Shunkun Liang
Robust Subpixel Localization of Diagonal Markers in Large-Scale Navigation via Multi-Layer Screening and Adaptive Matching
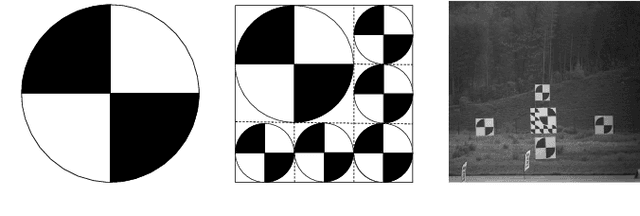
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:This paper proposes a robust, high-precision positioning methodology to address localization failures arising from complex background interference in large-scale flight navigation and the computational inefficiency inherent in conventional sliding window matching techniques. The proposed methodology employs a three-tiered framework incorporating multi-layer corner screening and adaptive template matching. Firstly, dimensionality is reduced through illumination equalization and structural information extraction. A coarse-to-fine candidate selection strategy minimizes sliding window computational costs, enabling rapid estimation of the marker's position. Finally, adaptive templates are generated for candidate points, achieving subpixel precision through improved template matching with correlation coefficient extremum fitting. Experimental results demonstrate the method's effectiveness in extracting and localizing diagonal markers in complex, large-scale environments, making it ideal for field-of-view measurement in navigation tasks.
A Minimal Solver for Relative Pose Estimation with Unknown Focal Length from Two Affine Correspondences
Dec 28, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we aim to estimate the relative pose and focal length between two views with known intrinsic parameters except for an unknown focal length from two affine correspondences (ACs). Cameras are commonly used in combination with inertial measurement units (IMUs) in applications such as self-driving cars, smartphones, and unmanned aerial vehicles. The vertical direction of camera views can be obtained by IMU measurements. The relative pose between two cameras is reduced from 5DOF to 3DOF. We propose a new solver to estimate the 3DOF relative pose and focal length. First, we establish constraint equations from two affine correspondences when the vertical direction is known. Then, based on the properties of the equation system with nontrivial solutions, four equations can be derived. These four equations only involve two parameters: the focal length and the relative rotation angle. Finally, the polynomial eigenvalue method is utilized to solve the problem of focal length and relative rotation angle. The proposed solver is evaluated using synthetic and real-world datasets. The results show that our solver performs better than the existing state-of-the-art solvers.
Optical Flow-Guided 6DoF Object Pose Tracking with an Event Camera
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:Object pose tracking is one of the pivotal technologies in multimedia, attracting ever-growing attention in recent years. Existing methods employing traditional cameras encounter numerous challenges such as motion blur, sensor noise, partial occlusion, and changing lighting conditions. The emerging bio-inspired sensors, particularly event cameras, possess advantages such as high dynamic range and low latency, which hold the potential to address the aforementioned challenges. In this work, we present an optical flow-guided 6DoF object pose tracking method with an event camera. A 2D-3D hybrid feature extraction strategy is firstly utilized to detect corners and edges from events and object models, which characterizes object motion precisely. Then, we search for the optical flow of corners by maximizing the event-associated probability within a spatio-temporal window, and establish the correlation between corners and edges guided by optical flow. Furthermore, by minimizing the distances between corners and edges, the 6DoF object pose is iteratively optimized to achieve continuous pose tracking. Experimental results of both simulated and real events demonstrate that our methods outperform event-based state-of-the-art methods in terms of both accuracy and robustness.
Globally Optimal Solution to the Generalized Relative Pose Estimation Problem using Affine Correspondences
Dec 19, 2025Abstract:Mobile devices equipped with a multi-camera system and an inertial measurement unit (IMU) are widely used nowadays, such as self-driving cars. The task of relative pose estimation using visual and inertial information has important applications in various fields. To improve the accuracy of relative pose estimation of multi-camera systems, we propose a globally optimal solver using affine correspondences to estimate the generalized relative pose with a known vertical direction. First, a cost function about the relative rotation angle is established after decoupling the rotation matrix and translation vector, which minimizes the algebraic error of geometric constraints from affine correspondences. Then, the global optimization problem is converted into two polynomials with two unknowns based on the characteristic equation and its first derivative is zero. Finally, the relative rotation angle can be solved using the polynomial eigenvalue solver, and the translation vector can be obtained from the eigenvector. Besides, a new linear solution is proposed when the relative rotation is small. The proposed solver is evaluated on synthetic data and real-world datasets. The experiment results demonstrate that our method outperforms comparable state-of-the-art methods in accuracy.
Collimator-assisted high-precision calibration method for event cameras
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:Event cameras are a new type of brain-inspired visual sensor with advantages such as high dynamic range and high temporal resolution. The geometric calibration of event cameras, which involves determining their intrinsic and extrinsic parameters, particularly in long-range measurement scenarios, remains a significant challenge. To address the dual requirements of long-distance and high-precision measurement, we propose an event camera calibration method utilizing a collimator with flickering star-based patterns. The proposed method first linearly solves camera parameters using the sphere motion model of the collimator, followed by nonlinear optimization to refine these parameters with high precision. Through comprehensive real-world experiments across varying conditions, we demonstrate that the proposed method consistently outperforms existing event camera calibration methods in terms of accuracy and reliability.
* 4 pages, 3 figures
Flexible Camera Calibration using a Collimator System
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:Camera calibration is a crucial step in photogrammetry and 3D vision applications. This paper introduces a novel camera calibration method using a designed collimator system. Our collimator system provides a reliable and controllable calibration environment for the camera. Exploiting the unique optical geometry property of our collimator system, we introduce an angle invariance constraint and further prove that the relative motion between the calibration target and camera conforms to a spherical motion model. This constraint reduces the original 6DOF relative motion between target and camera to a 3DOF pure rotation motion. Using spherical motion constraint, a closed-form linear solver for multiple images and a minimal solver for two images are proposed for camera calibration. Furthermore, we propose a single collimator image calibration algorithm based on the angle invariance constraint. This algorithm eliminates the requirement for camera motion, providing a novel solution for flexible and fast calibration. The performance of our method is evaluated in both synthetic and real-world experiments, which verify the feasibility of calibration using the collimator system and demonstrate that our method is superior to existing baseline methods. Demo code is available at https://github.com/LiangSK98/CollimatorCalibration
Accurate Pose Estimation for Flight Platforms based on Divergent Multi-Aperture Imaging System
Feb 27, 2025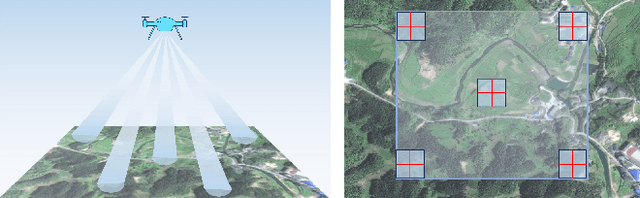

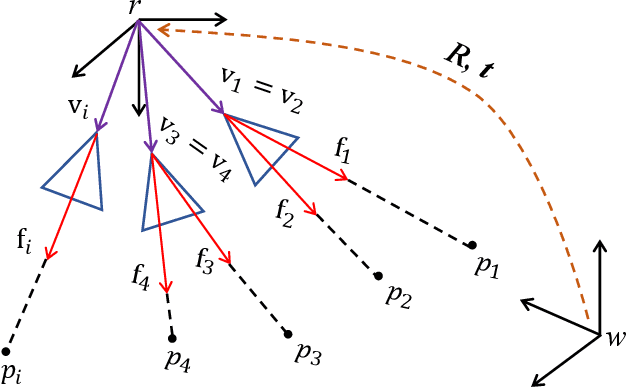
Abstract:Vision-based pose estimation plays a crucial role in the autonomous navigation of flight platforms. However, the field of view and spatial resolution of the camera limit pose estimation accuracy. This paper designs a divergent multi-aperture imaging system (DMAIS), equivalent to a single imaging system to achieve simultaneous observation of a large field of view and high spatial resolution. The DMAIS overcomes traditional observation limitations, allowing accurate pose estimation for the flight platform. {Before conducting pose estimation, the DMAIS must be calibrated. To this end we propose a calibration method for DMAIS based on the 3D calibration field.} The calibration process determines the imaging parameters of the DMAIS, which allows us to model DMAIS as a generalized camera. Subsequently, a new algorithm for accurately determining the pose of flight platform is introduced. We transform the absolute pose estimation problem into a nonlinear minimization problem. New optimality conditions are established for solving this problem based on Lagrange multipliers. Finally, real calibration experiments show the effectiveness and accuracy of the proposed method. Results from real flight experiments validate the system's ability to achieve centimeter-level positioning accuracy and arc-minute-level orientation accuracy.
High-precision visual navigation device calibration method based on collimator
Feb 25, 2025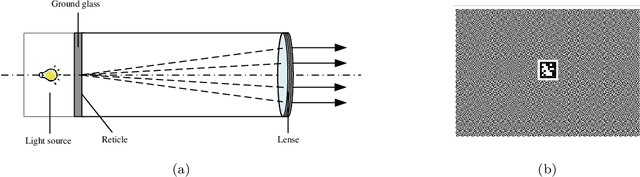
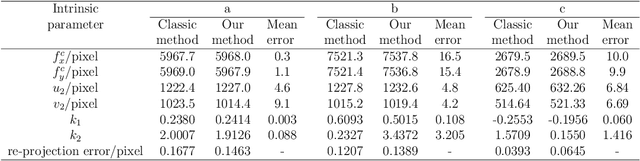
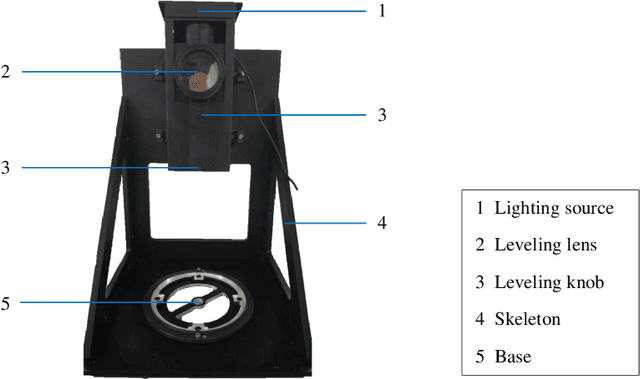

Abstract:Visual navigation devices require precise calibration to achieve high-precision localization and navigation, which includes camera and attitude calibration. To address the limitations of time-consuming camera calibration and complex attitude adjustment processes, this study presents a collimator-based calibration method and system. Based on the optical characteristics of the collimator, a single-image camera calibration algorithm is introduced. In addition, integrated with the precision adjustment mechanism of the calibration frame, a rotation transfer model between coordinate systems enables efficient attitude calibration. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method achieves accuracy and stability comparable to traditional multi-image calibration techniques. Specifically, the re-projection errors are less than 0.1463 pixels, and average attitude angle errors are less than 0.0586 degrees with a standard deviation less than 0.0257 degrees, demonstrating high precision and robustness.
Camera Calibration using a Collimator System
Sep 30, 2024



Abstract:Camera calibration is a crucial step in photogrammetry and 3D vision applications. In practical scenarios with a long working distance to cover a wide area, target-based calibration methods become complicated and inflexible due to site limitations. This paper introduces a novel camera calibration method using a collimator system, which can provide a reliable and controllable calibration environment for cameras with varying working distances. Based on the optical geometry of the collimator system, we prove that the relative motion between the target and camera conforms to the spherical motion model, reducing the original 6DOF relative motion to 3DOF pure rotation motion. Furthermore, a closed-form solver for multiple views and a minimal solver for two views are proposed for camera calibration. The performance of our method is evaluated in both synthetic and real-world experiments, which verify the feasibility of calibration using the collimator system and demonstrate that our method is superior to the state-of-the-art methods. Demo code is available at https://github.com/LiangSK98/CollimatorCalibration.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge