Seojin Lee
Mitigating Cognitive Inertia in Large Reasoning Models via Latent Spike Steering
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:While Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) have achieved remarkable performance by scaling test-time compute, they frequently suffer from Cognitive Inertia, a failure pattern manifesting as either overthinking (inertia of motion) or reasoning rigidity (inertia of direction). Existing detection methods, typically relying on superficial textual heuristics like self-correction tokens, often fail to capture the model's unvoiced internal conflicts. To address this, we propose STARS (Spike-Triggered Adaptive Reasoning Steering), a training-free framework designed to rectify cognitive inertia by monitoring latent dynamics. STARS identifies Cognitive Pivots-critical moments of reasoning transition-by detecting distinct L2 distance spikes in the hidden states. Upon detection, the framework employs geometric trajectory analysis to diagnose the structural nature of the transition and injects state-aware language cues to steer the model in real-time. Our experiments across diverse benchmarks confirm that STARS efficiently curtails redundant loops while improving accuracy through the adaptive correction of erroneous trajectories. STARS offers a robust, unsupervised mechanism to optimize the reasoning process of LRMs without requiring additional fine-tuning.
A.X K1 Technical Report
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:We introduce A.X K1, a 519B-parameter Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) language model trained from scratch. Our design leverages scaling laws to optimize training configurations and vocabulary size under fixed computational budgets. A.X K1 is pre-trained on a corpus of approximately 10T tokens, curated by a multi-stage data processing pipeline. Designed to bridge the gap between reasoning capability and inference efficiency, A.X K1 supports explicitly controllable reasoning to facilitate scalable deployment across diverse real-world scenarios. We propose a simple yet effective Think-Fusion training recipe, enabling user-controlled switching between thinking and non-thinking modes within a single unified model. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that A.X K1 achieves performance competitive with leading open-source models, while establishing a distinctive advantage in Korean-language benchmarks.
WHAT, WHEN, and HOW to Ground: Designing User Persona-Aware Conversational Agents for Engaging Dialogue
Jun 21, 2023



Abstract:This paper presents a method for building a personalized open-domain dialogue system to address the $\textit{WWH}$ ($\textit{WHAT}$, $\textit{WHEN}$, and $\textit{HOW}$) problem for natural response generation in a commercial setting, where personalized dialogue responses are heavily interleaved with casual response turns. The proposed approach involves weighted dataset blending, negative persona information augmentation methods, and the design of personalized conversation datasets to address the challenges of $\textit{WWH}$ in personalized, open-domain dialogue systems. Our work effectively balances dialogue fluency and tendency to ground, while also introducing a response-type label to improve the controllability and explainability of the grounded responses. The combination of these methods leads to more fluent conversations, as evidenced by subjective human evaluations as well as objective evaluations.
An Evaluation Dataset and Strategy for Building Robust Multi-turn Response Selection Model
Sep 10, 2021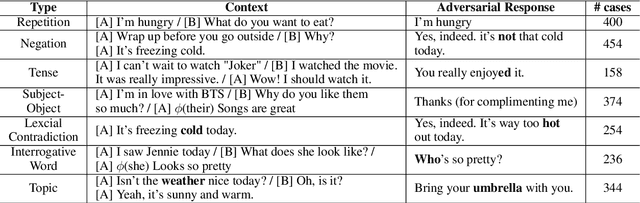

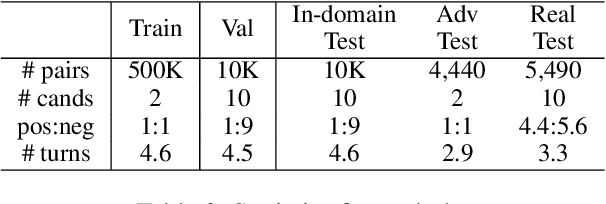
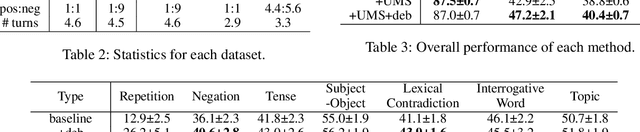
Abstract:Multi-turn response selection models have recently shown comparable performance to humans in several benchmark datasets. However, in the real environment, these models often have weaknesses, such as making incorrect predictions based heavily on superficial patterns without a comprehensive understanding of the context. For example, these models often give a high score to the wrong response candidate containing several keywords related to the context but using the inconsistent tense. In this study, we analyze the weaknesses of the open-domain Korean Multi-turn response selection models and publish an adversarial dataset to evaluate these weaknesses. We also suggest a strategy to build a robust model in this adversarial environment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge