Seungbae Kim
Gesture-Aware Zero-Shot Speech Recognition for Patients with Language Disorders
Feb 18, 2025Abstract:Individuals with language disorders often face significant communication challenges due to their limited language processing and comprehension abilities, which also affect their interactions with voice-assisted systems that mostly rely on Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR). Despite advancements in ASR that address disfluencies, there has been little attention on integrating non-verbal communication methods, such as gestures, which individuals with language disorders substantially rely on to supplement their communication. Recognizing the need to interpret the latent meanings of visual information not captured by speech alone, we propose a gesture-aware ASR system utilizing a multimodal large language model with zero-shot learning for individuals with speech impairments. Our experiment results and analyses show that including gesture information significantly enhances semantic understanding. This study can help develop effective communication technologies, specifically designed to meet the unique needs of individuals with language impairments.
HiQuE: Hierarchical Question Embedding Network for Multimodal Depression Detection
Aug 07, 2024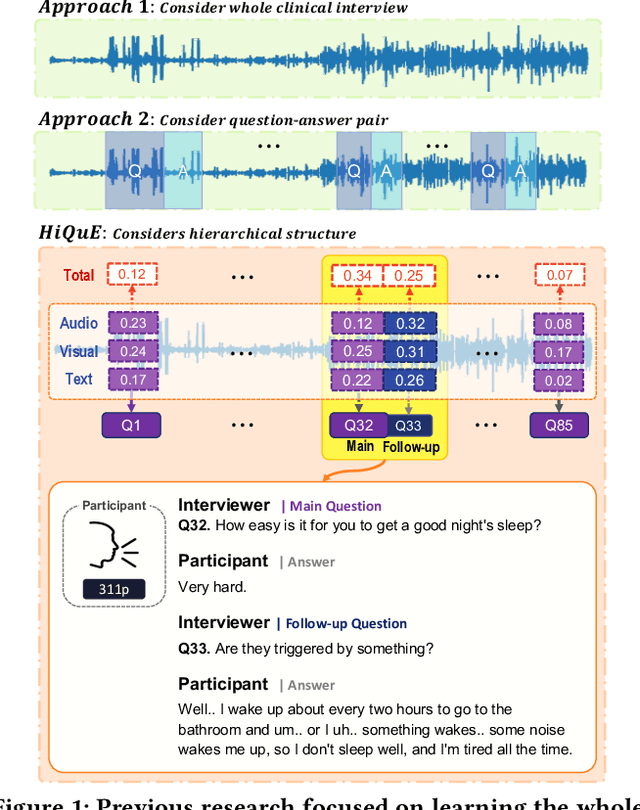

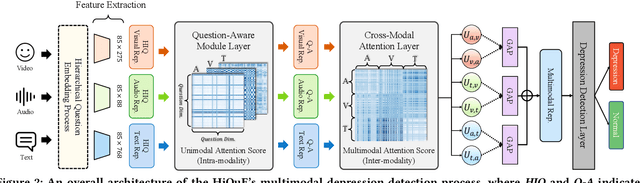

Abstract:The utilization of automated depression detection significantly enhances early intervention for individuals experiencing depression. Despite numerous proposals on automated depression detection using recorded clinical interview videos, limited attention has been paid to considering the hierarchical structure of the interview questions. In clinical interviews for diagnosing depression, clinicians use a structured questionnaire that includes routine baseline questions and follow-up questions to assess the interviewee's condition. This paper introduces HiQuE (Hierarchical Question Embedding network), a novel depression detection framework that leverages the hierarchical relationship between primary and follow-up questions in clinical interviews. HiQuE can effectively capture the importance of each question in diagnosing depression by learning mutual information across multiple modalities. We conduct extensive experiments on the widely-used clinical interview data, DAIC-WOZ, where our model outperforms other state-of-the-art multimodal depression detection models and emotion recognition models, showcasing its clinical utility in depression detection.
* 11 pages, 6 figures, Proceedings of the 33rd ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management (CIKM '24)
A Dual-Prompting for Interpretable Mental Health Language Models
Feb 20, 2024Abstract:Despite the increasing demand for AI-based mental health monitoring tools, their practical utility for clinicians is limited by the lack of interpretability.The CLPsych 2024 Shared Task (Chim et al., 2024) aims to enhance the interpretability of Large Language Models (LLMs), particularly in mental health analysis, by providing evidence of suicidality through linguistic content. We propose a dual-prompting approach: (i) Knowledge-aware evidence extraction by leveraging the expert identity and a suicide dictionary with a mental health-specific LLM; and (ii) Evidence summarization by employing an LLM-based consistency evaluator. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of combining domain-specific information, revealing performance improvements and the approach's potential to aid clinicians in assessing mental state progression.
Learning Co-Speech Gesture for Multimodal Aphasia Type Detection
Oct 20, 2023Abstract:Aphasia, a language disorder resulting from brain damage, requires accurate identification of specific aphasia types, such as Broca's and Wernicke's aphasia, for effective treatment. However, little attention has been paid to developing methods to detect different types of aphasia. Recognizing the importance of analyzing co-speech gestures for distinguish aphasia types, we propose a multimodal graph neural network for aphasia type detection using speech and corresponding gesture patterns. By learning the correlation between the speech and gesture modalities for each aphasia type, our model can generate textual representations sensitive to gesture information, leading to accurate aphasia type detection. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of our approach over existing methods, achieving state-of-the-art results (F1 84.2\%). We also show that gesture features outperform acoustic features, highlighting the significance of gesture expression in detecting aphasia types. We provide the codes for reproducibility purposes.
Towards Suicide Prevention from Bipolar Disorder with Temporal Symptom-Aware Multitask Learning
Jul 03, 2023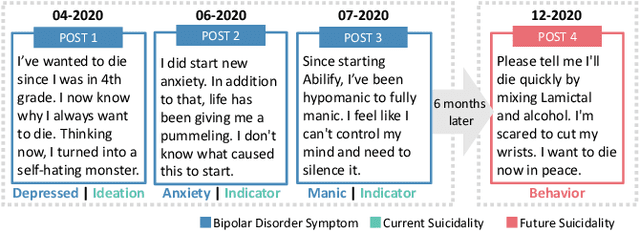
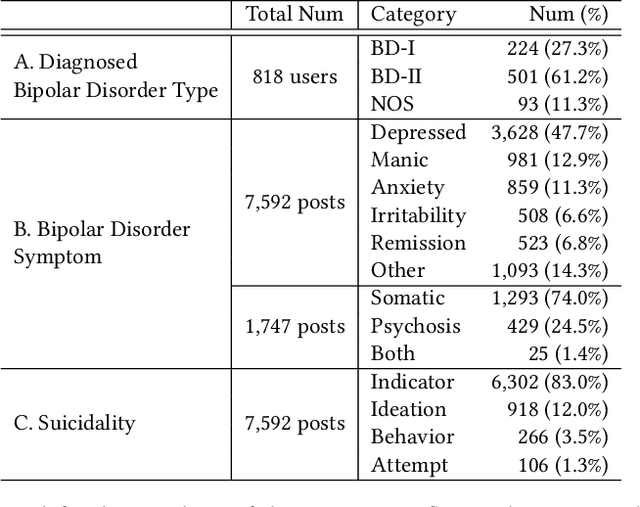
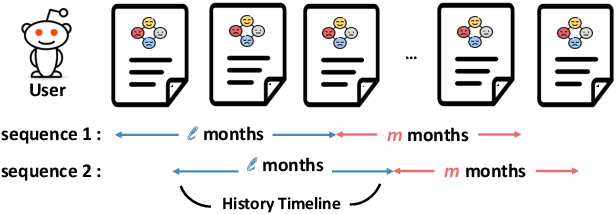
Abstract:Bipolar disorder (BD) is closely associated with an increased risk of suicide. However, while the prior work has revealed valuable insight into understanding the behavior of BD patients on social media, little attention has been paid to developing a model that can predict the future suicidality of a BD patient. Therefore, this study proposes a multi-task learning model for predicting the future suicidality of BD patients by jointly learning current symptoms. We build a novel BD dataset clinically validated by psychiatrists, including 14 years of posts on bipolar-related subreddits written by 818 BD patients, along with the annotations of future suicidality and BD symptoms. We also suggest a temporal symptom-aware attention mechanism to determine which symptoms are the most influential for predicting future suicidality over time through a sequence of BD posts. Our experiments demonstrate that the proposed model outperforms the state-of-the-art models in both BD symptom identification and future suicidality prediction tasks. In addition, the proposed temporal symptom-aware attention provides interpretable attention weights, helping clinicians to apprehend BD patients more comprehensively and to provide timely intervention by tracking mental state progression.
* KDD 2023 accepted
InfluencerRank: Discovering Effective Influencers via Graph Convolutional Attentive Recurrent Neural Networks
Apr 12, 2023Abstract:As influencers play considerable roles in social media marketing, companies increase the budget for influencer marketing. Hiring effective influencers is crucial in social influencer marketing, but it is challenging to find the right influencers among hundreds of millions of social media users. In this paper, we propose InfluencerRank that ranks influencers by their effectiveness based on their posting behaviors and social relations over time. To represent the posting behaviors and social relations, the graph convolutional neural networks are applied to model influencers with heterogeneous networks during different historical periods. By learning the network structure with the embedded node features, InfluencerRank can derive informative representations for influencers at each period. An attentive recurrent neural network finally distinguishes highly effective influencers from other influencers by capturing the knowledge of the dynamics of influencer representations over time. Extensive experiments have been conducted on an Instagram dataset that consists of 18,397 influencers with their 2,952,075 posts published within 12 months. The experimental results demonstrate that InfluencerRank outperforms existing baseline methods. An in-depth analysis further reveals that all of our proposed features and model components are beneficial to discover effective influencers.
FairGRAPE: Fairness-aware GRAdient Pruning mEthod for Face Attribute Classification
Jul 22, 2022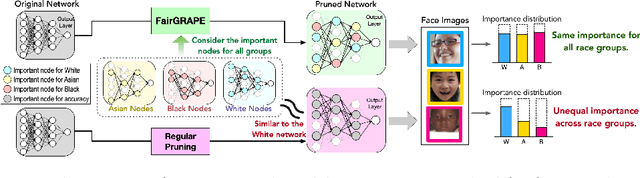
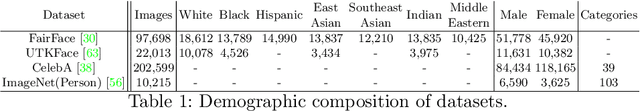
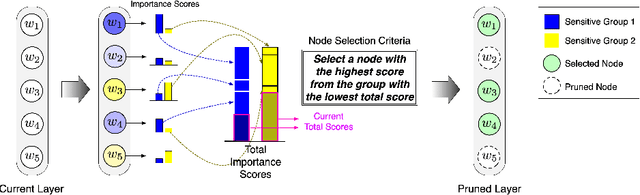
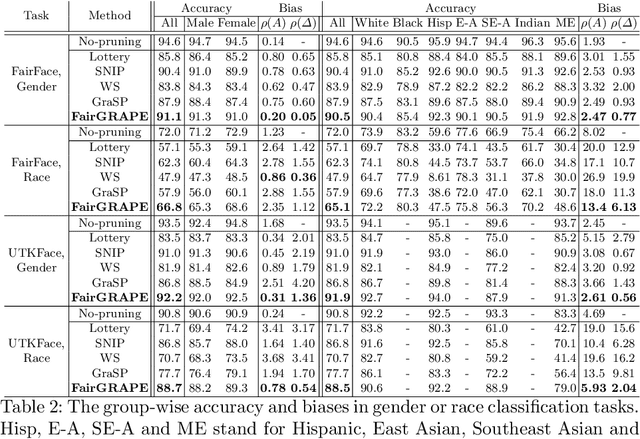
Abstract:Existing pruning techniques preserve deep neural networks' overall ability to make correct predictions but may also amplify hidden biases during the compression process. We propose a novel pruning method, Fairness-aware GRAdient Pruning mEthod (FairGRAPE), that minimizes the disproportionate impacts of pruning on different sub-groups. Our method calculates the per-group importance of each model weight and selects a subset of weights that maintain the relative between-group total importance in pruning. The proposed method then prunes network edges with small importance values and repeats the procedure by updating importance values. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our method on four different datasets, FairFace, UTKFace, CelebA, and ImageNet, for the tasks of face attribute classification where our method reduces the disparity in performance degradation by up to 90% compared to the state-of-the-art pruning algorithms. Our method is substantially more effective in a setting with a high pruning rate (99%). The code and dataset used in the experiments are available at https://github.com/Bernardo1998/FairGRAPE
Explaining Deep Convolutional Neural Networks via Latent Visual-Semantic Filter Attention
Apr 10, 2022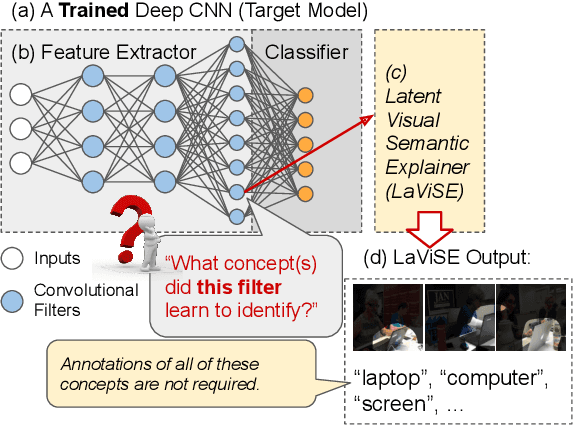
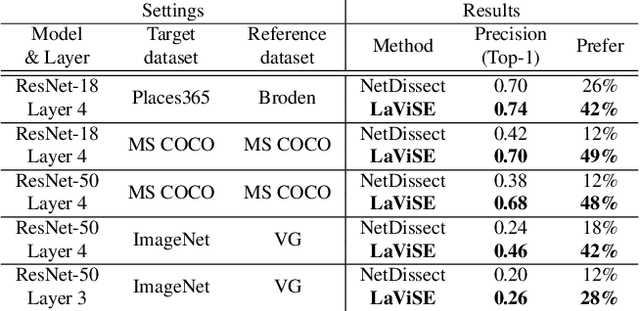
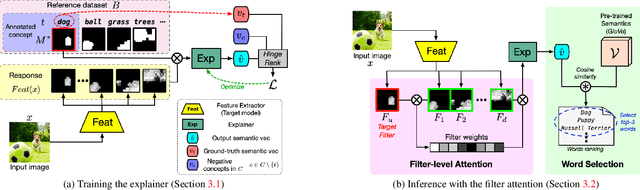
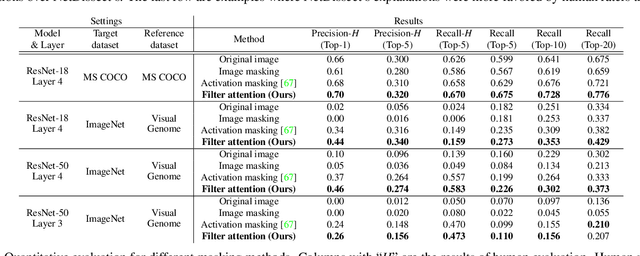
Abstract:Interpretability is an important property for visual models as it helps researchers and users understand the internal mechanism of a complex model. However, generating semantic explanations about the learned representation is challenging without direct supervision to produce such explanations. We propose a general framework, Latent Visual Semantic Explainer (LaViSE), to teach any existing convolutional neural network to generate text descriptions about its own latent representations at the filter level. Our method constructs a mapping between the visual and semantic spaces using generic image datasets, using images and category names. It then transfers the mapping to the target domain which does not have semantic labels. The proposed framework employs a modular structure and enables to analyze any trained network whether or not its original training data is available. We show that our method can generate novel descriptions for learned filters beyond the set of categories defined in the training dataset and perform an extensive evaluation on multiple datasets. We also demonstrate a novel application of our method for unsupervised dataset bias analysis which allows us to automatically discover hidden biases in datasets or compare different subsets without using additional labels. The dataset and code are made public to facilitate further research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge