Subeen Lee
Explainable AI-Based Interface System for Weather Forecasting Model
Apr 01, 2025Abstract:Machine learning (ML) is becoming increasingly popular in meteorological decision-making. Although the literature on explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) is growing steadily, user-centered XAI studies have not extend to this domain yet. This study defines three requirements for explanations of black-box models in meteorology through user studies: statistical model performance for different rainfall scenarios to identify model bias, model reasoning, and the confidence of model outputs. Appropriate XAI methods are mapped to each requirement, and the generated explanations are tested quantitatively and qualitatively. An XAI interface system is designed based on user feedback. The results indicate that the explanations increase decision utility and user trust. Users prefer intuitive explanations over those based on XAI algorithms even for potentially easy-to-recognize examples. These findings can provide evidence for future research on user-centered XAI algorithms, as well as a basis to improve the usability of AI systems in practice.
* 19 pages, 16 figures
Example-Based Concept Analysis Framework for Deep Weather Forecast Models
Apr 01, 2025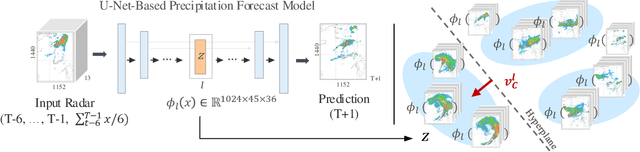
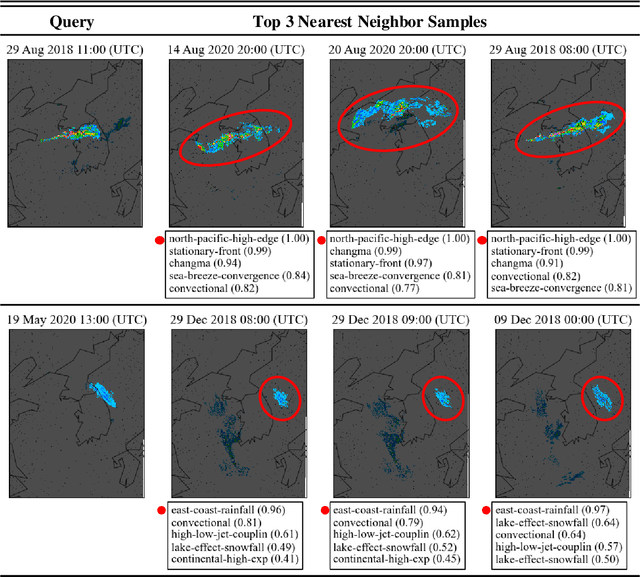
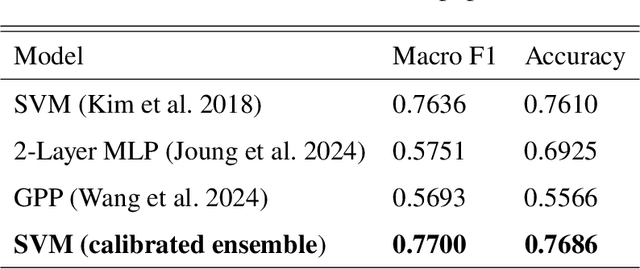
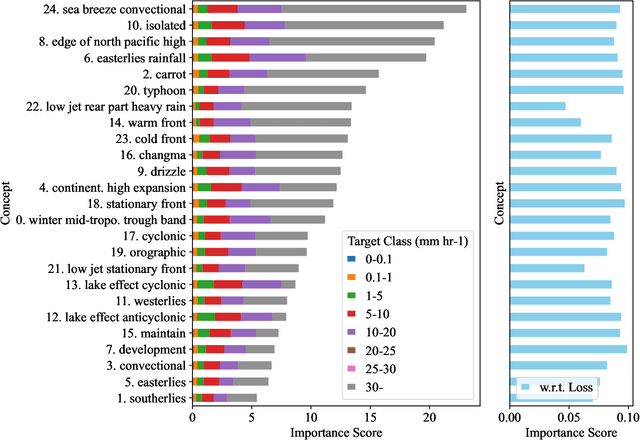
Abstract:To improve the trustworthiness of an AI model, finding consistent, understandable representations of its inference process is essential. This understanding is particularly important in high-stakes operations such as weather forecasting, where the identification of underlying meteorological mechanisms is as critical as the accuracy of the predictions. Despite the growing literature that addresses this issue through explainable AI, the applicability of their solutions is often limited due to their AI-centric development. To fill this gap, we follow a user-centric process to develop an example-based concept analysis framework, which identifies cases that follow a similar inference process as the target instance in a target model and presents them in a user-comprehensible format. Our framework provides the users with visually and conceptually analogous examples, including the probability of concept assignment to resolve ambiguities in weather mechanisms. To bridge the gap between vector representations identified from models and human-understandable explanations, we compile a human-annotated concept dataset and implement a user interface to assist domain experts involved in the the framework development.
* 39 pages, 10 figures
Diverse Rare Sample Generation with Pretrained GANs
Dec 27, 2024



Abstract:Deep generative models are proficient in generating realistic data but struggle with producing rare samples in low density regions due to their scarcity of training datasets and the mode collapse problem. While recent methods aim to improve the fidelity of generated samples, they often reduce diversity and coverage by ignoring rare and novel samples. This study proposes a novel approach for generating diverse rare samples from high-resolution image datasets with pretrained GANs. Our method employs gradient-based optimization of latent vectors within a multi-objective framework and utilizes normalizing flows for density estimation on the feature space. This enables the generation of diverse rare images, with controllable parameters for rarity, diversity, and similarity to a reference image. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach both qualitatively and quantitatively across various datasets and GANs without retraining or fine-tuning the pretrained GANs.
Mutually-Aware Feature Learning for Few-Shot Object Counting
Aug 19, 2024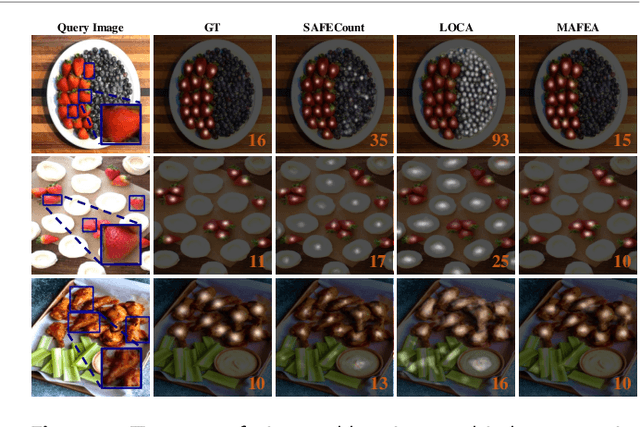
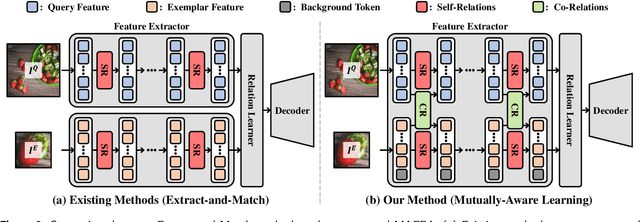
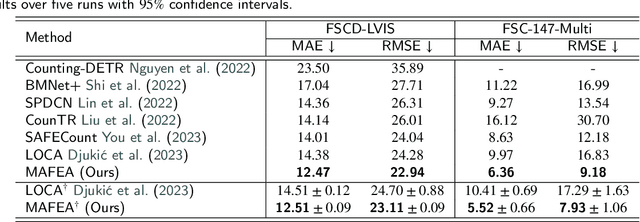
Abstract:Few-shot object counting has garnered significant attention for its practicality as it aims to count target objects in a query image based on given exemplars without the need for additional training. However, there is a shortcoming in the prevailing extract-and-match approach: query and exemplar features lack interaction during feature extraction since they are extracted unaware of each other and later correlated based on similarity. This can lead to insufficient target awareness of the extracted features, resulting in target confusion in precisely identifying the actual target when multiple class objects coexist. To address this limitation, we propose a novel framework, Mutually-Aware FEAture learning(MAFEA), which encodes query and exemplar features mutually aware of each other from the outset. By encouraging interaction between query and exemplar features throughout the entire pipeline, we can obtain target-aware features that are robust to a multi-category scenario. Furthermore, we introduce a background token to effectively associate the target region of query with exemplars and decouple its background region from them. Our extensive experiments demonstrate that our model reaches a new state-of-the-art performance on the two challenging benchmarks, FSCD-LVIS and FSC-147, with a remarkably reduced degree of the target confusion problem.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge