Sirui Wu
Compound Attention and Neighbor Matching Network for Multi-contrast MRI Super-resolution
Jul 24, 2023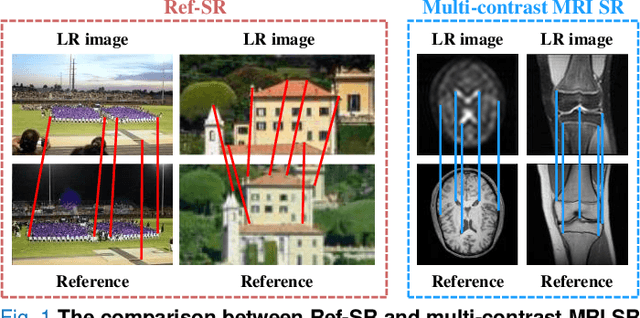
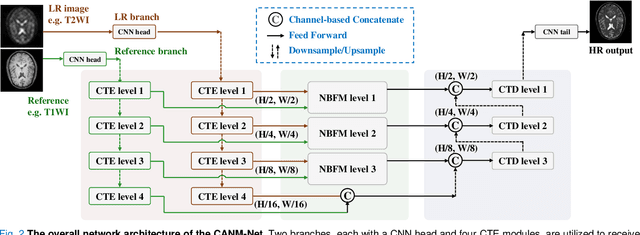

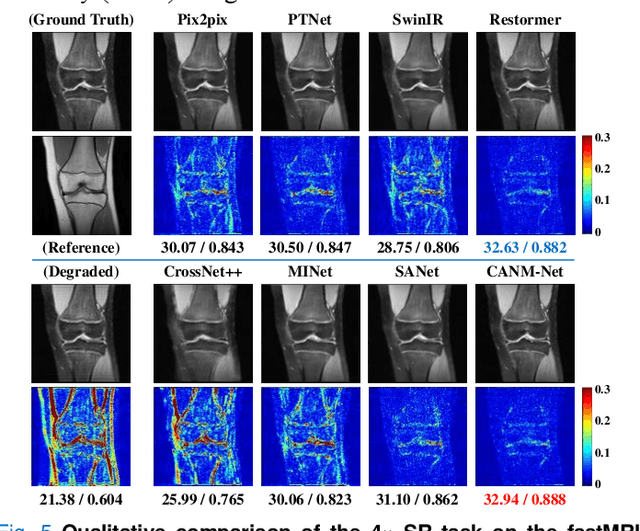
Abstract:Multi-contrast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) reflects information about human tissue from different perspectives and has many clinical applications. By utilizing the complementary information among different modalities, multi-contrast super-resolution (SR) of MRI can achieve better results than single-image super-resolution. However, existing methods of multi-contrast MRI SR have the following shortcomings that may limit their performance: First, existing methods either simply concatenate the reference and degraded features or exploit global feature-matching between them, which are unsuitable for multi-contrast MRI SR. Second, although many recent methods employ transformers to capture long-range dependencies in the spatial dimension, they neglect that self-attention in the channel dimension is also important for low-level vision tasks. To address these shortcomings, we proposed a novel network architecture with compound-attention and neighbor matching (CANM-Net) for multi-contrast MRI SR: The compound self-attention mechanism effectively captures the dependencies in both spatial and channel dimension; the neighborhood-based feature-matching modules are exploited to match degraded features and adjacent reference features and then fuse them to obtain the high-quality images. We conduct experiments of SR tasks on the IXI, fastMRI, and real-world scanning datasets. The CANM-Net outperforms state-of-the-art approaches in both retrospective and prospective experiments. Moreover, the robustness study in our work shows that the CANM-Net still achieves good performance when the reference and degraded images are imperfectly registered, proving good potential in clinical applications.
Towards Generalizable Medical Image Segmentation with Pixel-wise Uncertainty Estimation
May 13, 2023Abstract:Deep neural networks (DNNs) achieve promising performance in visual recognition under the independent and identically distributed (IID) hypothesis. In contrast, the IID hypothesis is not universally guaranteed in numerous real-world applications, especially in medical image analysis. Medical image segmentation is typically formulated as a pixel-wise classification task in which each pixel is classified into a category. However, this formulation ignores the hard-to-classified pixels, e.g., some pixels near the boundary area, as they usually confuse DNNs. In this paper, we first explore that hard-to-classified pixels are associated with high uncertainty. Based on this, we propose a novel framework that utilizes uncertainty estimation to highlight hard-to-classified pixels for DNNs, thereby improving its generalization. We evaluate our method on two popular benchmarks: prostate and fundus datasets. The results of the experiment demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge