Sriram N. N.
A Hierarchical Network for Diverse Trajectory Proposals
Jun 09, 2019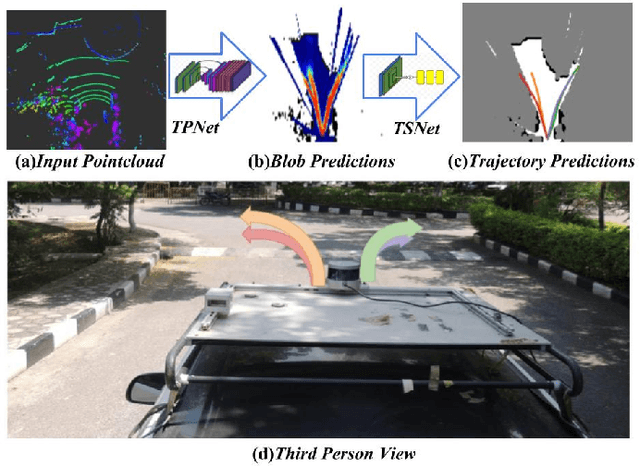
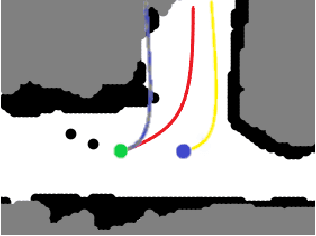
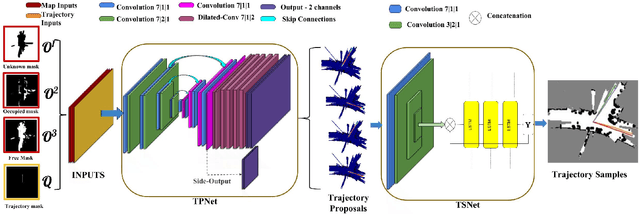
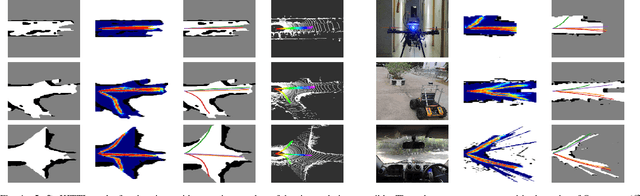
Abstract:Autonomous explorative robots frequently encounter scenarios where multiple future trajectories can be pursued. Often these are cases with multiple paths around an obstacle or trajectory options towards various frontiers. Humans in such situations can inherently perceive and reason about the surrounding environment to identify several possibilities of either manoeuvring around the obstacles or moving towards various frontiers. In this work, we propose a 2 stage Convolutional Neural Network architecture which mimics such an ability to map the perceived surroundings to multiple trajectories that a robot can choose to traverse. The first stage is a Trajectory Proposal Network which suggests diverse regions in the environment which can be occupied in the future. The second stage is a Trajectory Sampling network which provides a finegrained trajectory over the regions proposed by Trajectory Proposal Network. We evaluate our framework in diverse and complicated real life settings. For the outdoor case, we use the KITTI dataset and our own outdoor driving dataset. In the indoor setting, we use an autonomous drone to navigate various scenarios and also a ground robot which can explore the environment using the trajectories proposed by our framework. Our experiments suggest that the framework is able to develop a semantic understanding of the obstacles, open regions and identify diverse trajectories that a robot can traverse. Our comparisons portray the performance gain of the proposed architecture over a diverse set of methods against which it is compared.
Gradient Aware - Shrinking Domain based Control Design for Reactive Planning Frameworks used in Autonomous Vehicles
Apr 23, 2018

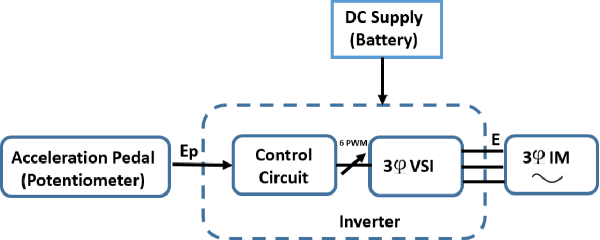
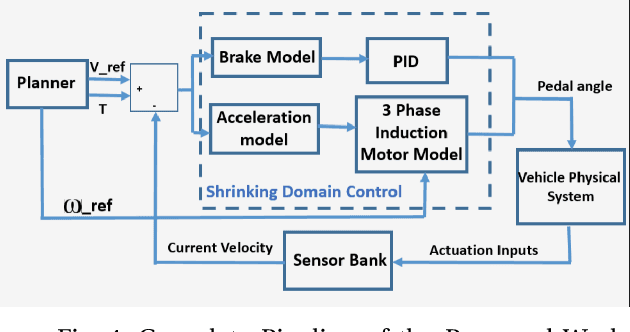
Abstract:In this paper, we present a novel control law for longitudinal speed control of autonomous vehicles. The key contributions of the proposed work include the design of a control law that reactively integrates the longitudinal surface gradient of road into its operation. In contrast to the existing works, we found that integrating the path gradient into the control framework improves the speed tracking efficacy. Since the control law is implemented over a shrinking domain scheme, it minimizes the integrated error by recomputing the control inputs at every discretized step and consequently provides less reaction time. This makes our control law suitable for motion planning frameworks that are operating at high frequencies. Furthermore, our work is implemented using a generalized vehicle model and can be easily extended to other classes of vehicles. The performance of gradient aware-shrinking domain based controller is implemented and tested on a stock electric vehicle on which a number of sensors are mounted. Results from the tests show the robustness of our control law for speed tracking on a terrain with varying gradient while also considering stringent time constraints imposed by the planning framework.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge