Sujeevan Ratnasingham
Taxonomic Reasoning for Rare Arthropods: Combining Dense Image Captioning and RAG for Interpretable Classification
Mar 13, 2025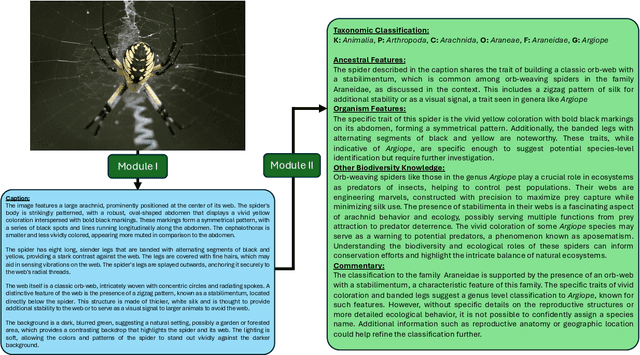
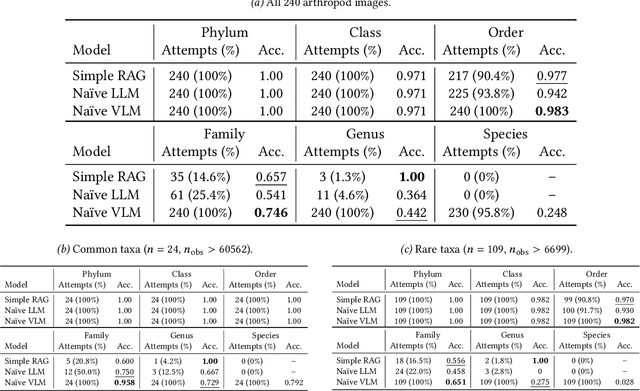
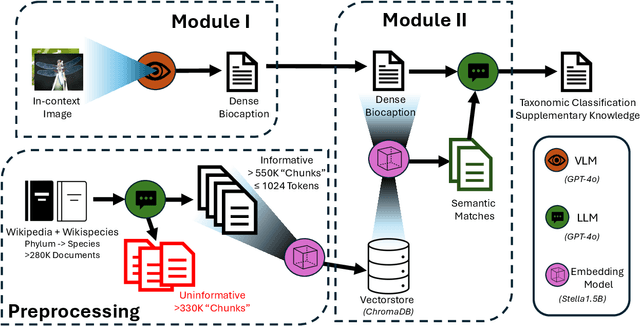
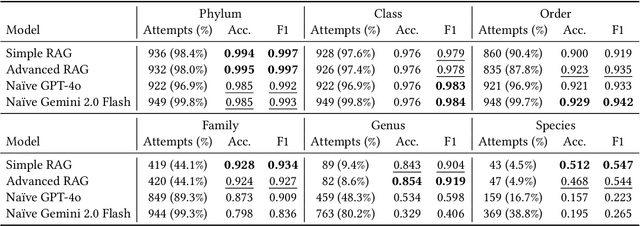
Abstract:In the context of pressing climate change challenges and the significant biodiversity loss among arthropods, automated taxonomic classification from organismal images is a subject of intense research. However, traditional AI pipelines based on deep neural visual architectures such as CNNs or ViTs face limitations such as degraded performance on the long-tail of classes and the inability to reason about their predictions. We integrate image captioning and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) with large language models (LLMs) to enhance biodiversity monitoring, showing particular promise for characterizing rare and unknown arthropod species. While a naive Vision-Language Model (VLM) excels in classifying images of common species, the RAG model enables classification of rarer taxa by matching explicit textual descriptions of taxonomic features to contextual biodiversity text data from external sources. The RAG model shows promise in reducing overconfidence and enhancing accuracy relative to naive LLMs, suggesting its viability in capturing the nuances of taxonomic hierarchy, particularly at the challenging family and genus levels. Our findings highlight the potential for modern vision-language AI pipelines to support biodiversity conservation initiatives, emphasizing the role of comprehensive data curation and collaboration with citizen science platforms to improve species identification, unknown species characterization and ultimately inform conservation strategies.
A Step Towards Worldwide Biodiversity Assessment: The BIOSCAN-1M Insect Dataset
Jul 19, 2023Abstract:In an effort to catalog insect biodiversity, we propose a new large dataset of hand-labelled insect images, the BIOSCAN-Insect Dataset. Each record is taxonomically classified by an expert, and also has associated genetic information including raw nucleotide barcode sequences and assigned barcode index numbers, which are genetically-based proxies for species classification. This paper presents a curated million-image dataset, primarily to train computer-vision models capable of providing image-based taxonomic assessment, however, the dataset also presents compelling characteristics, the study of which would be of interest to the broader machine learning community. Driven by the biological nature inherent to the dataset, a characteristic long-tailed class-imbalance distribution is exhibited. Furthermore, taxonomic labelling is a hierarchical classification scheme, presenting a highly fine-grained classification problem at lower levels. Beyond spurring interest in biodiversity research within the machine learning community, progress on creating an image-based taxonomic classifier will also further the ultimate goal of all BIOSCAN research: to lay the foundation for a comprehensive survey of global biodiversity. This paper introduces the dataset and explores the classification task through the implementation and analysis of a baseline classifier.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge