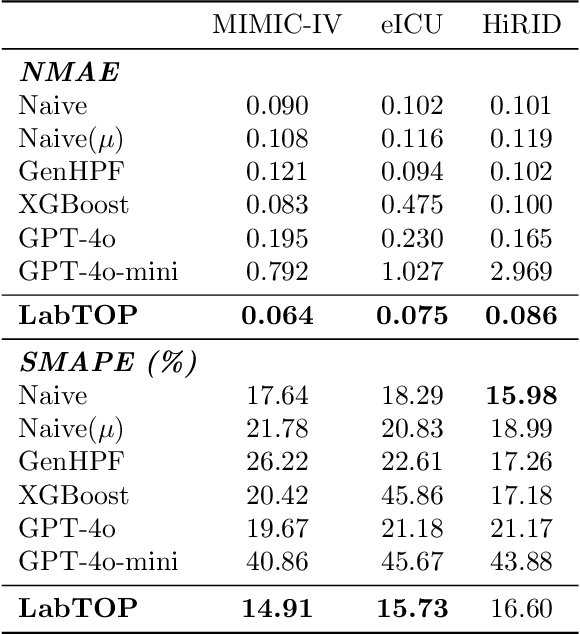
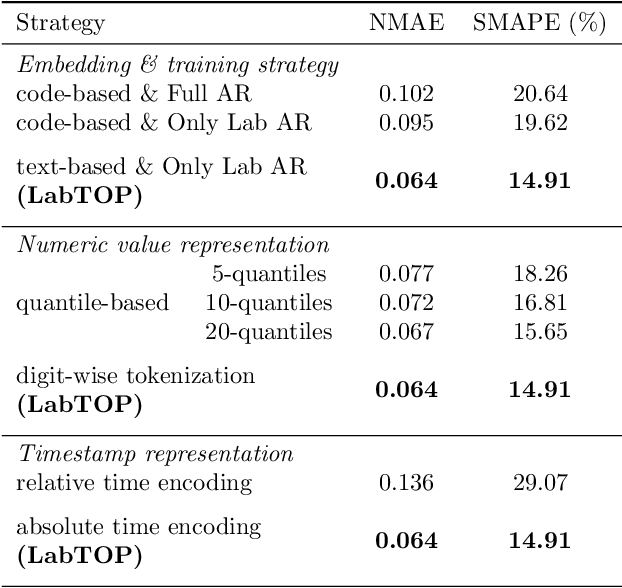
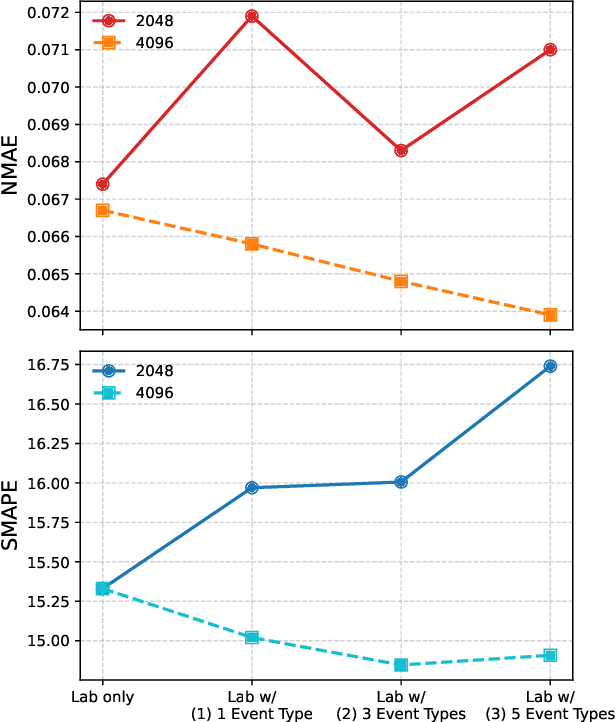
Abstract:Lab tests are fundamental for diagnosing diseases and monitoring patient conditions. However, frequent testing can be burdensome for patients, and test results may not always be immediately available. To address these challenges, we propose LabTOP, a unified model that predicts lab test outcomes by leveraging a language modeling approach on EHR data. Unlike conventional methods that estimate only a subset of lab tests or classify discrete value ranges, LabTOP performs continuous numerical predictions for a diverse range of lab items. We evaluate LabTOP on three publicly available EHR datasets and demonstrate that it outperforms existing methods, including traditional machine learning models and state-of-the-art large language models. We also conduct extensive ablation studies to confirm the effectiveness of our design choices. We believe that LabTOP will serve as an accurate and generalizable framework for lab test outcome prediction, with potential applications in clinical decision support and early detection of critical conditions.
Publicly Shareable Clinical Large Language Model Built on Synthetic Clinical Notes
Sep 06, 2023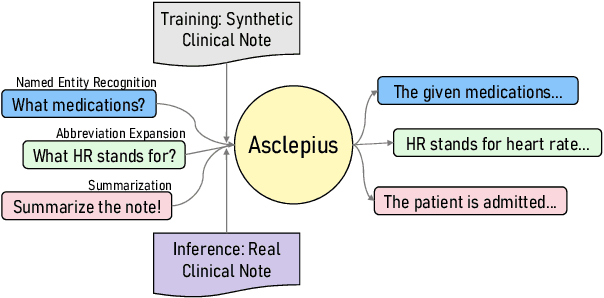
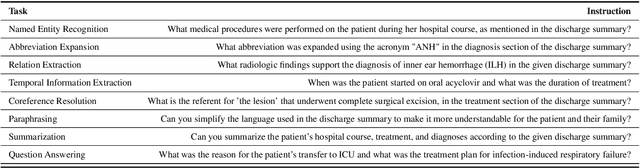
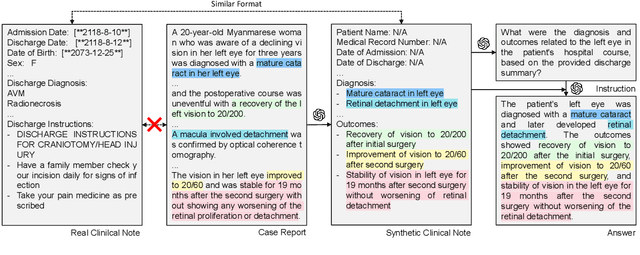
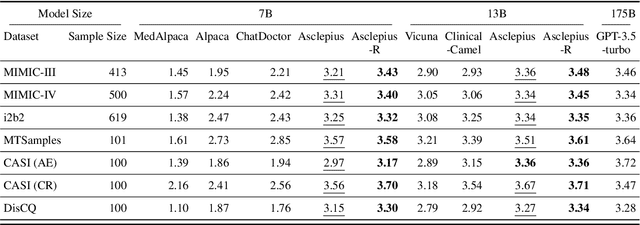
Abstract:The development of large language models tailored for handling patients' clinical notes is often hindered by the limited accessibility and usability of these notes due to strict privacy regulations. To address these challenges, we first create synthetic large-scale clinical notes using publicly available case reports extracted from biomedical literature. We then use these synthetic notes to train our specialized clinical large language model, Asclepius. While Asclepius is trained on synthetic data, we assess its potential performance in real-world applications by evaluating it using real clinical notes. We benchmark Asclepius against several other large language models, including GPT-3.5-turbo and other open-source alternatives. To further validate our approach using synthetic notes, we also compare Asclepius with its variants trained on real clinical notes. Our findings convincingly demonstrate that synthetic clinical notes can serve as viable substitutes for real ones when constructing high-performing clinical language models. This conclusion is supported by detailed evaluations conducted by both GPT-4 and medical professionals. All resources including weights, codes, and data used in the development of Asclepius are made publicly accessible for future research.
Clinical Decision Transformer: Intended Treatment Recommendation through Goal Prompting
Feb 01, 2023



Abstract:With recent achievements in tasks requiring context awareness, foundation models have been adopted to treat large-scale data from electronic health record (EHR) systems. However, previous clinical recommender systems based on foundation models have a limited purpose of imitating clinicians' behavior and do not directly consider a problem of missing values. In this paper, we propose Clinical Decision Transformer (CDT), a recommender system that generates a sequence of medications to reach a desired range of clinical states given as goal prompts. For this, we conducted goal-conditioned sequencing, which generated a subsequence of treatment history with prepended future goal state, and trained the CDT to model sequential medications required to reach that goal state. For contextual embedding over intra-admission and inter-admissions, we adopted a GPT-based architecture with an admission-wise attention mask and column embedding. In an experiment, we extracted a diabetes dataset from an EHR system, which contained treatment histories of 4788 patients. We observed that the CDT achieved the intended treatment effect according to goal prompt ranges (e.g., NormalA1c, LowerA1c, and HigherA1c), contrary to the case with behavior cloning. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to explore clinical recommendations from the perspective of goal prompting. See https://clinical-decision-transformer.github.io for code and additional information.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge