Shijing Hu
LatentRefusal: Latent-Signal Refusal for Unanswerable Text-to-SQL Queries
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:In LLM-based text-to-SQL systems, unanswerable and underspecified user queries may generate not only incorrect text but also executable programs that yield misleading results or violate safety constraints, posing a major barrier to safe deployment. Existing refusal strategies for such queries either rely on output-level instruction following, which is brittle due to model hallucinations, or estimate output uncertainty, which adds complexity and overhead. To address this challenge, we formalize safe refusal in text-to-SQL systems as an answerability-gating problem and propose LatentRefusal, a latent-signal refusal mechanism that predicts query answerability from intermediate hidden activations of a large language model. We introduce the Tri-Residual Gated Encoder, a lightweight probing architecture, to suppress schema noise and amplify sparse, localized cues of question-schema mismatch that indicate unanswerability. Extensive empirical evaluations across diverse ambiguous and unanswerable settings, together with ablation studies and interpretability analyses, demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach and show that LatentRefusal provides an attachable and efficient safety layer for text-to-SQL systems. Across four benchmarks, LatentRefusal improves average F1 to 88.5 percent on both backbones while adding approximately 2 milliseconds of probe overhead.
Prefix Probing: Lightweight Harmful Content Detection for Large Language Models
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:Large language models often face a three-way trade-off among detection accuracy, inference latency, and deployment cost when used in real-world safety-sensitive applications. This paper introduces Prefix Probing, a black-box harmful content detection method that compares the conditional log-probabilities of "agreement/execution" versus "refusal/safety" opening prefixes and leverages prefix caching to reduce detection overhead to near first-token latency. During inference, the method requires only a single log-probability computation over the probe prefixes to produce a harmfulness score and apply a threshold, without invoking any additional models or multi-stage inference. To further enhance the discriminative power of the prefixes, we design an efficient prefix construction algorithm that automatically discovers highly informative prefixes, substantially improving detection performance. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Prefix Probing achieves detection effectiveness comparable to mainstream external safety models while incurring only minimal computational cost and requiring no extra model deployment, highlighting its strong practicality and efficiency.
Bridging Draft Policy Misalignment: Group Tree Optimization for Speculative Decoding
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:Speculative decoding accelerates large language model (LLM) inference by letting a lightweight draft model propose multiple tokens that the target model verifies in parallel. Yet existing training objectives optimize only a single greedy draft path, while decoding follows a tree policy that re-ranks and verifies multiple branches. This draft policy misalignment limits achievable speedups. We introduce Group Tree Optimization (GTO), which aligns training with the decoding-time tree policy through two components: (i) Draft Tree Reward, a sampling-free objective equal to the expected acceptance length of the draft tree under the target model, directly measuring decoding performance; (ii) Group-based Draft Policy Training, a stable optimization scheme that contrasts trees from the current and a frozen reference draft model, forming debiased group-standardized advantages and applying a PPO-style surrogate along the longest accepted sequence for robust updates. We further prove that increasing our Draft Tree Reward provably improves acceptance length and speedup. Across dialogue (MT-Bench), code (HumanEval), and math (GSM8K), and multiple LLMs (e.g., LLaMA-3.1-8B, LLaMA-3.3-70B, Vicuna-1.3-13B, DeepSeek-R1-Distill-LLaMA-8B), GTO increases acceptance length by 7.4% and yields an additional 7.7% speedup over prior state-of-the-art EAGLE-3. By bridging draft policy misalignment, GTO offers a practical, general solution for efficient LLM inference.
LAECIPS: Large Vision Model Assisted Adaptive Edge-Cloud Collaboration for IoT-based Perception System
Apr 16, 2024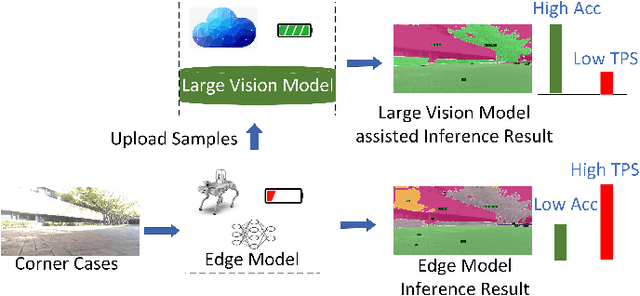
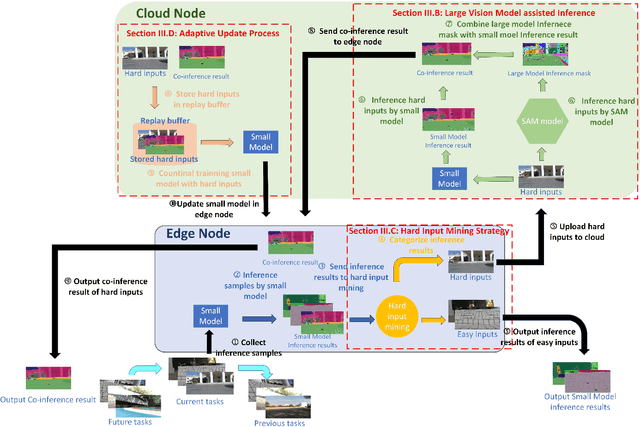
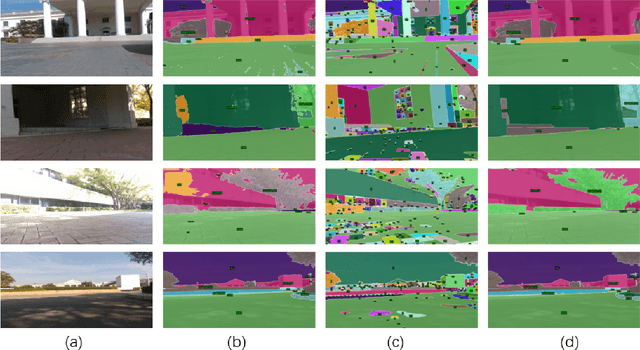

Abstract:Recent large vision models (e.g., SAM) enjoy great potential to facilitate intelligent perception with high accuracy. Yet, the resource constraints in the IoT environment tend to limit such large vision models to be locally deployed, incurring considerable inference latency thereby making it difficult to support real-time applications, such as autonomous driving and robotics. Edge-cloud collaboration with large-small model co-inference offers a promising approach to achieving high inference accuracy and low latency. However, existing edge-cloud collaboration methods are tightly coupled with the model architecture and cannot adapt to the dynamic data drifts in heterogeneous IoT environments. To address the issues, we propose LAECIPS, a new edge-cloud collaboration framework. In LAECIPS, both the large vision model on the cloud and the lightweight model on the edge are plug-and-play. We design an edge-cloud collaboration strategy based on hard input mining, optimized for both high accuracy and low latency. We propose to update the edge model and its collaboration strategy with the cloud under the supervision of the large vision model, so as to adapt to the dynamic IoT data streams. Theoretical analysis of LAECIPS proves its feasibility. Experiments conducted in a robotic semantic segmentation system using real-world datasets show that LAECIPS outperforms its state-of-the-art competitors in accuracy, latency, and communication overhead while having better adaptability to dynamic environments.
Combined Federated and Split Learning in Edge Computing for Ubiquitous Intelligence in Internet of Things: State of the Art and Future Directions
Jul 20, 2022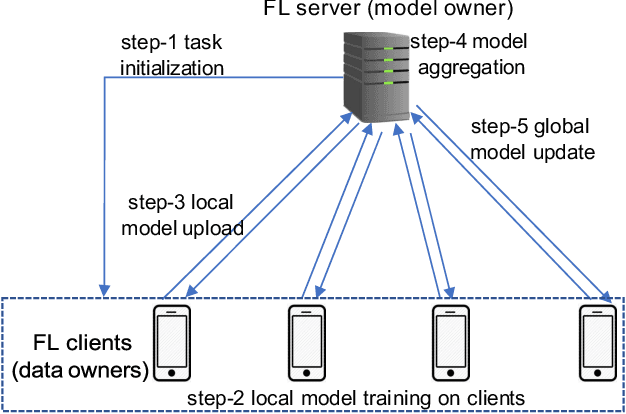
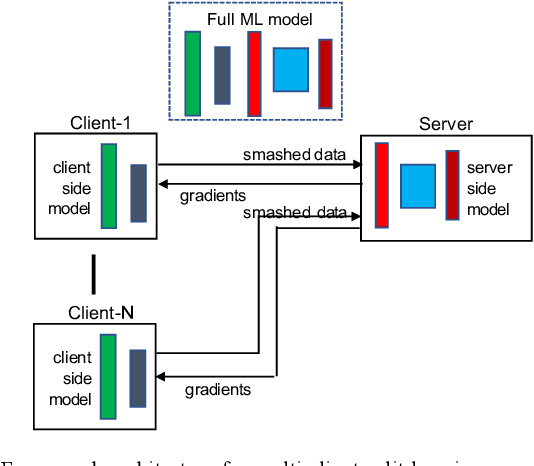
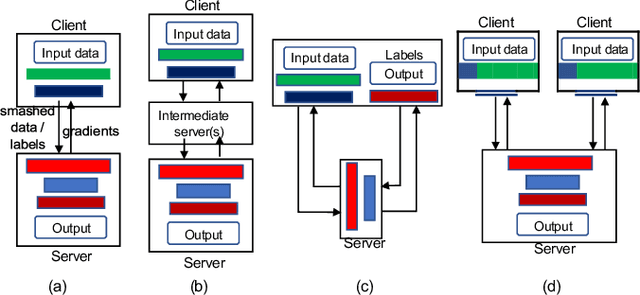
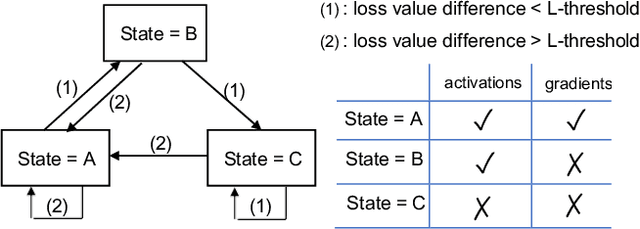
Abstract:Federated learning (FL) and split learning (SL) are two emerging collaborative learning methods that may greatly facilitate ubiquitous intelligence in Internet of Things (IoT). Federated learning enables machine learning (ML) models locally trained using private data to be aggregated into a global model. Split learning allows different portions of an ML model to be collaboratively trained on different workers in a learning framework. Federated learning and split learning, each has unique advantages and respective limitations, may complement each other toward ubiquitous intelligence in IoT. Therefore, combination of federated learning and split learning recently became an active research area attracting extensive interest. In this article, we review the latest developments in federated learning and split learning and present a survey on the state-of-the-art technologies for combining these two learning methods in an edge computing-based IoT environment. We also identify some open problems and discuss possible directions for future research in this area with a hope to further arouse the research community's interest in this emerging field.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge