Dongcai Tan
Fusion-Restoration Image Processing Algorithm to Improve the High-Temperature Deformation Measurement
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:In the deformation measurement of high-temperature structures, image degradation caused by thermal radiation and random errors introduced by heat haze restrict the accuracy and effectiveness of deformation measurement. To suppress thermal radiation and heat haze using fusion-restoration image processing methods, thereby improving the accuracy and effectiveness of DIC in the measurement of high-temperature deformation. For image degradation caused by thermal radiation, based on the image layered representation, the image is decomposed into positive and negative channels for parallel processing, and then optimized for quality by multi-exposure image fusion. To counteract the high-frequency, random errors introduced by heat haze, we adopt the FSIM as the objective function to guide the iterative optimization of model parameters, and the grayscale average algorithm is applied to equalize anomalous gray values, thereby reducing measurement error. The proposed multi-exposure image fusion algorithm effectively suppresses image degradation caused by complex illumination conditions, boosting the effective computation area from 26% to 50% for under-exposed images and from 32% to 40% for over-exposed images without degrading measurement accuracy in the experiment. Meanwhile, the image restoration combined with the grayscale average algorithm reduces static thermal deformation measurement errors. The error in ε_xx is reduced by 85.3%, while the errors in ε_yy and γ_xy are reduced by 36.0% and 36.4%, respectively. We present image processing methods to suppress the interference of thermal radiation and heat haze in high-temperature deformation measurement using DIC. The experimental results verify that the proposed method can effectively improve image quality, reduce deformation measurement errors, and has potential application value in thermal deformation measurement.
Flexible Camera Calibration using a Collimator System
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:Camera calibration is a crucial step in photogrammetry and 3D vision applications. This paper introduces a novel camera calibration method using a designed collimator system. Our collimator system provides a reliable and controllable calibration environment for the camera. Exploiting the unique optical geometry property of our collimator system, we introduce an angle invariance constraint and further prove that the relative motion between the calibration target and camera conforms to a spherical motion model. This constraint reduces the original 6DOF relative motion between target and camera to a 3DOF pure rotation motion. Using spherical motion constraint, a closed-form linear solver for multiple images and a minimal solver for two images are proposed for camera calibration. Furthermore, we propose a single collimator image calibration algorithm based on the angle invariance constraint. This algorithm eliminates the requirement for camera motion, providing a novel solution for flexible and fast calibration. The performance of our method is evaluated in both synthetic and real-world experiments, which verify the feasibility of calibration using the collimator system and demonstrate that our method is superior to existing baseline methods. Demo code is available at https://github.com/LiangSK98/CollimatorCalibration
Collimator-assisted high-precision calibration method for event cameras
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:Event cameras are a new type of brain-inspired visual sensor with advantages such as high dynamic range and high temporal resolution. The geometric calibration of event cameras, which involves determining their intrinsic and extrinsic parameters, particularly in long-range measurement scenarios, remains a significant challenge. To address the dual requirements of long-distance and high-precision measurement, we propose an event camera calibration method utilizing a collimator with flickering star-based patterns. The proposed method first linearly solves camera parameters using the sphere motion model of the collimator, followed by nonlinear optimization to refine these parameters with high precision. Through comprehensive real-world experiments across varying conditions, we demonstrate that the proposed method consistently outperforms existing event camera calibration methods in terms of accuracy and reliability.
* 4 pages, 3 figures
High-precision visual navigation device calibration method based on collimator
Feb 25, 2025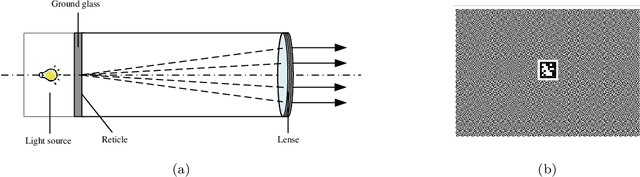
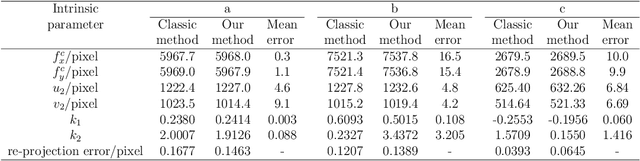
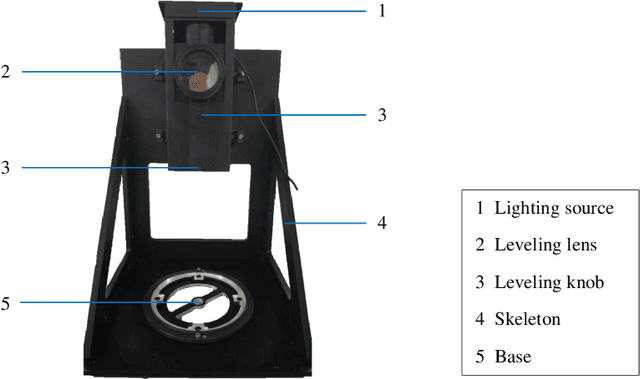

Abstract:Visual navigation devices require precise calibration to achieve high-precision localization and navigation, which includes camera and attitude calibration. To address the limitations of time-consuming camera calibration and complex attitude adjustment processes, this study presents a collimator-based calibration method and system. Based on the optical characteristics of the collimator, a single-image camera calibration algorithm is introduced. In addition, integrated with the precision adjustment mechanism of the calibration frame, a rotation transfer model between coordinate systems enables efficient attitude calibration. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method achieves accuracy and stability comparable to traditional multi-image calibration techniques. Specifically, the re-projection errors are less than 0.1463 pixels, and average attitude angle errors are less than 0.0586 degrees with a standard deviation less than 0.0257 degrees, demonstrating high precision and robustness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge