Shidang Xu
SyncAnimation: A Real-Time End-to-End Framework for Audio-Driven Human Pose and Talking Head Animation
Jan 24, 2025Abstract:Generating talking avatar driven by audio remains a significant challenge. Existing methods typically require high computational costs and often lack sufficient facial detail and realism, making them unsuitable for applications that demand high real-time performance and visual quality. Additionally, while some methods can synchronize lip movement, they still face issues with consistency between facial expressions and upper body movement, particularly during silent periods. In this paper, we introduce SyncAnimation, the first NeRF-based method that achieves audio-driven, stable, and real-time generation of speaking avatar by combining generalized audio-to-pose matching and audio-to-expression synchronization. By integrating AudioPose Syncer and AudioEmotion Syncer, SyncAnimation achieves high-precision poses and expression generation, progressively producing audio-synchronized upper body, head, and lip shapes. Furthermore, the High-Synchronization Human Renderer ensures seamless integration of the head and upper body, and achieves audio-sync lip. The project page can be found at https://syncanimation.github.io
Towards Efficient Information Fusion: Concentric Dual Fusion Attention Based Multiple Instance Learning for Whole Slide Images
Mar 21, 2024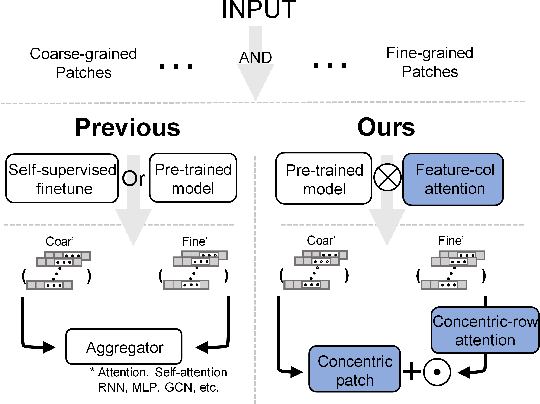
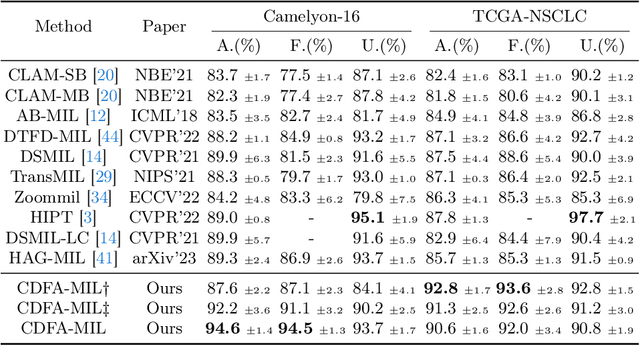
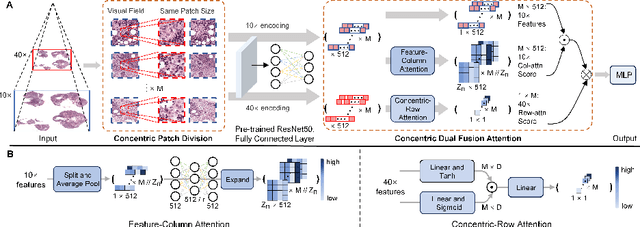

Abstract:In the realm of digital pathology, multi-magnification Multiple Instance Learning (multi-mag MIL) has proven effective in leveraging the hierarchical structure of Whole Slide Images (WSIs) to reduce information loss and redundant data. However, current methods fall short in bridging the domain gap between pretrained models and medical imaging, and often fail to account for spatial relationships across different magnifications. Addressing these challenges, we introduce the Concentric Dual Fusion Attention-MIL (CDFA-MIL) framework,which innovatively combines point-to-area feature-colum attention and point-to-point concentric-row attention using concentric patch. This approach is designed to effectively fuse correlated information, enhancing feature representation and providing stronger correlation guidance for WSI analysis. CDFA-MIL distinguishes itself by offering a robust fusion strategy that leads to superior WSI recognition. Its application has demonstrated exceptional performance, significantly surpassing existing MIL methods in accuracy and F1 scores on prominent datasets like Camelyon16 and TCGA-NSCLC. Specifically, CDFA-MIL achieved an average accuracy and F1-score of 93.7\% and 94.1\% respectively on these datasets, marking a notable advancement over traditional MIL approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge