Siqi Gu
Real-centric Consistency Learning for Deepfake Detection
May 15, 2022
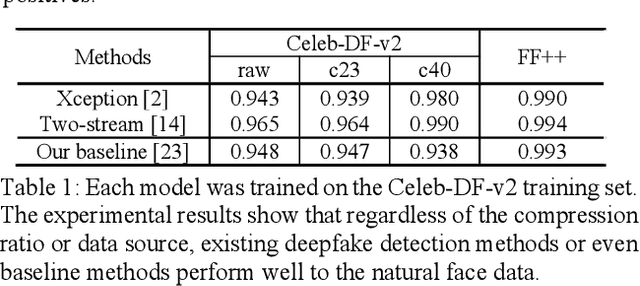

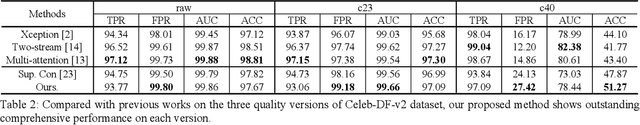
Abstract:Most of previous deepfake detection researches bent their efforts to describe and discriminate artifacts in human perceptible ways, which leave a bias in the learned networks of ignoring some critical invariance features intra-class and underperforming the robustness of internet interference. Essentially, the target of deepfake detection problem is to represent natural faces and fake faces at the representation space discriminatively, and it reminds us whether we could optimize the feature extraction procedure at the representation space through constraining intra-class consistence and inter-class inconsistence to bring the intra-class representations close and push the inter-class representations apart? Therefore, inspired by contrastive representation learning, we tackle the deepfake detection problem through learning the invariant representations of both classes and propose a novel real-centric consistency learning method. We constraint the representation from both the sample level and the feature level. At the sample level, we take the procedure of deepfake synthesis into consideration and propose a novel forgery semantical-based pairing strategy to mine latent generation-related features. At the feature level, based on the centers of natural faces at the representation space, we design a hard positive mining and synthesizing method to simulate the potential marginal features. Besides, a hard negative fusion method is designed to improve the discrimination of negative marginal features with the help of supervised contrastive margin loss we developed. The effectiveness and robustness of the proposed method has been demonstrated through extensive experiments.
A Unified Multi-Task Learning Framework of Real-Time Drone Supervision for Crowd Counting
Feb 08, 2022



Abstract:In this paper, a novel Unified Multi-Task Learning Framework of Real-Time Drone Supervision for Crowd Counting (MFCC) is proposed, which utilizes an image fusion network architecture to fuse images from the visible and thermal infrared image, and a crowd counting network architecture to estimate the density map. The purpose of our framework is to fuse two modalities, including visible and thermal infrared images captured by drones in real-time, that exploit the complementary information to accurately count the dense population and then automatically guide the flight of the drone to supervise the dense crowd. To this end, we propose the unified multi-task learning framework for crowd counting for the first time and re-design the unified training loss functions to align the image fusion network and crowd counting network. We also design the Assisted Learning Module (ALM) to fuse the density map feature to the image fusion encoder process for learning the counting features. To improve the accuracy, we propose the Extensive Context Extraction Module (ECEM) that is based on a dense connection architecture to encode multi-receptive-fields contextual information and apply the Multi-domain Attention Block (MAB) for concerning the head region in the drone view. Finally, we apply the prediction map to automatically guide the drones to supervise the dense crowd. The experimental results on the DroneRGBT dataset show that, compared with the existing methods, ours has comparable results on objective evaluations and an easier training process.
Block shuffling learning for Deepfake Detection
Feb 06, 2022



Abstract:Although the deepfake detection based on convolutional neural network has achieved good results, the detection results show that these detectors show obvious performance degradation when the input images undergo some common transformations (like resizing, blurring), which indicates that the generalization ability of the detector is insufficient. In this paper, we propose a novel block shuffling learning method to solve this problem. Specifically, we divide the images into blocks and then introduce the random shuffling to intra-block and inter-block. Intra-block shuffling increases the robustness of the detector and we also propose an adversarial loss algorithm to overcome the over-fitting problem brought by the noise introduced by shuffling. Moreover, we encourage the detector to focus on finding differences among the local features through inter-block shuffling, and reconstruct the spatial layout of the blocks to model the semantic associations between them. Especially, our method can be easily integrated with various CNN models. Extensive experiments show that our proposed method achieves state-of-the-art performance in forgery face detection, including good generalization ability in the face of common image transformations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge