Shanmin Yang
Masked Conditional Diffusion Model for Enhancing Deepfake Detection
Feb 01, 2024
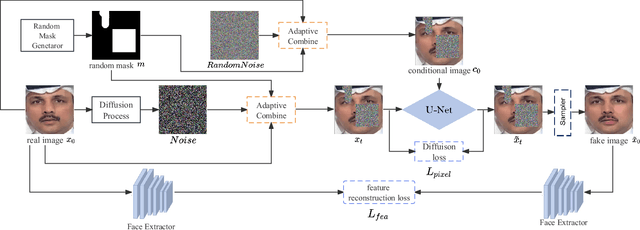


Abstract:Recent studies on deepfake detection have achieved promising results when training and testing faces are from the same dataset. However, their results severely degrade when confronted with forged samples that the model has not yet seen during training. In this paper, deepfake data to help detect deepfakes. this paper present we put a new insight into diffusion model-based data augmentation, and propose a Masked Conditional Diffusion Model (MCDM) for enhancing deepfake detection. It generates a variety of forged faces from a masked pristine one, encouraging the deepfake detection model to learn generic and robust representations without overfitting to special artifacts. Extensive experiments demonstrate that forgery images generated with our method are of high quality and helpful to improve the performance of deepfake detection models.
Improving Cross-dataset Deepfake Detection with Deep Information Decomposition
Sep 30, 2023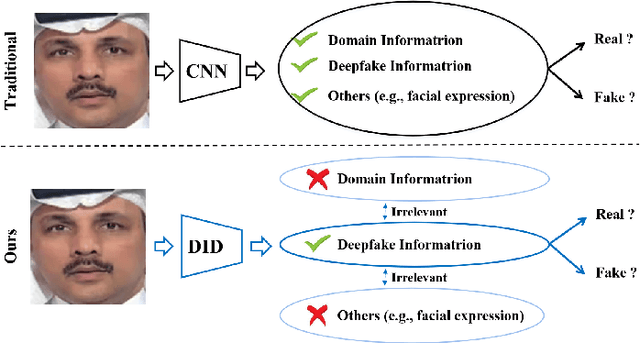
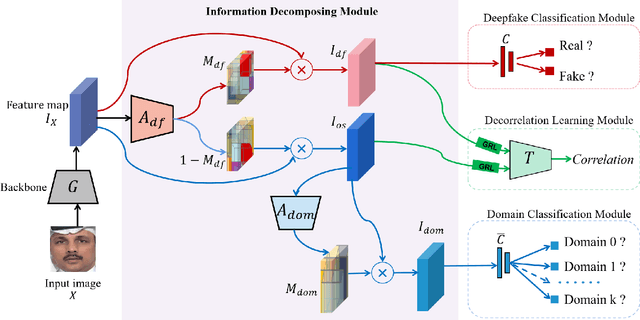
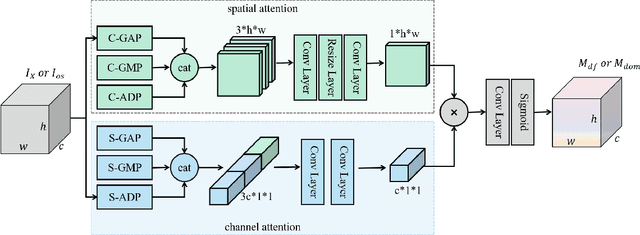
Abstract:Deepfake technology poses a significant threat to security and social trust. Although existing detection methods have demonstrated high performance in identifying forgeries within datasets using the same techniques for training and testing, they suffer from sharp performance degradation when faced with cross-dataset scenarios where unseen deepfake techniques are tested. To address this challenge, we propose a deep information decomposition (DID) framework in this paper. Unlike most existing deepfake detection methods, our framework prioritizes high-level semantic features over visual artifacts. Specifically, it decomposes facial features into deepfake-related and irrelevant information and optimizes the deepfake information for real/fake discrimination to be independent of other factors. Our approach improves the robustness of deepfake detection against various irrelevant information changes and enhances the generalization ability of the framework to detect unseen forgery methods. Extensive experimental comparisons with existing state-of-the-art detection methods validate the effectiveness and superiority of the DID framework on cross-dataset deepfake detection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge