Siqi Zuo
Unlocking the `Why' of Buying: Introducing a New Dataset and Benchmark for Purchase Reason and Post-Purchase Experience
Feb 20, 2024
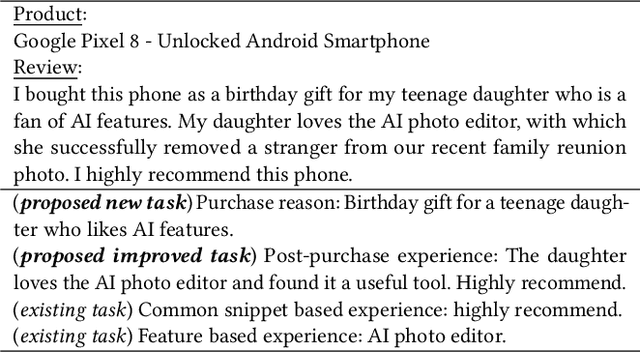
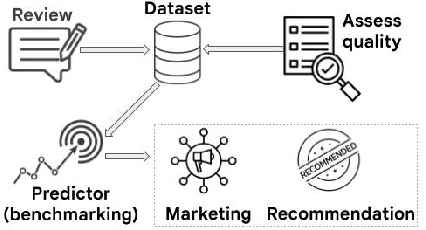

Abstract:Explanations are crucial for enhancing user trust and understanding within modern recommendation systems. To build truly explainable systems, we need high-quality datasets that elucidate why users make choices. While previous efforts have focused on extracting users' post-purchase sentiment in reviews, they ignore the reasons behind the decision to buy. In our work, we propose a novel purchase reason explanation task. To this end, we introduce an LLM-based approach to generate a dataset that consists of textual explanations of why real users make certain purchase decisions. We induce LLMs to explicitly distinguish between the reasons behind purchasing a product and the experience after the purchase in a user review. An automated, LLM-driven evaluation, as well as a small scale human evaluation, confirms the effectiveness of our approach to obtaining high-quality, personalized explanations. We benchmark this dataset on two personalized explanation generation tasks. We release the code and prompts to spur further research.
DynamicEmbedding: Extending TensorFlow for Colossal-Scale Applications
Apr 17, 2020
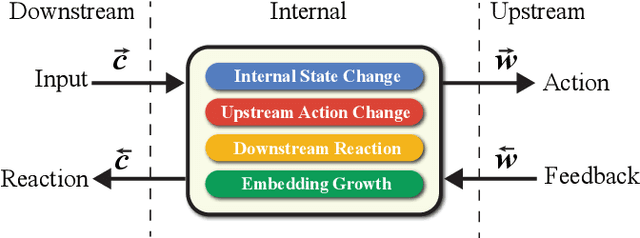

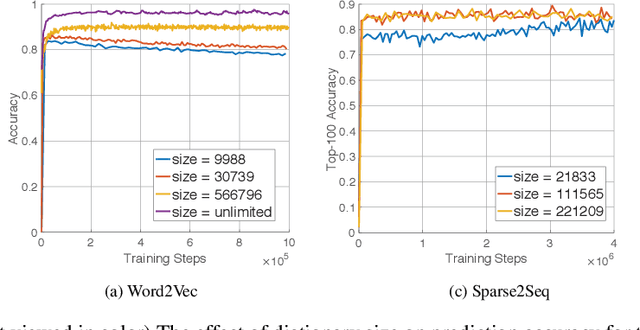
Abstract:One of the limitations of deep learning models with sparse features today stems from the predefined nature of their input, which requires a dictionary be defined prior to the training. With this paper we propose both a theory and a working system design which remove this limitation, and show that the resulting models are able to perform better and efficiently run at a much larger scale. Specifically, we achieve this by decoupling a model's content from its form to tackle architecture evolution and memory growth separately. To efficiently handle model growth, we propose a new neuron model, called DynamicCell, drawing inspiration from from the free energy principle [15] to introduce the concept of reaction to discharge non-digestive energy, which also subsumes gradient descent based approaches as its special cases. We implement DynamicCell by introducing a new server into TensorFlow to take over most of the work involving model growth. Consequently, it enables any existing deep learning models to efficiently handle arbitrary number of distinct sparse features (e.g., search queries), and grow incessantly without redefining the model. Most notably, one of our models, which has been reliably running in production for over a year, is capable of suggesting high quality keywords for advertisers of Google Smart Campaigns and achieved significant accuracy gains based on a challenging metric -- evidence that data-driven, self-evolving systems can potentially exceed the performance of traditional rule-based approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge