Srayanta Mukherjee
AI-Guided Discovery of Novel Ionic Liquid Solvents for Industrial CO2 Capture
Jan 02, 2026Abstract:We present an AI-driven approach to discover compounds with optimal properties for CO2 capture from flue gas-refinery emissions' primary source. Focusing on ionic liquids (ILs) as alternatives to traditional amine-based solvents, we successfully identify new IL candidates with high working capacity, manageable viscosity, favorable regeneration energy, and viable synthetic routes. Our approach follows a five-stage pipeline. First, we generate IL candidates by pairing available cation and anion molecules, then predict temperature- and pressure-dependent CO2 solubility and viscosity using a GNN-based molecular property prediction model. Next, we convert solubility to working capacity and regeneration energy via Van't Hoff modeling, and then find the best set of candidates using Pareto optimization, before finally filtering those based on feasible synthesis routes. We identify 36 feasible candidates that could enable 5-10% OPEX savings and up to 10% CAPEX reductions through lower regeneration energy requirements and reduced corrosivity-offering a novel carbon-capture strategy for refineries moving forward.
TEDDY: A Family Of Foundation Models For Understanding Single Cell Biology
Mar 05, 2025Abstract:Understanding the biological mechanism of disease is critical for medicine, and in particular drug discovery. AI-powered analysis of genome-scale biological data hold great potential in this regard. The increasing availability of single-cell RNA sequencing data has enabled the development of large foundation models for disease biology. However, existing foundation models either do not improve or only modestly improve over task-specific models in downstream applications. Here, we explored two avenues for improving the state-of-the-art. First, we scaled the pre-training dataset to 116 million cells, which is larger than those used by previous models. Second, we leveraged the availability of large-scale biological annotations as a form of supervision during pre-training. We trained the TEDDY family of models comprising six transformer-based state-of-the-art single-cell foundation models with 70 million, 160 million, and 400 million parameters. We vetted our models on two downstream evaluation tasks -- identifying the underlying disease state of held-out donors not seen during training and distinguishing healthy cells from diseased ones for disease conditions and donors not seen during training. Scaling experiments showed that performance improved predictably with both data volume and parameter count. Our models showed substantial improvement over existing work on the first task and more muted improvements on the second.
Graph-Based Retriever Captures the Long Tail of Biomedical Knowledge
Feb 19, 2024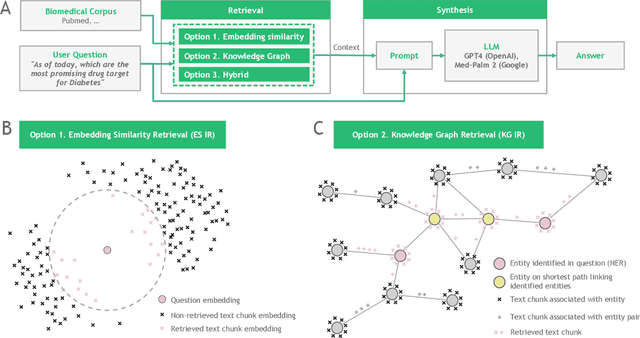
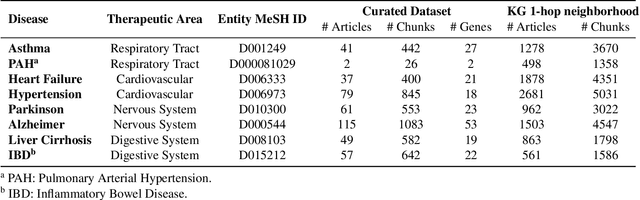
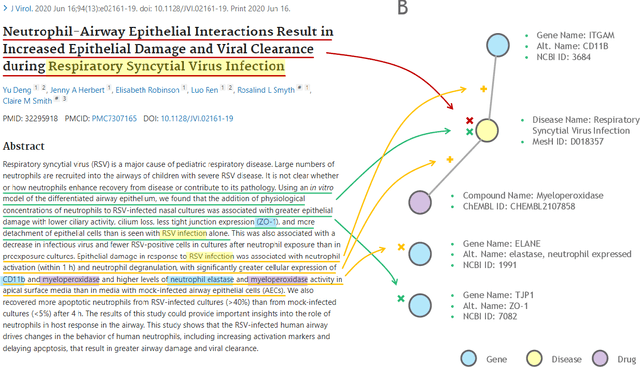
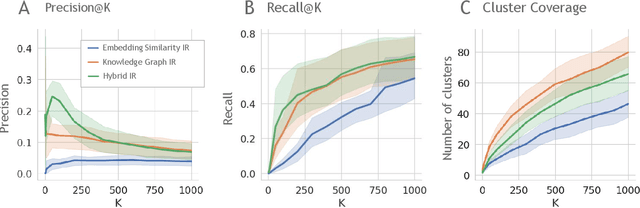
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are transforming the way information is retrieved with vast amounts of knowledge being summarized and presented via natural language conversations. Yet, LLMs are prone to highlight the most frequently seen pieces of information from the training set and to neglect the rare ones. In the field of biomedical research, latest discoveries are key to academic and industrial actors and are obscured by the abundance of an ever-increasing literature corpus (the information overload problem). Surfacing new associations between biomedical entities, e.g., drugs, genes, diseases, with LLMs becomes a challenge of capturing the long-tail knowledge of the biomedical scientific production. To overcome this challenge, Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) has been proposed to alleviate some of the shortcomings of LLMs by augmenting the prompts with context retrieved from external datasets. RAG methods typically select the context via maximum similarity search over text embeddings. In this study, we show that RAG methods leave out a significant proportion of relevant information due to clusters of over-represented concepts in the biomedical literature. We introduce a novel information-retrieval method that leverages a knowledge graph to downsample these clusters and mitigate the information overload problem. Its retrieval performance is about twice better than embedding similarity alternatives on both precision and recall. Finally, we demonstrate that both embedding similarity and knowledge graph retrieval methods can be advantageously combined into a hybrid model that outperforms both, enabling potential improvements to biomedical question-answering models.
ARMDN: Associative and Recurrent Mixture Density Networks for eRetail Demand Forecasting
Mar 16, 2018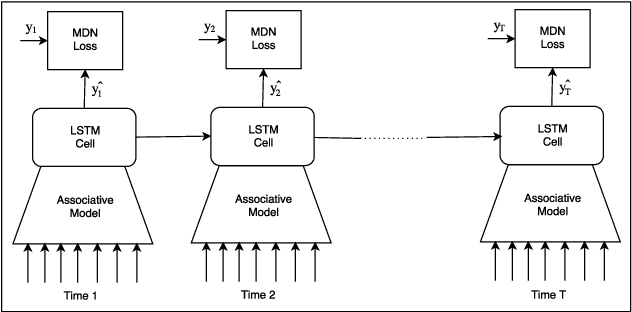
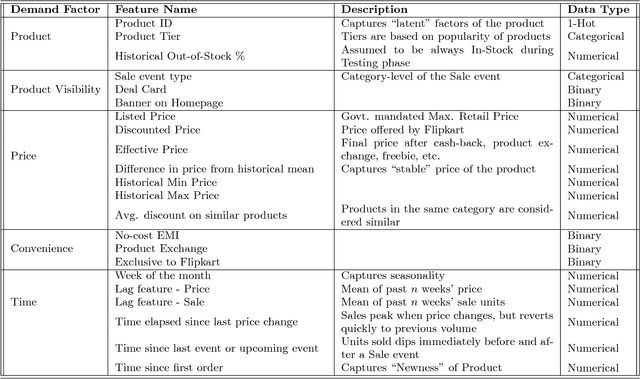
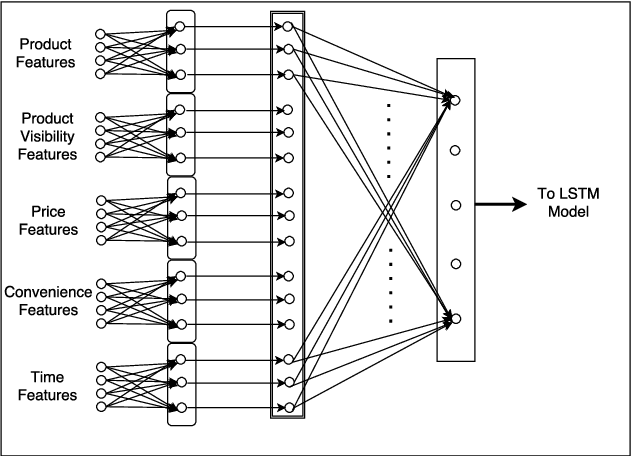
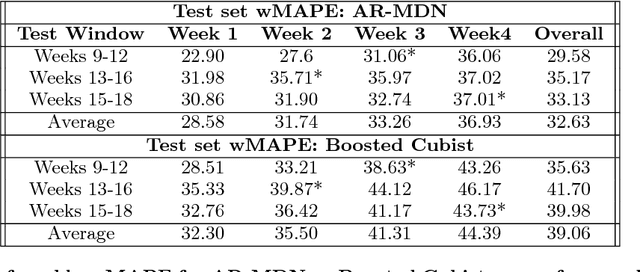
Abstract:Accurate demand forecasts can help on-line retail organizations better plan their supply-chain processes. The challenge, however, is the large number of associative factors that result in large, non-stationary shifts in demand, which traditional time series and regression approaches fail to model. In this paper, we propose a Neural Network architecture called AR-MDN, that simultaneously models associative factors, time-series trends and the variance in the demand. We first identify several causal features and use a combination of feature embeddings, MLP and LSTM to represent them. We then model the output density as a learned mixture of Gaussian distributions. The AR-MDN can be trained end-to-end without the need for additional supervision. We experiment on a dataset of an year's worth of data over tens-of-thousands of products from Flipkart. The proposed architecture yields a significant improvement in forecasting accuracy when compared with existing alternatives.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge