Shenghui Liu
Triple GNNs: Introducing Syntactic and Semantic Information for Conversational Aspect-Based Quadruple Sentiment Analysis
Mar 15, 2024Abstract:Conversational Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis (DiaASQ) aims to detect quadruples \{target, aspect, opinion, sentiment polarity\} from given dialogues. In DiaASQ, elements constituting these quadruples are not necessarily confined to individual sentences but may span across multiple utterances within a dialogue. This necessitates a dual focus on both the syntactic information of individual utterances and the semantic interaction among them. However, previous studies have primarily focused on coarse-grained relationships between utterances, thus overlooking the potential benefits of detailed intra-utterance syntactic information and the granularity of inter-utterance relationships. This paper introduces the Triple GNNs network to enhance DiaAsQ. It employs a Graph Convolutional Network (GCN) for modeling syntactic dependencies within utterances and a Dual Graph Attention Network (DualGATs) to construct interactions between utterances. Experiments on two standard datasets reveal that our model significantly outperforms state-of-the-art baselines. The code is available at \url{https://github.com/nlperi2b/Triple-GNNs-}.
DXSLAM: A Robust and Efficient Visual SLAM System with Deep Features
Aug 12, 2020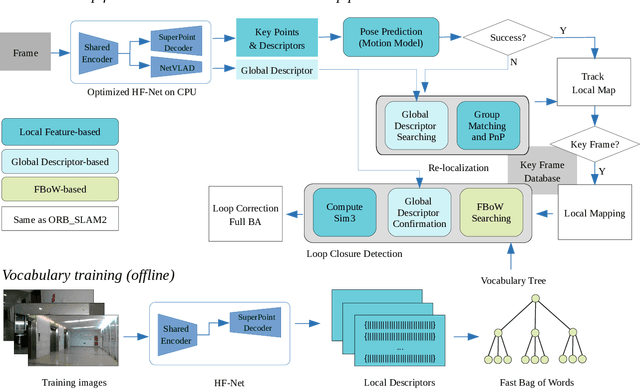
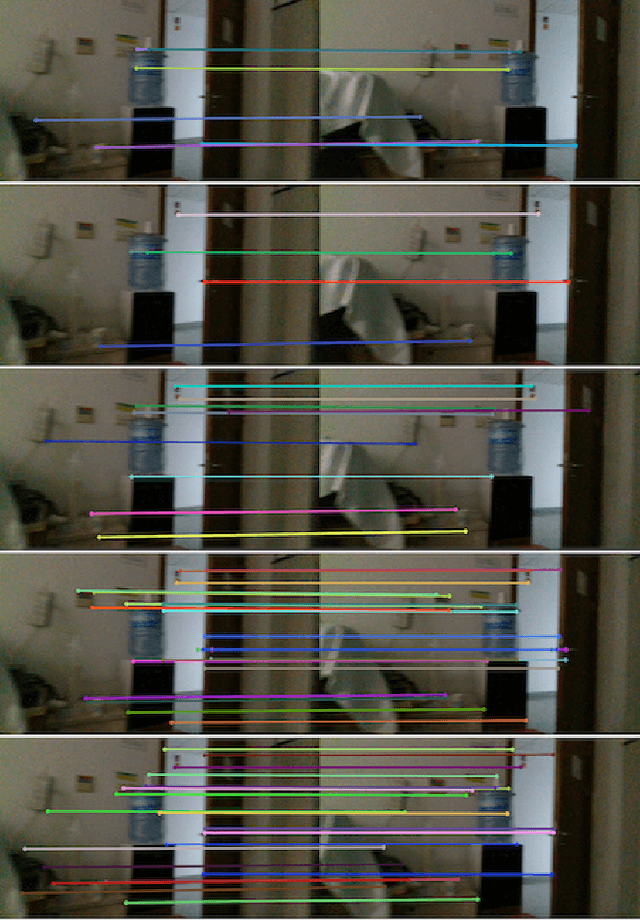
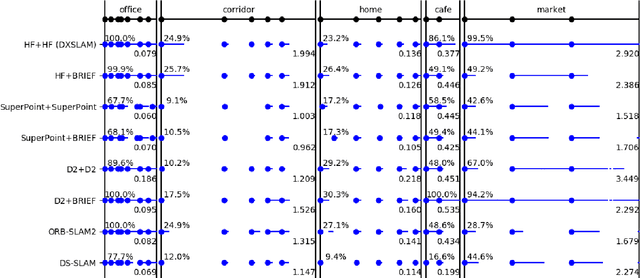

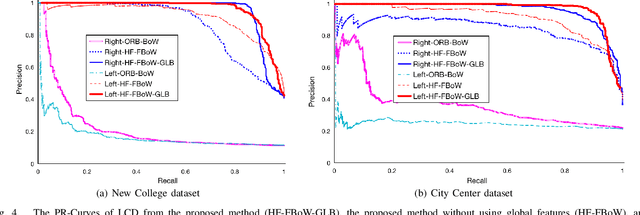
Abstract:A robust and efficient Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) system is essential for robot autonomy. For visual SLAM algorithms, though the theoretical framework has been well established for most aspects, feature extraction and association is still empirically designed in most cases, and can be vulnerable in complex environments. This paper shows that feature extraction with deep convolutional neural networks (CNNs) can be seamlessly incorporated into a modern SLAM framework. The proposed SLAM system utilizes a state-of-the-art CNN to detect keypoints in each image frame, and to give not only keypoint descriptors, but also a global descriptor of the whole image. These local and global features are then used by different SLAM modules, resulting in much more robustness against environmental changes and viewpoint changes compared with using hand-crafted features. We also train a visual vocabulary of local features with a Bag of Words (BoW) method. Based on the local features, global features, and the vocabulary, a highly reliable loop closure detection method is built. Experimental results show that all the proposed modules significantly outperforms the baseline, and the full system achieves much lower trajectory errors and much higher correct rates on all evaluated data. Furthermore, by optimizing the CNN with Intel OpenVINO toolkit and utilizing the Fast BoW library, the system benefits greatly from the SIMD (single-instruction-multiple-data) techniques in modern CPUs. The full system can run in real-time without any GPU or other accelerators. The code is public at https://github.com/ivipsourcecode/dxslam.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge