Shuwen Xiao
CoNRec: Context-Discerning Negative Recommendation with LLMs
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Understanding what users like is relatively straightforward; understanding what users dislike, however, remains a challenging and underexplored problem. Research into users' negative preferences has gained increasing importance in modern recommendation systems. Numerous platforms have introduced explicit negative feedback mechanisms and leverage such signals to refine their recommendation models. Beyond traditional business metrics, user experience-driven metrics, such as negative feedback rates, have become critical indicators for evaluating system performance. However, most existing approaches primarily use negative feedback as an auxiliary signal to enhance positive recommendations, paying little attention to directly modeling negative interests, which can be highly valuable in offline applications. Moreover, due to the inherent sparsity of negative feedback data, models often suffer from context understanding biases induced by positive feedback dominance. To address these challenges, we propose the first large language model framework for negative feedback modeling with special designed context-discerning modules. We use semantic ID Representation to replace text-based item descriptions and introduce an item-level alignment task that enhances the LLM's understanding of the semantic context behind negative feedback. Furthermore, we design a Progressive GRPO training paradigm that enables the model to dynamically balance the positive and negative behavioral context utilization. Besides, our investigation further reveals a fundamental misalignment between the conventional next-negative-item prediction objective and users' true negative preferences, which is heavily influenced by the system's recommendation order. To mitigate this, we propose a novel reward function and evaluation metric grounded in multi-day future negative feedback and their collaborative signals.
ReaSeq: Unleashing World Knowledge via Reasoning for Sequential Modeling
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:Industrial recommender systems face two fundamental limitations under the log-driven paradigm: (1) knowledge poverty in ID-based item representations that causes brittle interest modeling under data sparsity, and (2) systemic blindness to beyond-log user interests that constrains model performance within platform boundaries. These limitations stem from an over-reliance on shallow interaction statistics and close-looped feedback while neglecting the rich world knowledge about product semantics and cross-domain behavioral patterns that Large Language Models have learned from vast corpora. To address these challenges, we introduce ReaSeq, a reasoning-enhanced framework that leverages world knowledge in Large Language Models to address both limitations through explicit and implicit reasoning. Specifically, ReaSeq employs explicit Chain-of-Thought reasoning via multi-agent collaboration to distill structured product knowledge into semantically enriched item representations, and latent reasoning via Diffusion Large Language Models to infer plausible beyond-log behaviors. Deployed on Taobao's ranking system serving hundreds of millions of users, ReaSeq achieves substantial gains: >6.0% in IPV and CTR, >2.9% in Orders, and >2.5% in GMV, validating the effectiveness of world-knowledge-enhanced reasoning over purely log-driven approaches.
Masked Contrastive Pre-Training for Efficient Video-Text Retrieval
Dec 05, 2022



Abstract:We present a simple yet effective end-to-end Video-language Pre-training (VidLP) framework, Masked Contrastive Video-language Pretraining (MAC), for video-text retrieval tasks. Our MAC aims to reduce video representation's spatial and temporal redundancy in the VidLP model by a mask sampling mechanism to improve pre-training efficiency. Comparing conventional temporal sparse sampling, we propose to randomly mask a high ratio of spatial regions and only feed visible regions into the encoder as sparse spatial sampling. Similarly, we adopt the mask sampling technique for text inputs for consistency. Instead of blindly applying the mask-then-prediction paradigm from MAE, we propose a masked-then-alignment paradigm for efficient video-text alignment. The motivation is that video-text retrieval tasks rely on high-level alignment rather than low-level reconstruction, and multimodal alignment with masked modeling encourages the model to learn a robust and general multimodal representation from incomplete and unstable inputs. Coupling these designs enables efficient end-to-end pre-training: reduce FLOPs (60% off), accelerate pre-training (by 3x), and improve performance. Our MAC achieves state-of-the-art results on various video-text retrieval datasets, including MSR-VTT, DiDeMo, and ActivityNet. Our approach is omnivorous to input modalities. With minimal modifications, we achieve competitive results on image-text retrieval tasks.
Convolutional Hierarchical Attention Network for Query-Focused Video Summarization
Feb 15, 2020
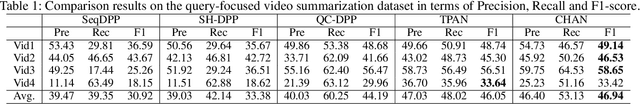

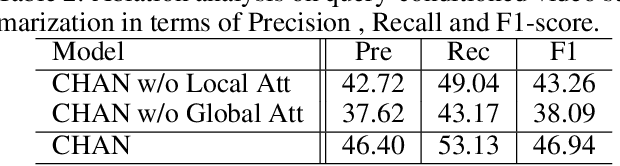
Abstract:Previous approaches for video summarization mainly concentrate on finding the most diverse and representative visual contents as video summary without considering the user's preference. This paper addresses the task of query-focused video summarization, which takes user's query and a long video as inputs and aims to generate a query-focused video summary. In this paper, we consider the task as a problem of computing similarity between video shots and query. To this end, we propose a method, named Convolutional Hierarchical Attention Network (CHAN), which consists of two parts: feature encoding network and query-relevance computing module. In the encoding network, we employ a convolutional network with local self-attention mechanism and query-aware global attention mechanism to learns visual information of each shot. The encoded features will be sent to query-relevance computing module to generate queryfocused video summary. Extensive experiments on the benchmark dataset demonstrate the competitive performance and show the effectiveness of our approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge