Shrestha Ghosh
Mining the Mind: What 100M Beliefs Reveal About Frontier LLM Knowledge
Oct 08, 2025



Abstract:LLMs are remarkable artifacts that have revolutionized a range of NLP and AI tasks. A significant contributor is their factual knowledge, which, to date, remains poorly understood, and is usually analyzed from biased samples. In this paper, we take a deep tour into the factual knowledge (or beliefs) of a frontier LLM, based on GPTKB v1.5 (Hu et al., 2025a), a recursively elicited set of 100 million beliefs of one of the strongest currently available frontier LLMs, GPT-4.1. We find that the models' factual knowledge differs quite significantly from established knowledge bases, and that its accuracy is significantly lower than indicated by previous benchmarks. We also find that inconsistency, ambiguity and hallucinations are major issues, shedding light on future research opportunities concerning factual LLM knowledge.
Cohort Discovery: A Survey on LLM-Assisted Clinical Trial Recruitment
Jun 18, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in LLMs have greatly improved general-domain NLP tasks. Yet, their adoption in critical domains, such as clinical trial recruitment, remains limited. As trials are designed in natural language and patient data is represented as both structured and unstructured text, the task of matching trials and patients benefits from knowledge aggregation and reasoning abilities of LLMs. Classical approaches are trial-specific and LLMs with their ability to consolidate distributed knowledge hold the potential to build a more general solution. Yet recent applications of LLM-assisted methods rely on proprietary models and weak evaluation benchmarks. In this survey, we are the first to analyze the task of trial-patient matching and contextualize emerging LLM-based approaches in clinical trial recruitment. We critically examine existing benchmarks, approaches and evaluation frameworks, the challenges to adopting LLM technologies in clinical research and exciting future directions.
GPTKB: Building Very Large Knowledge Bases from Language Models
Nov 07, 2024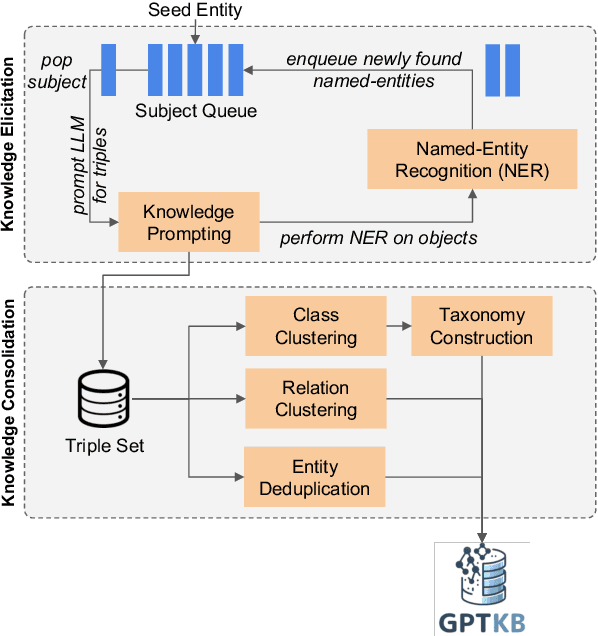
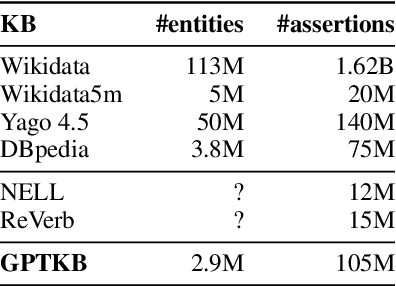
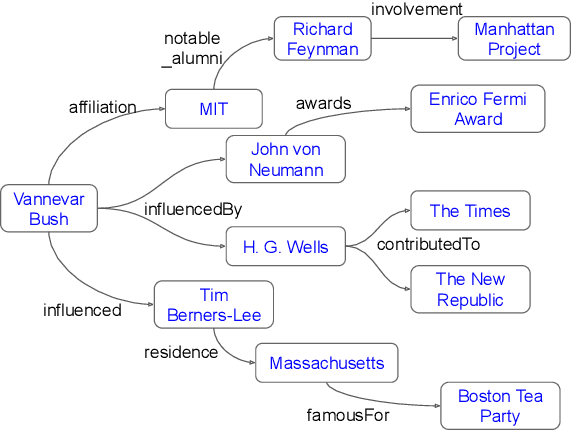

Abstract:General-domain knowledge bases (KB), in particular the "big three" -- Wikidata, Yago and DBpedia -- are the backbone of many intelligent applications. While these three have seen steady development, comprehensive KB construction at large has seen few fresh attempts. In this work, we propose to build a large general-domain KB entirely from a large language model (LLM). We demonstrate the feasibility of large-scale KB construction from LLMs, while highlighting specific challenges arising around entity recognition, entity and property canonicalization, and taxonomy construction. As a prototype, we use GPT-4o-mini to construct GPTKB, which contains 105 million triples for more than 2.9 million entities, at a cost 100x less than previous KBC projects. Our work is a landmark for two fields: For NLP, for the first time, it provides \textit{constructive} insights into the knowledge (or beliefs) of LLMs. For the Semantic Web, it shows novel ways forward for the long-standing challenge of general-domain KB construction. GPTKB is accessible at https://gptkb.org.
Completeness, Recall, and Negation in Open-World Knowledge Bases: A Survey
May 09, 2023Abstract:General-purpose knowledge bases (KBs) are a cornerstone of knowledge-centric AI. Many of them are constructed pragmatically from Web sources, and are thus far from complete. This poses challenges for the consumption as well as the curation of their content. While several surveys target the problem of completing incomplete KBs, the first problem is arguably to know whether and where the KB is incomplete in the first place, and to which degree. In this survey we discuss how knowledge about completeness, recall, and negation in KBs can be expressed, extracted, and inferred. We cover (i) the logical foundations of knowledge representation and querying under partial closed-world semantics; (ii) the estimation of this information via statistical patterns; (iii) the extraction of information about recall from KBs and text; (iv) the identification of interesting negative statements; and (v) relaxed notions of relative recall. This survey is targeted at two types of audiences: (1) practitioners who are interested in tracking KB quality, focusing extraction efforts, and building quality-aware downstream applications; and (2) data management, knowledge base and semantic web researchers who wish to understand the state of the art of knowledge bases beyond the open-world assumption. Consequently, our survey presents both fundamental methodologies and their working, and gives practice-oriented recommendations on how to choose between different approaches for a problem at hand.
* 33 pages, 5 tables
Class Cardinality Comparison as a Fermi Problem
Mar 08, 2023


Abstract:Questions on class cardinality comparisons are quite tricky to answer and come with its own challenges. They require some kind of reasoning since web documents and knowledge bases, indispensable sources of information, rarely store direct answers to questions, such as, ``Are there more astronauts or Physics Nobel Laureates?'' We tackle questions on class cardinality comparison by tapping into three sources for absolute cardinalities as well as the cardinalities of orthogonal subgroups of the classes. We propose novel techniques for aggregating signals with partial coverage for more reliable estimates and evaluate them on a dataset of 4005 class pairs, achieving an accuracy of 83.7%.
Answering Count Questions with Structured Answers from Text
Sep 15, 2022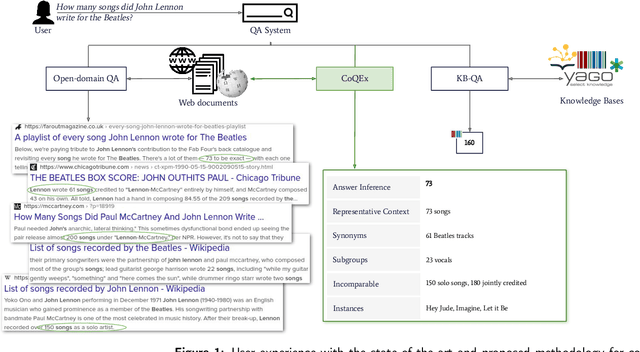

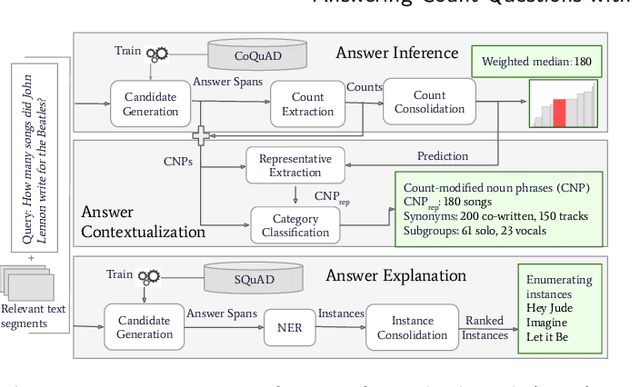

Abstract:In this work we address the challenging case of answering count queries in web search, such as ``number of songs by John Lennon''. Prior methods merely answer these with a single, and sometimes puzzling number or return a ranked list of text snippets with different numbers. This paper proposes a methodology for answering count queries with inference, contextualization and explanatory evidence. Unlike previous systems, our method infers final answers from multiple observations, supports semantic qualifiers for the counts, and provides evidence by enumerating representative instances. Experiments with a wide variety of queries, including existing benchmark show the benefits of our method, and the influence of specific parameter settings. Our code, data and an interactive system demonstration are publicly available at https://github.com/ghoshs/CoQEx and https://nlcounqer.mpi-inf.mpg.de/.
Answering Count Queries with Explanatory Evidence
Apr 11, 2022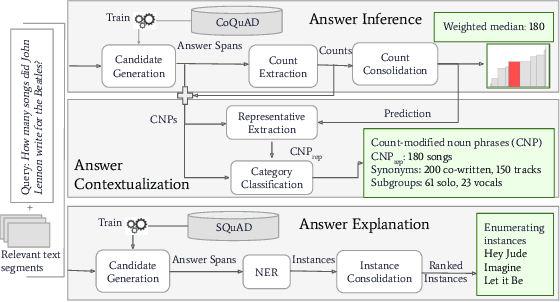
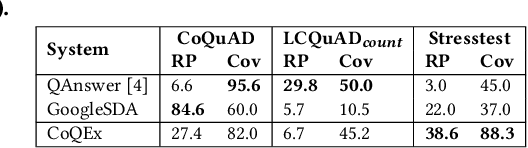
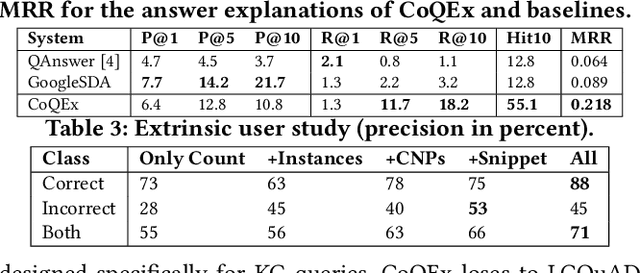
Abstract:A challenging case in web search and question answering are count queries, such as \textit{"number of songs by John Lennon"}. Prior methods merely answer these with a single, and sometimes puzzling number or return a ranked list of text snippets with different numbers. This paper proposes a methodology for answering count queries with inference, contextualization and explanatory evidence. Unlike previous systems, our method infers final answers from multiple observations, supports semantic qualifiers for the counts, and provides evidence by enumerating representative instances. Experiments with a wide variety of queries show the benefits of our method. To promote further research on this underexplored topic, we release an annotated dataset of 5k queries with 200k relevant text spans.
CounQER: A System for Discovering and Linking Count Information in Knowledge Bases
May 07, 2020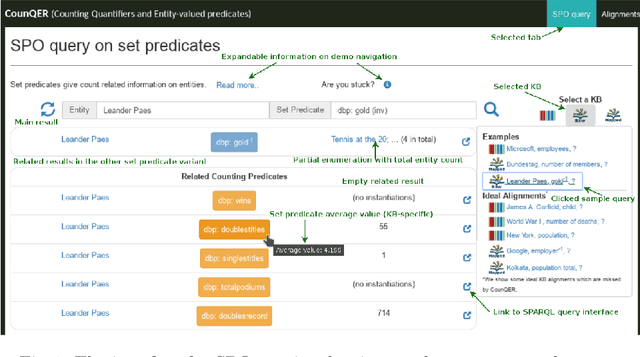
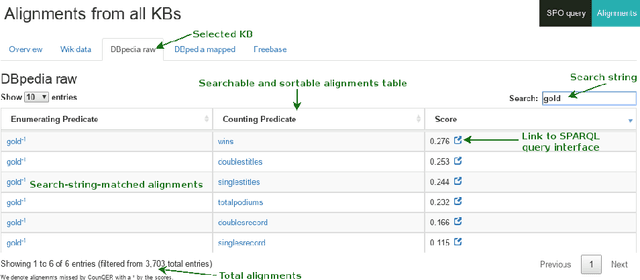
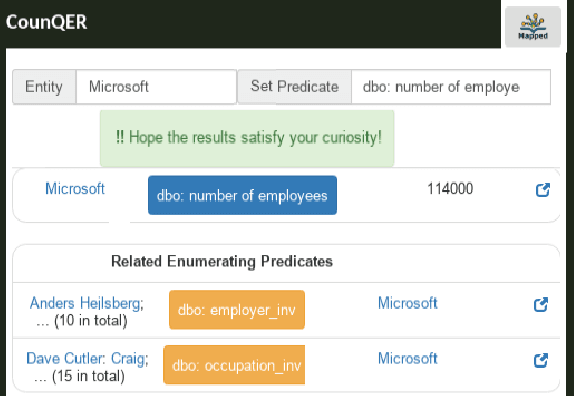
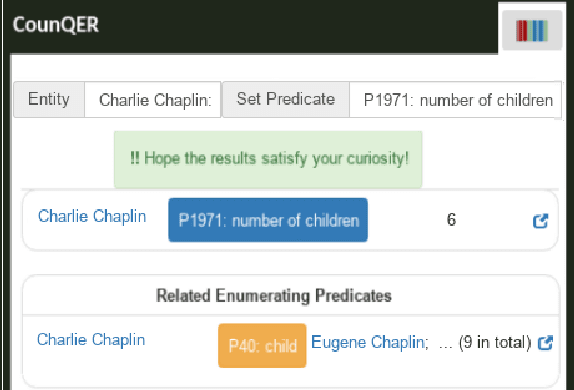
Abstract:Predicate constraints of general-purpose knowledge bases (KBs) like Wikidata, DBpedia and Freebase are often limited to subproperty, domain and range constraints. In this demo we showcase CounQER, a system that illustrates the alignment of counting predicates, like staffSize, and enumerating predicates, like workInstitution^{-1} . In the demonstration session, attendees can inspect these alignments, and will learn about the importance of these alignments for KB question answering and curation. CounQER is available at https://counqer.mpi-inf.mpg.de/spo.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge