Shaokang Yang
Residual Decoding: Mitigating Hallucinations in Large Vision-Language Models via History-Aware Residual Guidance
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) can reason effectively from image-text inputs and perform well in various multimodal tasks. Despite this success, they are affected by language priors and often produce hallucinations. Hallucinations denote generated content that is grammatically and syntactically coherent, yet bears no match or direct relevance to actual visual input. To address this problem, we propose Residual Decoding (ResDec). It is a novel training-free method that uses historical information to aid decoding. The method relies on the internal implicit reasoning mechanism and token logits evolution mechanism of LVLMs to correct biases. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ResDec effectively suppresses hallucinations induced by language priors, significantly improves visual grounding, and reduces object hallucinations. In addition to mitigating hallucinations, ResDec also performs exceptionally well on comprehensive LVLM benchmarks, highlighting its broad applicability.
PartImageNet: A Large, High-Quality Dataset of Parts
Dec 02, 2021
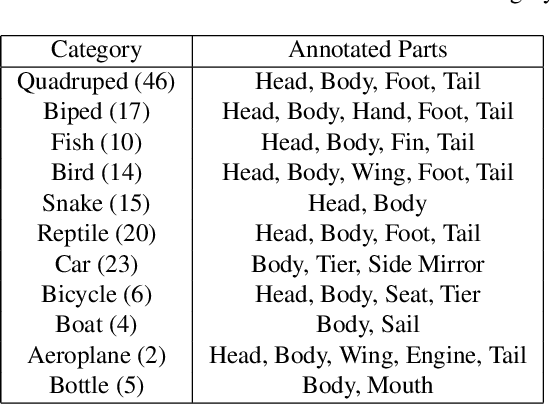

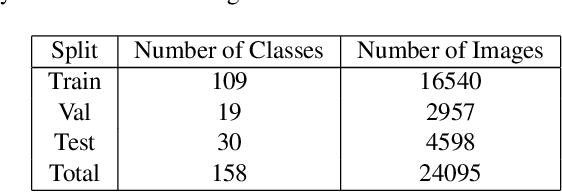
Abstract:A part-based object understanding facilitates efficient compositional learning and knowledge transfer, robustness to occlusion, and has the potential to increase the performance on general recognition and localization tasks. However, research on part-based models is hindered due to the lack of datasets with part annotations, which is caused by the extreme difficulty and high cost of annotating object parts in images. In this paper, we propose PartImageNet, a large, high-quality dataset with part segmentation annotations. It consists of 158 classes from ImageNet with approximately 24000 images. PartImageNet is unique because it offers part-level annotations on a general set of classes with non-rigid, articulated objects, while having an order of magnitude larger size compared to existing datasets. It can be utilized in multiple vision tasks including but not limited to: Part Discovery, Semantic Segmentation, Few-shot Learning. Comprehensive experiments are conducted to set up a set of baselines on PartImageNet and we find that existing works on part discovery can not always produce satisfactory results during complex variations. The exploit of parts on downstream tasks also remains insufficient. We believe that our PartImageNet will greatly facilitate the research on part-based models and their applications. The dataset and scripts will soon be released at https://github.com/TACJu/PartImageNet.
Rethinking Re-Sampling in Imbalanced Semi-Supervised Learning
Jun 01, 2021



Abstract:Semi-Supervised Learning (SSL) has shown its strong ability in utilizing unlabeled data when labeled data is scarce. However, most SSL algorithms work under the assumption that the class distributions are balanced in both training and test sets. In this work, we consider the problem of SSL on class-imbalanced data, which better reflects real-world situations but has only received limited attention so far. In particular, we decouple the training of the representation and the classifier, and systematically investigate the effects of different data re-sampling techniques when training the whole network including a classifier as well as fine-tuning the feature extractor only. We find that data re-sampling is of critical importance to learn a good classifier as it increases the accuracy of the pseudo-labels, in particular for the minority classes in the unlabeled data. Interestingly, we find that accurate pseudo-labels do not help when training the feature extractor, rather contrariwise, data re-sampling harms the training of the feature extractor. This finding is against the general intuition that wrong pseudo-labels always harm the model performance in SSL. Based on these findings, we suggest to re-think the current paradigm of having a single data re-sampling strategy and develop a simple yet highly effective Bi-Sampling (BiS) strategy for SSL on class-imbalanced data. BiS implements two different re-sampling strategies for training the feature extractor and the classifier and integrates this decoupled training into an end-to-end framework... Code will be released at https://github.com/TACJu/Bi-Sampling.
Re-rank Coarse Classification with Local Region Enhanced Features for Fine-Grained Image Recognition
Feb 19, 2021



Abstract:Fine-grained image recognition is very challenging due to the difficulty of capturing both semantic global features and discriminative local features. Meanwhile, these two features are not easy to be integrated, which are even conflicting when used simultaneously. In this paper, a retrieval-based coarse-to-fine framework is proposed, where we re-rank the TopN classification results by using the local region enhanced embedding features to improve the Top1 accuracy (based on the observation that the correct category usually resides in TopN results). To obtain the discriminative regions for distinguishing the fine-grained images, we introduce a weakly-supervised method to train a box generating branch with only image-level labels. In addition, to learn more effective semantic global features, we design a multi-level loss over an automatically constructed hierarchical category structure. Experimental results show that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on three benchmarks: CUB-200-2011, Stanford Cars, and FGVC Aircraft. Also, visualizations and analysis are provided for better understanding.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge