Stanislaw Drozdz
Universal versus system-specific features of punctuation usage patterns in~major Western~languages
Dec 21, 2022Abstract:The celebrated proverb that "speech is silver, silence is golden" has a long multinational history and multiple specific meanings. In written texts punctuation can in fact be considered one of its manifestations. Indeed, the virtue of effectively speaking and writing involves - often decisively - the capacity to apply the properly placed breaks. In the present study, based on a large corpus of world-famous and representative literary texts in seven major Western languages, it is shown that the distribution of intervals between consecutive punctuation marks in almost all texts can universally be characterised by only two parameters of the discrete Weibull distribution which can be given an intuitive interpretation in terms of the so-called hazard function. The values of these two parameters tend to be language-specific, however, and even appear to navigate translations. The properties of the computed hazard functions indicate that among the studied languages, English turns out to be the least constrained by the necessity to place a consecutive punctuation mark to partition a sequence of words. This may suggest that when compared to other studied languages, English is more flexible, in the sense of allowing longer uninterrupted sequences of words. Spanish reveals similar tendency to only a bit lesser extent.
Linguistic data mining with complex networks: a stylometric-oriented approach
Aug 16, 2018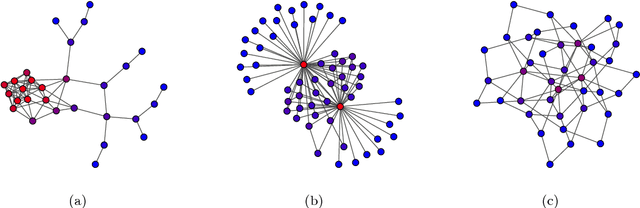
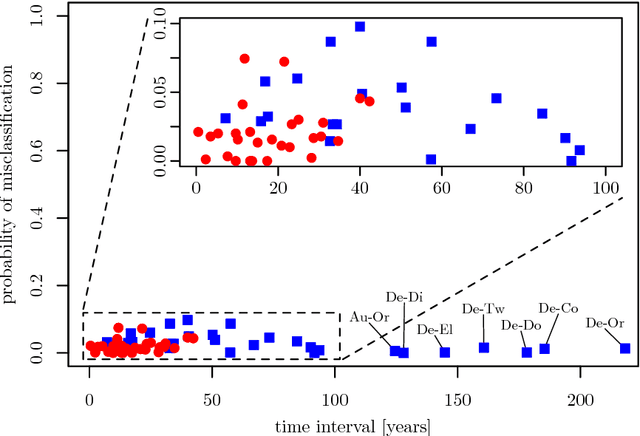
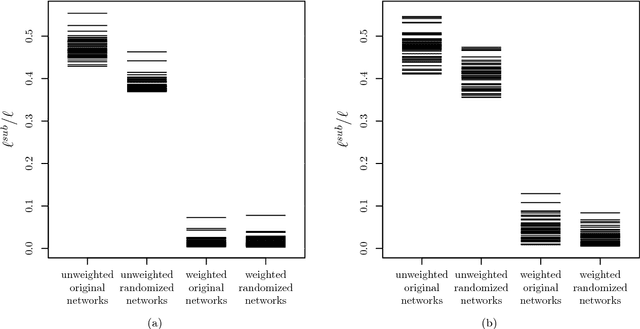
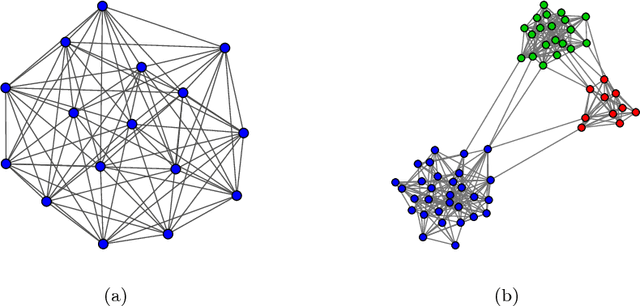
Abstract:By representing a text by a set of words and their co-occurrences, one obtains a word-adjacency network - a network being in a way a reduced representation of the given language sample. In this paper, the possibility of using network representation in order to extract information about individual language styles of literary texts is studied. By determining selected quantitative characteristics of the networks and applying machine learning algorithms, it is made possible to distinguish between texts of different authors. It turns out that within the studied set of texts in English and Polish, the properly rescaled weighted clustering coefficients and weighted degrees of only a few nodes in the word-adjacency networks are sufficient to obtain the accuracy of authorship attribution over 90\%. A correspondence between the authorship of texts and the structure of word-adjacency networks can therefore clearly be found; it may be stated that the network representation allows to distinguish individual language styles by comparing the way the authors use particular words and punctuation marks. The presented approach can be viewed as a generalization of the authorship attribution methods based on simplest lexical features. Apart from the characteristics given above, other network parameters are studied, both local and global ones, for both the unweighted and weighted networks. Their potential to capture the diversity of writing styles is discussed; some differences between languages are also observed.
Universal features of mountain ridge patterns on Earth
Apr 10, 2018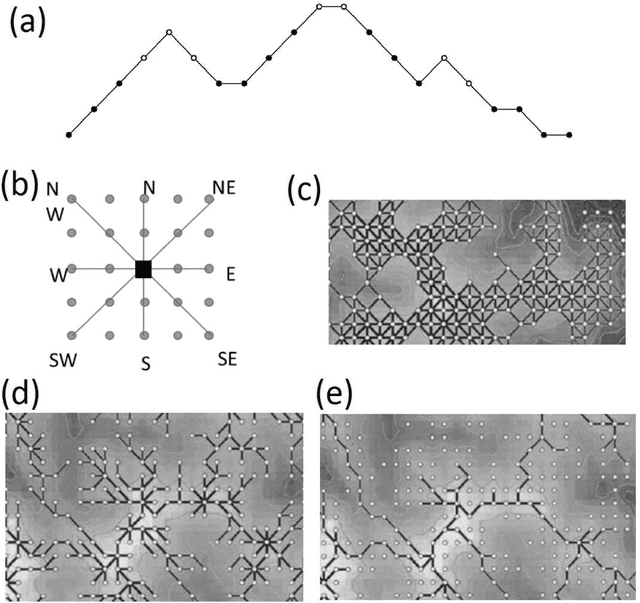
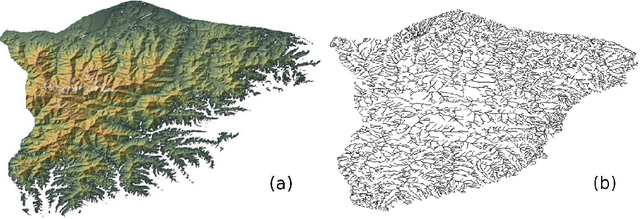
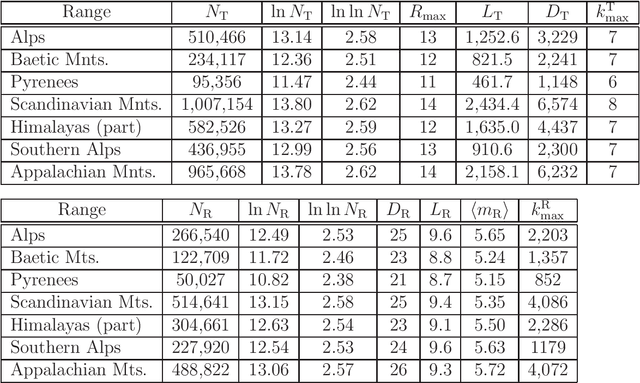
Abstract:We study structure of the mountain ridge systems based on the empirical elevation data collected by Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM). We consider several prominent mountain ranges from different geological periods and different geographical locations: the Alps, the Pyrenees, the Baetic Mountains, the Scandinavian Mountains, the Southern Alps, the Appalachian Mountains, and a part of the Himalayas. By using a network-based approach, for each mountain range we construct a simple "topographic" network representation (i.e., the ridge junctions as nodes and the ridges connecting them as edges) as well as a "ridge" representation (i.e., the ridges as nodes and the ridge junctions as edges). Then we calculate the main parameters characterizing these networks, like the node degree distribution and the average shortest path length. We observe that the topographic networks inherit the fractal structure of the mountain ranges but do not show any other complex features. In contrast, the ridge networks, while lacking the proper fractality, reveal the power-law cumulative degree distributions (cdfs) with a scaling exponent $1.6 \le \beta \le 1.7$. By taking into account the fact that the analyzed mountains differ in many properties, like their area, height, age, and geological origin, these values of $\beta$ seem to be universal for the earthly mountainous terrain.
In narrative texts punctuation marks obey the same statistics as words
Sep 27, 2016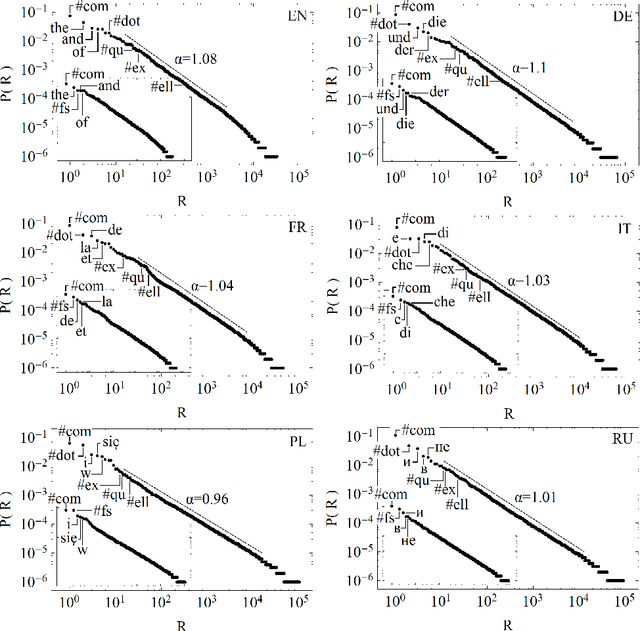
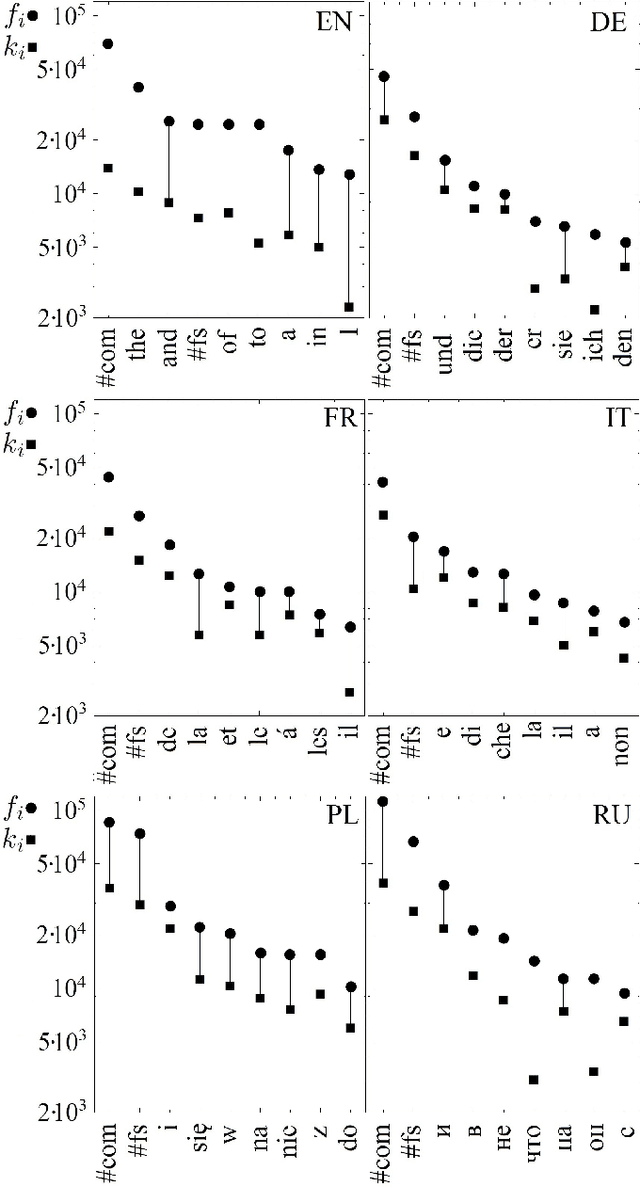
Abstract:From a grammar point of view, the role of punctuation marks in a sentence is formally defined and well understood. In semantic analysis punctuation plays also a crucial role as a method of avoiding ambiguity of the meaning. A different situation can be observed in the statistical analyses of language samples, where the decision on whether the punctuation marks should be considered or should be neglected is seen rather as arbitrary and at present it belongs to a researcher's preference. An objective of this work is to shed some light onto this problem by providing us with an answer to the question whether the punctuation marks may be treated as ordinary words and whether they should be included in any analysis of the word co-occurences. We already know from our previous study (S.~Dro\.zd\.z {\it et al.}, Inf. Sci. 331 (2016) 32-44) that full stops that determine the length of sentences are the main carrier of long-range correlations. Now we extend that study and analyze statistical properties of the most common punctuation marks in a few Indo-European languages, investigate their frequencies, and locate them accordingly in the Zipf rank-frequency plots as well as study their role in the word-adjacency networks. We show that, from a statistical viewpoint, the punctuation marks reveal properties that are qualitatively similar to the properties of the most frequent words like articles, conjunctions, pronouns, and prepositions. This refers to both the Zipfian analysis and the network analysis. By adding the punctuation marks to the Zipf plots, we also show that these plots that are normally described by the Zipf-Mandelbrot distribution largely restore the power-law Zipfian behaviour for the most frequent items.
* Information Sciences (inprint)
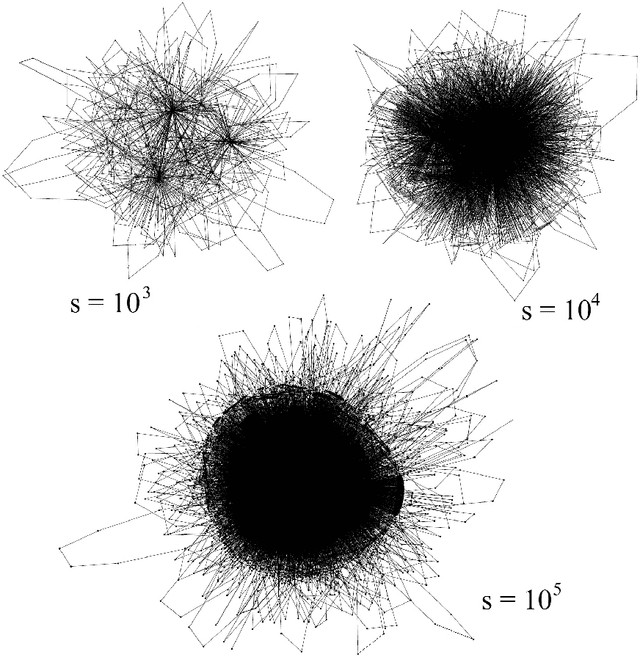
Modeling the average shortest path length in growth of word-adjacency networks
Mar 06, 2015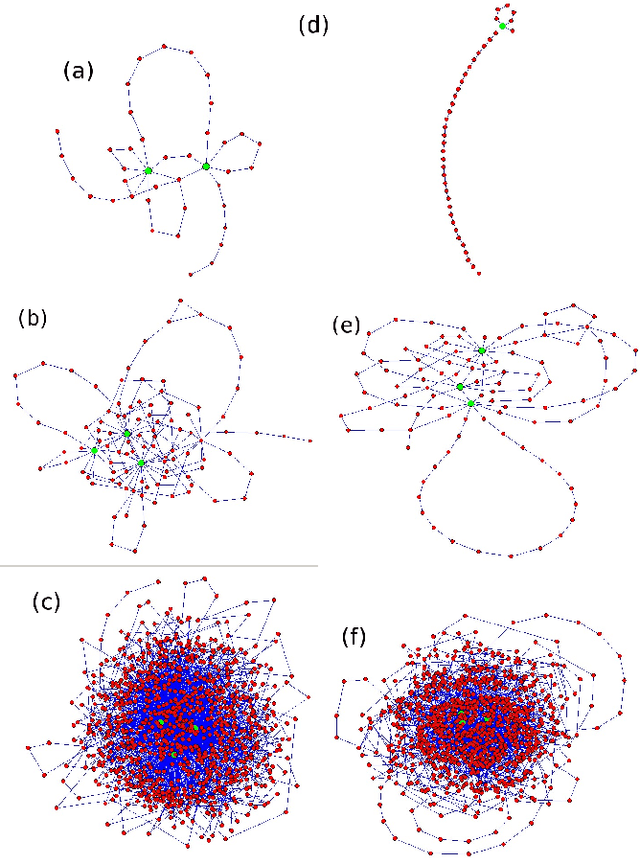
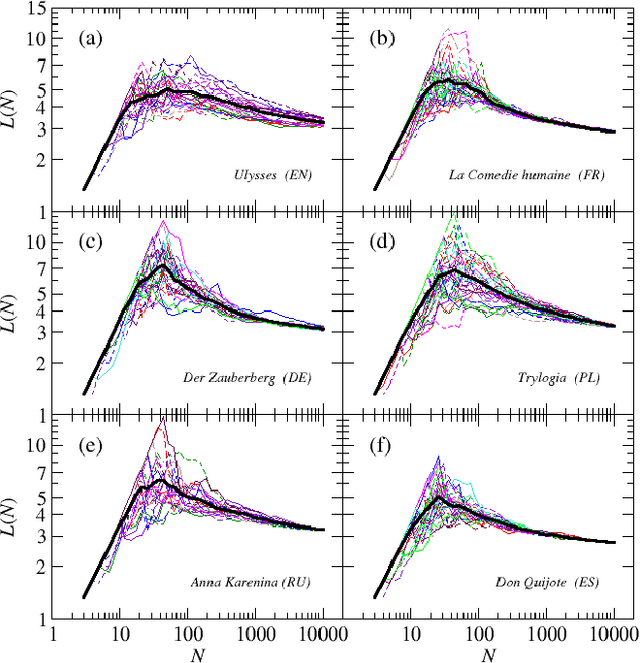
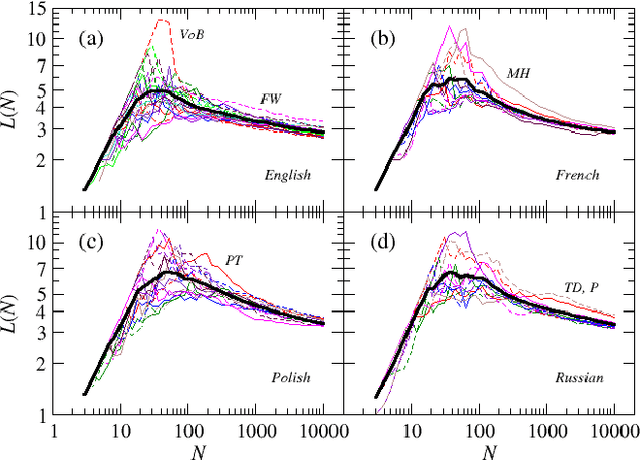
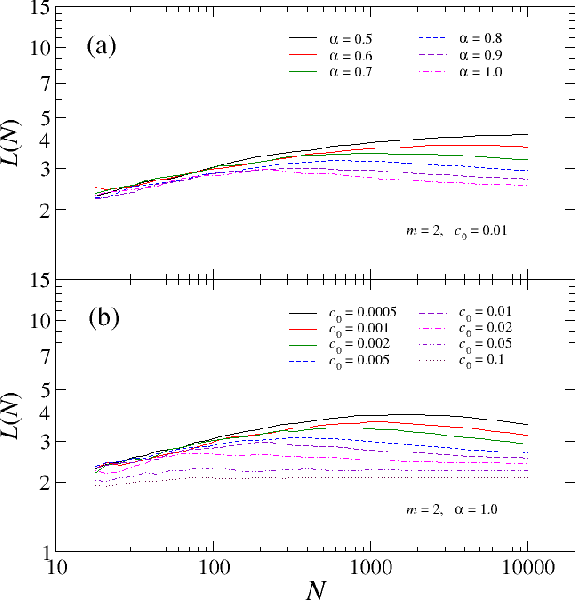
Abstract:We investigate properties of evolving linguistic networks defined by the word-adjacency relation. Such networks belong to the category of networks with accelerated growth but their shortest path length appears to reveal the network size dependence of different functional form than the ones known so far. We thus compare the networks created from literary texts with their artificial substitutes based on different variants of the Dorogovtsev-Mendes model and observe that none of them is able to properly simulate the novel asymptotics of the shortest path length. Then, we identify the local chain-like linear growth induced by grammar and style as a missing element in this model and extend it by incorporating such effects. It is in this way that a satisfactory agreement with the empirical result is obtained.
* Accepted for publication in Physical Review E
Linguistic complexity: English vs. Polish, text vs. corpus
Jul 06, 2010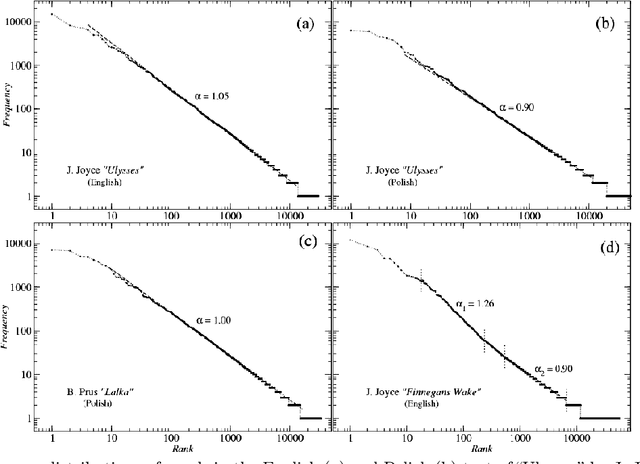
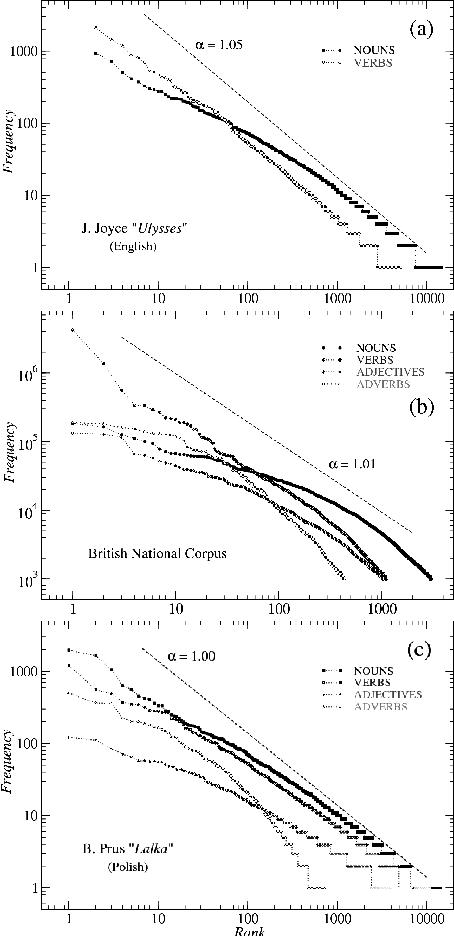
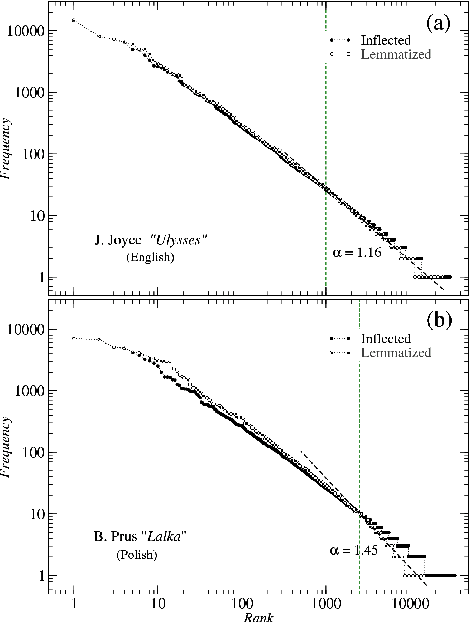
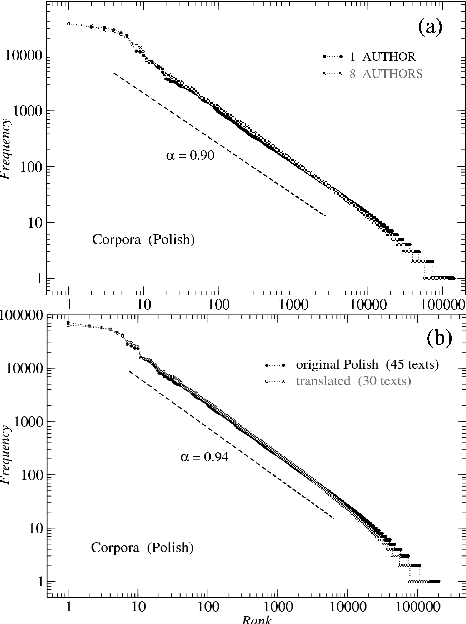
Abstract:We analyze the rank-frequency distributions of words in selected English and Polish texts. We show that for the lemmatized (basic) word forms the scale-invariant regime breaks after about two decades, while it might be consistent for the whole range of ranks for the inflected word forms. We also find that for a corpus consisting of texts written by different authors the basic scale-invariant regime is broken more strongly than in the case of comparable corpus consisting of texts written by the same author. Similarly, for a corpus consisting of texts translated into Polish from other languages the scale-invariant regime is broken more strongly than for a comparable corpus of native Polish texts. Moreover, we find that if the words are tagged with their proper part of speech, only verbs show rank-frequency distribution that is almost scale-invariant.
Approaching the linguistic complexity
Jan 21, 2009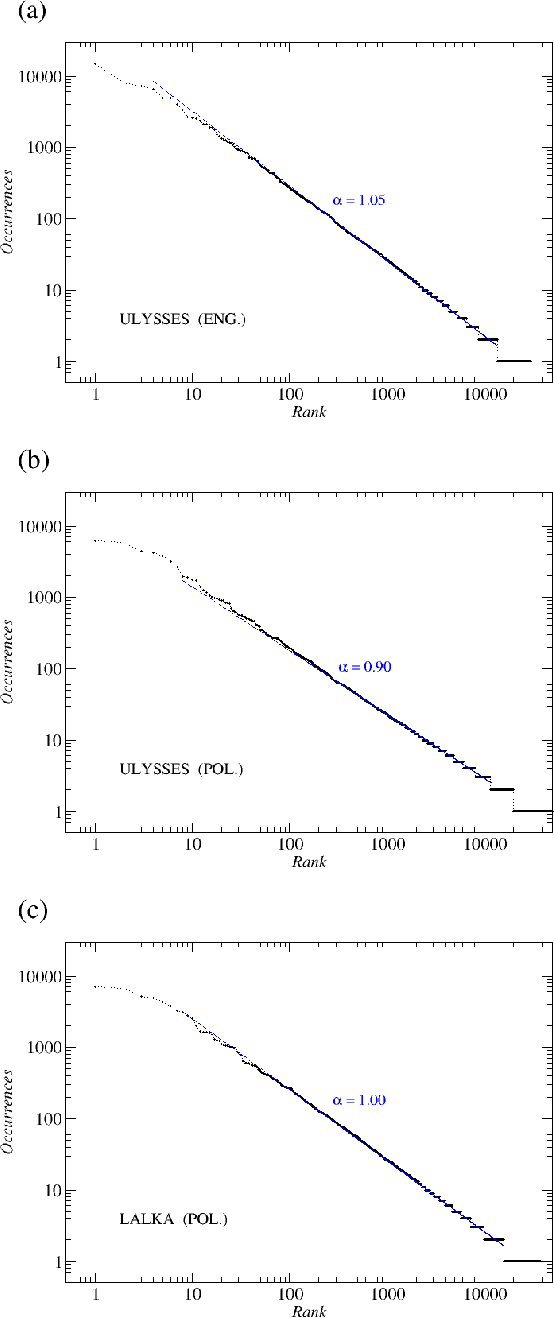
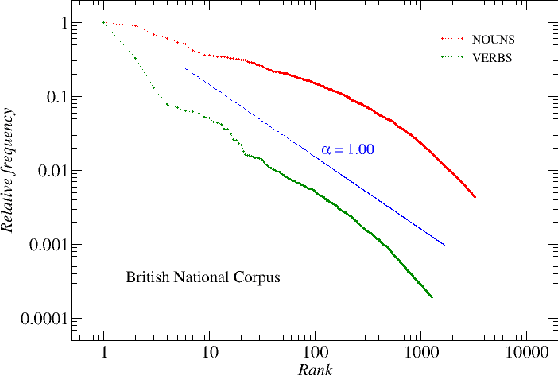
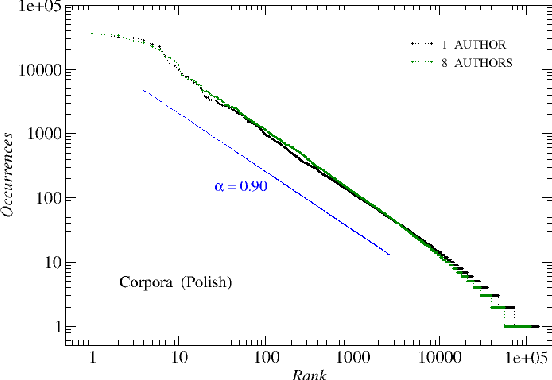
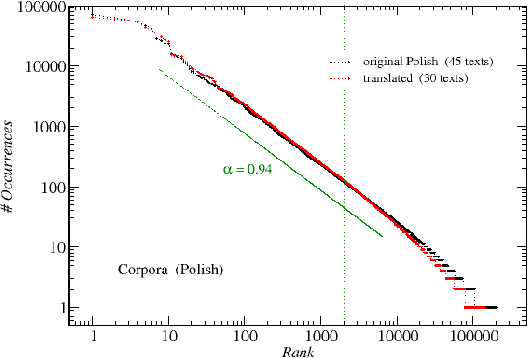
Abstract:We analyze the rank-frequency distributions of words in selected English and Polish texts. We compare scaling properties of these distributions in both languages. We also study a few small corpora of Polish literary texts and find that for a corpus consisting of texts written by different authors the basic scaling regime is broken more strongly than in the case of comparable corpus consisting of texts written by the same author. Similarly, for a corpus consisting of texts translated into Polish from other languages the scaling regime is broken more strongly than for a comparable corpus of native Polish texts. Moreover, based on the British National Corpus, we consider the rank-frequency distributions of the grammatically basic forms of words (lemmas) tagged with their proper part of speech. We find that these distributions do not scale if each part of speech is analyzed separately. The only part of speech that independently develops a trace of scaling is verbs.
* to be published in conference proceedings
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge