Seunghun Ji
SupertonicTTS: Towards Highly Scalable and Efficient Text-to-Speech System
Mar 29, 2025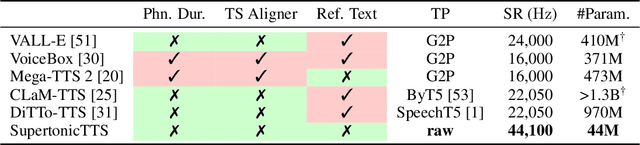
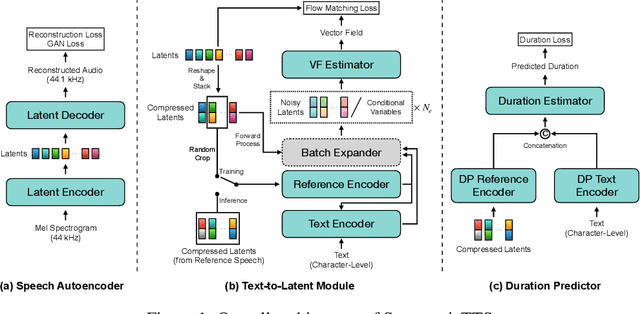
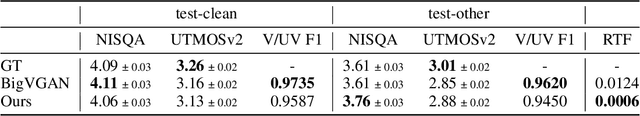
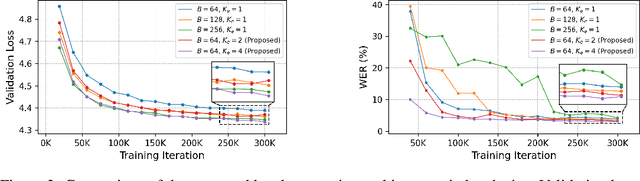
Abstract:We present a novel text-to-speech (TTS) system, namely SupertonicTTS, for improved scalability and efficiency in speech synthesis. SupertonicTTS is comprised of three components: a speech autoencoder for continuous latent representation, a text-to-latent module leveraging flow-matching for text-to-latent mapping, and an utterance-level duration predictor. To enable a lightweight architecture, we employ a low-dimensional latent space, temporal compression of latents, and ConvNeXt blocks. We further simplify the TTS pipeline by operating directly on raw character-level text and employing cross-attention for text-speech alignment, thus eliminating the need for grapheme-to-phoneme (G2P) modules and external aligners. In addition, we introduce context-sharing batch expansion that accelerates loss convergence and stabilizes text-speech alignment. Experimental results demonstrate that SupertonicTTS achieves competitive performance while significantly reducing architectural complexity and computational overhead compared to contemporary TTS models. Audio samples demonstrating the capabilities of SupertonicTTS are available at: https://supertonictts.github.io/.
DualSpeech: Enhancing Speaker-Fidelity and Text-Intelligibility Through Dual Classifier-Free Guidance
Aug 27, 2024


Abstract:Text-to-Speech (TTS) models have advanced significantly, aiming to accurately replicate human speech's diversity, including unique speaker identities and linguistic nuances. Despite these advancements, achieving an optimal balance between speaker-fidelity and text-intelligibility remains a challenge, particularly when diverse control demands are considered. Addressing this, we introduce DualSpeech, a TTS model that integrates phoneme-level latent diffusion with dual classifier-free guidance. This approach enables exceptional control over speaker-fidelity and text-intelligibility. Experimental results demonstrate that by utilizing the sophisticated control, DualSpeech surpasses existing state-of-the-art TTS models in performance. Demos are available at https://bit.ly/48Ewoib.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge