Sinan Keten
TimeSliver : Symbolic-Linear Decomposition for Explainable Time Series Classification
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Identifying the extent to which every temporal segment influences a model's predictions is essential for explaining model decisions and increasing transparency. While post-hoc explainable methods based on gradients and feature-based attributions have been popular, they suffer from reference state sensitivity and struggle to generalize across time-series datasets, as they treat time points independently and ignore sequential dependencies. Another perspective on explainable time-series classification is through interpretable components of the model, for instance, leveraging self-attention mechanisms to estimate temporal attribution; however, recent findings indicate that these attention weights often fail to provide faithful measures of temporal importance. In this work, we advance this perspective and present a novel explainability-driven deep learning framework, TimeSliver, which jointly utilizes raw time-series data and its symbolic abstraction to construct a representation that maintains the original temporal structure. Each element in this representation linearly encodes the contribution of each temporal segment to the final prediction, allowing us to assign a meaningful importance score to every time point. For time-series classification, TimeSliver outperforms other temporal attribution methods by 11% on 7 distinct synthetic and real-world multivariate time-series datasets. TimeSliver also achieves predictive performance within 2% of state-of-the-art baselines across 26 UEA benchmark datasets, positioning it as a strong and explainable framework for general time-series classification.
Forces are not Enough: Benchmark and Critical Evaluation for Machine Learning Force Fields with Molecular Simulations
Oct 13, 2022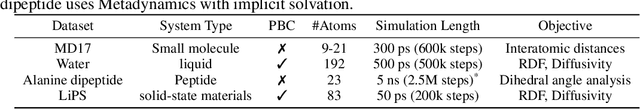
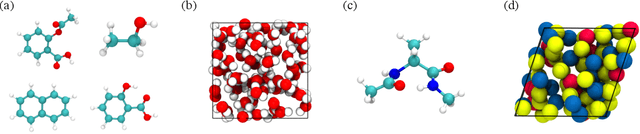

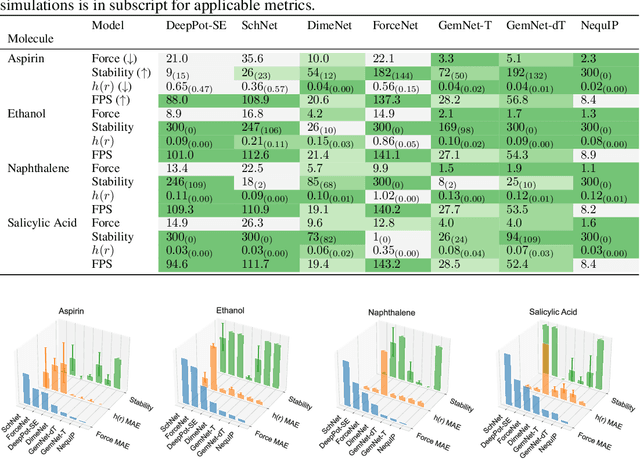
Abstract:Molecular dynamics (MD) simulation techniques are widely used for various natural science applications. Increasingly, machine learning (ML) force field (FF) models begin to replace ab-initio simulations by predicting forces directly from atomic structures. Despite significant progress in this area, such techniques are primarily benchmarked by their force/energy prediction errors, even though the practical use case would be to produce realistic MD trajectories. We aim to fill this gap by introducing a novel benchmark suite for ML MD simulation. We curate representative MD systems, including water, organic molecules, peptide, and materials, and design evaluation metrics corresponding to the scientific objectives of respective systems. We benchmark a collection of state-of-the-art (SOTA) ML FF models and illustrate, in particular, how the commonly benchmarked force accuracy is not well aligned with relevant simulation metrics. We demonstrate when and how selected SOTA methods fail, along with offering directions for further improvement. Specifically, we identify stability as a key metric for ML models to improve. Our benchmark suite comes with a comprehensive open-source codebase for training and simulation with ML FFs to facilitate further work.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge