Sennay Ghebreab
Inequality in Congestion Games with Learning Agents
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Who benefits from expanding transport networks? While designed to improve mobility, such interventions can also create inequality. In this paper, we show that disparities arise not only from the structure of the network itself but also from differences in how commuters adapt to it. We model commuters as reinforcement learning agents who adapt their travel choices at different learning rates, reflecting unequal access to resources and information. To capture potential efficiency-fairness tradeoffs, we introduce the Price of Learning (PoL), a measure of inefficiency during learning. We analyze both a stylized network -- inspired in the well-known Braess's paradox, yet with two-source nodes -- and an abstraction of a real-world metro system (Amsterdam). Our simulations show that network expansions can simultaneously increase efficiency and amplify inequality, especially when faster learners disproportionately benefit from new routes before others adapt. These results highlight that transport policies must account not only for equilibrium outcomes but also for the heterogeneous ways commuters adapt, since both shape the balance between efficiency and fairness.
Same Content, Different Answers: Cross-Modal Inconsistency in MLLMs
Dec 09, 2025Abstract:We introduce two new benchmarks REST and REST+(Render-Equivalence Stress Tests) to enable systematic evaluation of cross-modal inconsistency in multimodal large language models (MLLMs). MLLMs are trained to represent vision and language in the same embedding space, yet they cannot perform the same tasks in both modalities. Our benchmarks contain samples with the same semantic information in three modalities (image, text, mixed) and we show that state-of-the-art MLLMs cannot consistently reason over these different modalities. We evaluate 15 MLLMs and find that the degree of modality inconsistency varies substantially, even when accounting for problems with text recognition (OCR). Neither rendering text as image nor rendering an image as text solves the inconsistency. Even if OCR is correct, we find that visual characteristics (text colour and resolution, but not font) and the number of vision tokens have an impact on model performance. Finally, we find that our consistency score correlates with the modality gap between text and images, highlighting a mechanistic interpretation of cross-modal inconsistent MLLMs.
Artifacts of Idiosyncracy in Global Street View Data
May 16, 2025Abstract:Street view data is increasingly being used in computer vision applications in recent years. Machine learning datasets are collected for these applications using simple sampling techniques. These datasets are assumed to be a systematic representation of cities, especially when densely sampled. Prior works however, show that there are clear gaps in coverage, with certain cities or regions being covered poorly or not at all. Here we demonstrate that a cities' idiosyncracies, such as city layout, may lead to biases in street view data for 28 cities across the globe, even when they are densely covered. We quantitatively uncover biases in the distribution of coverage of street view data and propose a method for evaluation of such distributions to get better insight in idiosyncracies in a cities' coverage. In addition, we perform a case study of Amsterdam with semi-structured interviews, showing how idiosyncracies of the collection process impact representation of cities and regions and allowing us to address biases at their source.
The Cloud Weaving Model for AI development
Apr 23, 2025Abstract:While analysing challenges in pilot projects developing AI with marginalized communities, we found it difficult to express them within commonly used paradigms. We therefore constructed an alternative conceptual framework to ground AI development in the social fabric -- the Cloud Weaving Model -- inspired (amongst others) by indigenous knowledge, motifs from nature, and Eastern traditions. This paper introduces and elaborates on the fundamental elements of the model (clouds, spiders, threads, spiderwebs, and weather) and their interpretation in an AI context. The framework is then applied to comprehend patterns observed in co-creation pilots approaching marginalized communities, highlighting neglected yet relevant dimensions for responsible AI development.
Scalable Multi-Objective Reinforcement Learning with Fairness Guarantees using Lorenz Dominance
Nov 27, 2024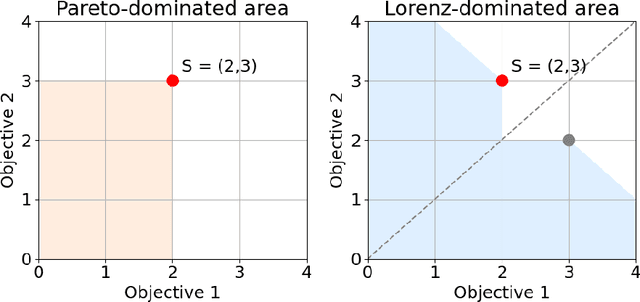
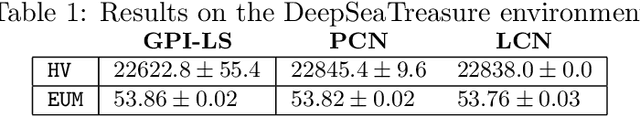
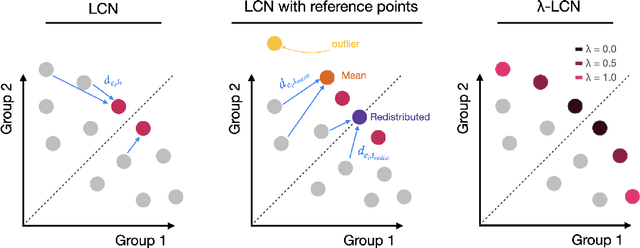
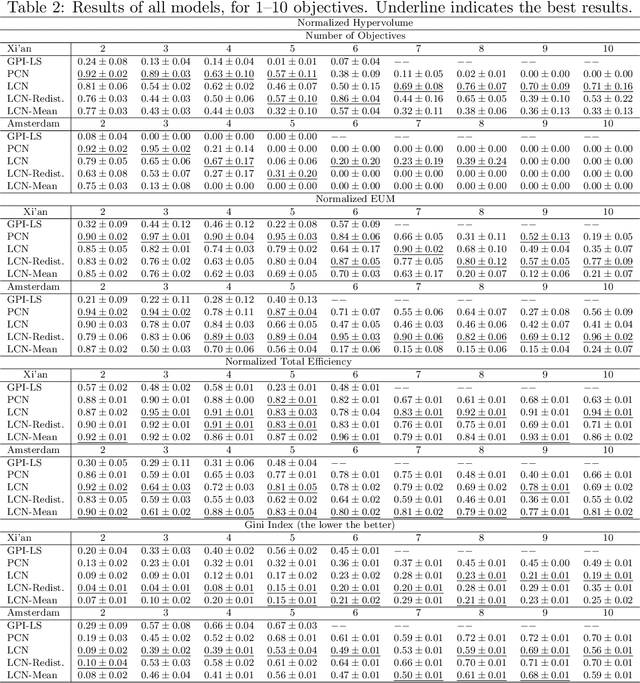
Abstract:Multi-Objective Reinforcement Learning (MORL) aims to learn a set of policies that optimize trade-offs between multiple, often conflicting objectives. MORL is computationally more complex than single-objective RL, particularly as the number of objectives increases. Additionally, when objectives involve the preferences of agents or groups, ensuring fairness is socially desirable. This paper introduces a principled algorithm that incorporates fairness into MORL while improving scalability to many-objective problems. We propose using Lorenz dominance to identify policies with equitable reward distributions and introduce {\lambda}-Lorenz dominance to enable flexible fairness preferences. We release a new, large-scale real-world transport planning environment and demonstrate that our method encourages the discovery of fair policies, showing improved scalability in two large cities (Xi'an and Amsterdam). Our methods outperform common multi-objective approaches, particularly in high-dimensional objective spaces.
Privacy-Aware Visual Language Models
May 27, 2024Abstract:This paper aims to advance our understanding of how Visual Language Models (VLMs) handle privacy-sensitive information, a crucial concern as these technologies become integral to everyday life. To this end, we introduce a new benchmark PrivBench, which contains images from 8 sensitive categories such as passports, or fingerprints. We evaluate 10 state-of-the-art VLMs on this benchmark and observe a generally limited understanding of privacy, highlighting a significant area for model improvement. Based on this we introduce PrivTune, a new instruction-tuning dataset aimed at equipping VLMs with knowledge about visual privacy. By tuning two pretrained VLMs, TinyLLaVa and MiniGPT-v2, on this small dataset, we achieve strong gains in their ability to recognize sensitive content, outperforming even GPT4-V. At the same time, we show that privacy-tuning only minimally affects the VLMs performance on standard benchmarks such as VQA. Overall, this paper lays out a crucial challenge for making VLMs effective in handling real-world data safely and provides a simple recipe that takes the first step towards building privacy-aware VLMs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge