Shanshan Yu
A Benchmark for Vision-Centric HD Mapping by V2I Systems
Mar 31, 2025



Abstract:Autonomous driving faces safety challenges due to a lack of global perspective and the semantic information of vectorized high-definition (HD) maps. Information from roadside cameras can greatly expand the map perception range through vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) communications. However, there is still no dataset from the real world available for the study on map vectorization onboard under the scenario of vehicle-infrastructure cooperation. To prosper the research on online HD mapping for Vehicle-Infrastructure Cooperative Autonomous Driving (VICAD), we release a real-world dataset, which contains collaborative camera frames from both vehicles and roadside infrastructures, and provides human annotations of HD map elements. We also present an end-to-end neural framework (i.e., V2I-HD) leveraging vision-centric V2I systems to construct vectorized maps. To reduce computation costs and further deploy V2I-HD on autonomous vehicles, we introduce a directionally decoupled self-attention mechanism to V2I-HD. Extensive experiments show that V2I-HD has superior performance in real-time inference speed, as tested by our real-world dataset. Abundant qualitative results also demonstrate stable and robust map construction quality with low cost in complex and various driving scenes. As a benchmark, both source codes and the dataset have been released at OneDrive for the purpose of further study.
Multi-Relation Aware Temporal Interaction Network Embedding
Oct 09, 2021

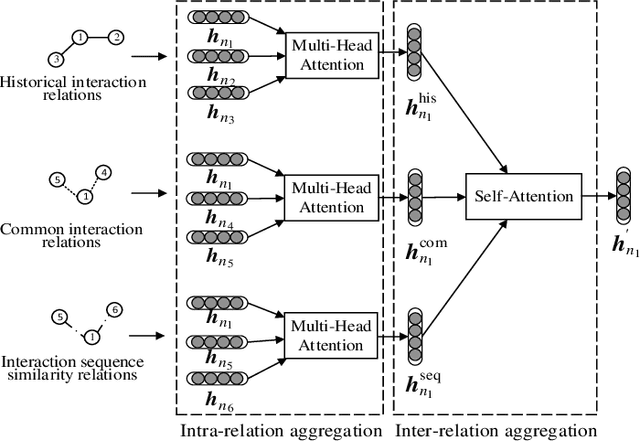

Abstract:Temporal interaction networks are formed in many fields, e.g., e-commerce, online education, and social network service. Temporal interaction network embedding can effectively mine the information in temporal interaction networks, which is of great significance to the above fields. Usually, the occurrence of an interaction affects not only the nodes directly involved in the interaction (interacting nodes), but also the neighbor nodes of interacting nodes. However, existing temporal interaction network embedding methods only use historical interaction relations to mine neighbor nodes, ignoring other relation types. In this paper, we propose a multi-relation aware temporal interaction network embedding method (MRATE). Based on historical interactions, MRATE mines historical interaction relations, common interaction relations, and interaction sequence similarity relations to obtain the neighbor based embeddings of interacting nodes. The hierarchical multi-relation aware aggregation method in MRATE first employs graph attention networks (GATs) to aggregate the interaction impacts propagated through a same relation type and then combines the aggregated interaction impacts from multiple relation types through the self-attention mechanism. Experiments are conducted on three public temporal interaction network datasets, and the experimental results show the effectiveness of MRATE.
Multi-Level Visual Similarity Based Personalized Tourist Attraction Recommendation Using Geo-Tagged Photos
Sep 17, 2021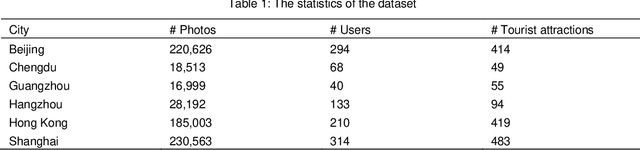
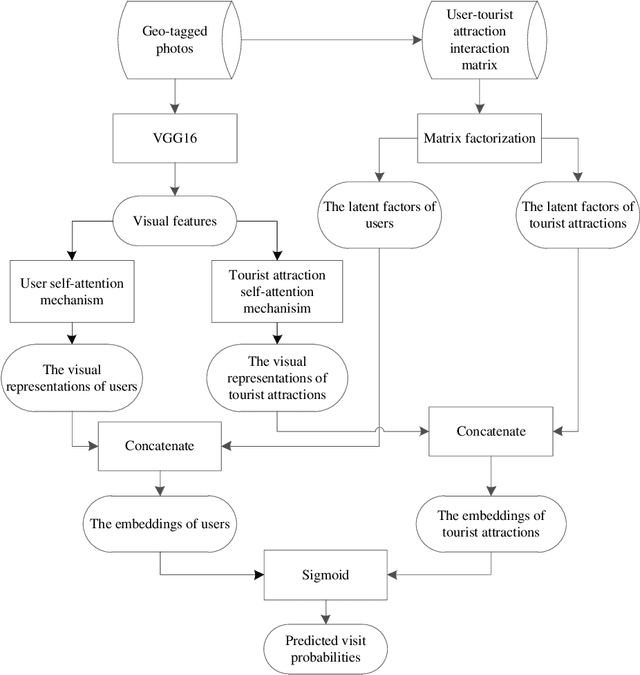
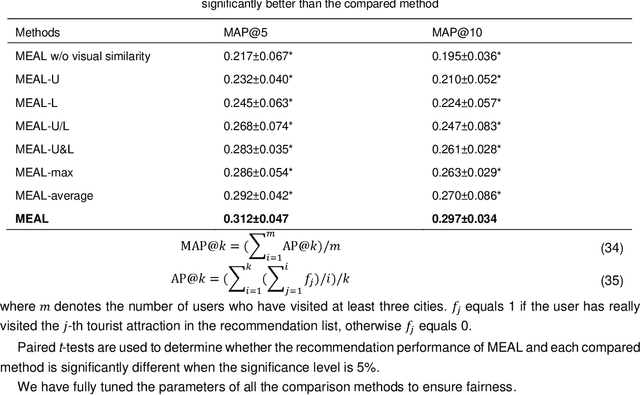
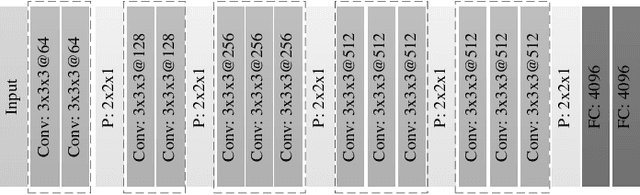
Abstract:Geo-tagged photo based tourist attraction recommendation can discover users' travel preferences from their taken photos, so as to recommend suitable tourist attractions to them. However, existing visual content based methods cannot fully exploit the user and tourist attraction information of photos to extract visual features, and do not differentiate the significances of different photos. In this paper, we propose multi-level visual similarity based personalized tourist attraction recommendation using geo-tagged photos (MEAL). MEAL utilizes the visual contents of photos and interaction behavior data to obtain the final embeddings of users and tourist attractions, which are then used to predict the visit probabilities. Specifically, by crossing the user and tourist attraction information of photos, we define four visual similarity levels and introduce a corresponding quintuplet loss to embed the visual contents of photos. In addition, to capture the significances of different photos, we exploit the self-attention mechanism to obtain the visual representations of users and tourist attractions. We conducted experiments on a dataset crawled from Flickr, and the experimental results proved the advantage of this method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge