Shaoxun Wu
BevSplat: Resolving Height Ambiguity via Feature-Based Gaussian Primitives for Weakly-Supervised Cross-View Localization
Feb 13, 2025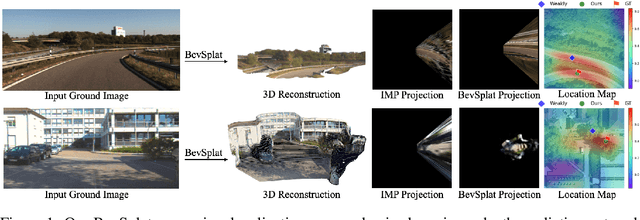
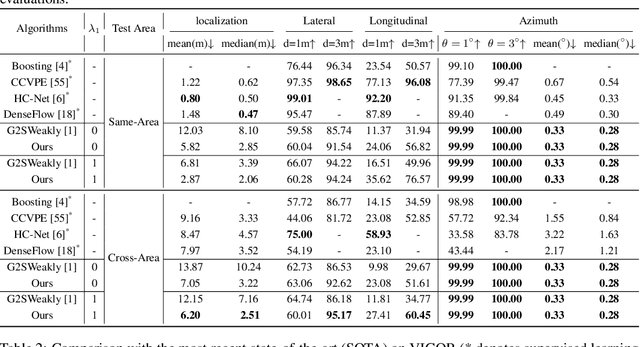
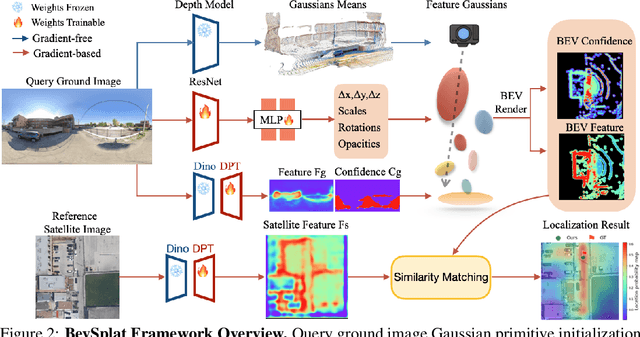
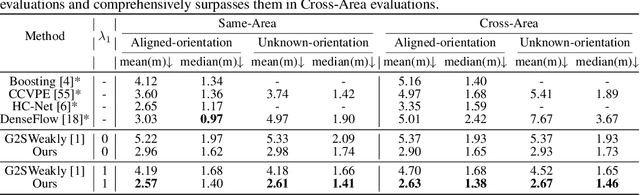
Abstract:This paper addresses the problem of weakly supervised cross-view localization, where the goal is to estimate the pose of a ground camera relative to a satellite image with noisy ground truth annotations. A common approach to bridge the cross-view domain gap for pose estimation is Bird's-Eye View (BEV) synthesis. However, existing methods struggle with height ambiguity due to the lack of depth information in ground images and satellite height maps. Previous solutions either assume a flat ground plane or rely on complex models, such as cross-view transformers. We propose BevSplat, a novel method that resolves height ambiguity by using feature-based Gaussian primitives. Each pixel in the ground image is represented by a 3D Gaussian with semantic and spatial features, which are synthesized into a BEV feature map for relative pose estimation. Additionally, to address challenges with panoramic query images, we introduce an icosphere-based supervision strategy for the Gaussian primitives. We validate our method on the widely used KITTI and VIGOR datasets, which include both pinhole and panoramic query images. Experimental results show that BevSplat significantly improves localization accuracy over prior approaches.
VECtor: A Versatile Event-Centric Benchmark for Multi-Sensor SLAM
Jul 04, 2022



Abstract:Event cameras have recently gained in popularity as they hold strong potential to complement regular cameras in situations of high dynamics or challenging illumination. An important problem that may benefit from the addition of an event camera is given by Simultaneous Localization And Mapping (SLAM). However, in order to ensure progress on event-inclusive multi-sensor SLAM, novel benchmark sequences are needed. Our contribution is the first complete set of benchmark datasets captured with a multi-sensor setup containing an event-based stereo camera, a regular stereo camera, multiple depth sensors, and an inertial measurement unit. The setup is fully hardware-synchronized and underwent accurate extrinsic calibration. All sequences come with ground truth data captured by highly accurate external reference devices such as a motion capture system. Individual sequences include both small and large-scale environments, and cover the specific challenges targeted by dynamic vision sensors.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge