An Evaluation Dataset and Strategy for Building Robust Multi-turn Response Selection Model
Paper and Code
Sep 10, 2021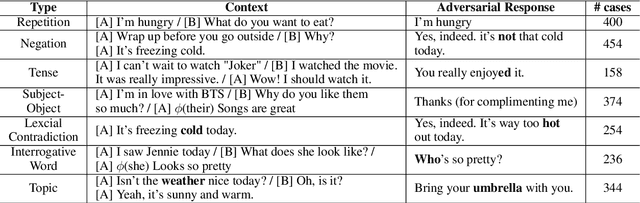

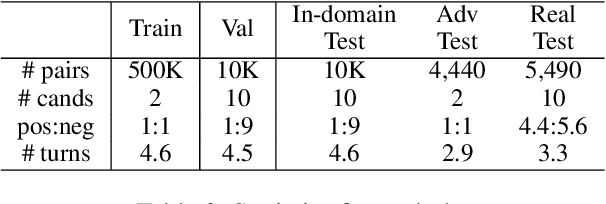
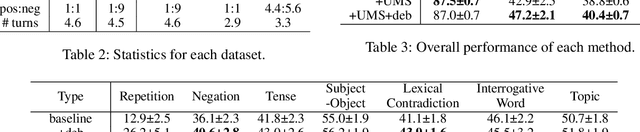
Multi-turn response selection models have recently shown comparable performance to humans in several benchmark datasets. However, in the real environment, these models often have weaknesses, such as making incorrect predictions based heavily on superficial patterns without a comprehensive understanding of the context. For example, these models often give a high score to the wrong response candidate containing several keywords related to the context but using the inconsistent tense. In this study, we analyze the weaknesses of the open-domain Korean Multi-turn response selection models and publish an adversarial dataset to evaluate these weaknesses. We also suggest a strategy to build a robust model in this adversarial environment.
* EMNLP 2021
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge