Giovanni Sileno
Exploring Structures of Inferential Mechanisms through Simplistic Digital Circuits
Oct 27, 2025Abstract:Cognitive studies and artificial intelligence have developed distinct models for various inferential mechanisms (categorization, induction, abduction, causal inference, contrast, merge, ...). Yet, both natural and artificial views on cognition lack apparently a unifying framework. This paper formulates a speculative answer attempting to respond to this gap. To postulate on higher-level activation processes from a material perspective, we consider inferential mechanisms informed by symbolic AI modelling techniques, through the simplistic lenses of electronic circuits based on logic gates. We observe that a logic gate view entails a different treatment of implication and negation compared to standard logic and logic programming. Then, by combinatorial exploration, we identify four main forms of dependencies that can be realized by these inferential circuits. Looking at how these forms are generally used in the context of logic programs, we identify eight common inferential patterns, exposing traditionally distinct inferential mechanisms in an unifying framework. Finally, following a probabilistic interpretation of logic programs, we unveil inner functional dependencies. The paper concludes elaborating in what sense, even if our arguments are mostly informed by symbolic means and digital systems infrastructures, our observations may pinpoint to more generally applicable structures.
The Cloud Weaving Model for AI development
Apr 23, 2025Abstract:While analysing challenges in pilot projects developing AI with marginalized communities, we found it difficult to express them within commonly used paradigms. We therefore constructed an alternative conceptual framework to ground AI development in the social fabric -- the Cloud Weaving Model -- inspired (amongst others) by indigenous knowledge, motifs from nature, and Eastern traditions. This paper introduces and elaborates on the fundamental elements of the model (clouds, spiders, threads, spiderwebs, and weather) and their interpretation in an AI context. The framework is then applied to comprehend patterns observed in co-creation pilots approaching marginalized communities, highlighting neglected yet relevant dimensions for responsible AI development.
Three Conjectures on Unexpectedeness
Nov 15, 2023Abstract:Unexpectedness is a central concept in Simplicity Theory, a theory of cognition relating various inferential processes to the computation of Kolmogorov complexities, rather than probabilities. Its predictive power has been confirmed by several experiments with human subjects, yet its theoretical basis remains largely unexplored: why does it work? This paper lays the groundwork for three theoretical conjectures. First, unexpectedness can be seen as a generalization of Bayes' rule. Second, the frequentist core of unexpectedness can be connected to the function of tracking ergodic properties of the world. Third, unexpectedness can be seen as constituent of various measures of divergence between the entropy of the world (environment) and the variety of the observer (system). The resulting framework hints to research directions that go beyond the division between probabilistic and logical approaches, potentially bringing new insights into the extraction of causal relations, and into the role of descriptive mechanisms in learning.
From Probabilistic Programming to Complexity-based Programming
Jul 28, 2023
Abstract:The paper presents the main characteristics and a preliminary implementation of a novel computational framework named CompLog. Inspired by probabilistic programming systems like ProbLog, CompLog builds upon the inferential mechanisms proposed by Simplicity Theory, relying on the computation of two Kolmogorov complexities (here implemented as min-path searches via ASP programs) rather than probabilistic inference. The proposed system enables users to compute ex-post and ex-ante measures of unexpectedness of a certain situation, mapping respectively to posterior and prior subjective probabilities. The computation is based on the specification of world and mental models by means of causal and descriptive relations between predicates weighted by complexity. The paper illustrates a few examples of application: generating relevant descriptions, and providing alternative approaches to disjunction and to negation.
DPCL: a Language Template for Normative Specifications
Jan 12, 2022Abstract:Several solutions for specifying normative artefacts (norms, contracts, policies) in a computational processable way have been presented in the literature. Legal core ontologies have been proposed to systematize concepts and relationships relevant to normative reasoning. However, no solution amongst those has achieved general acceptance, and no common ground (representational, computational) has been identified enabling us to easily compare them. Yet, all these efforts share the same motivation of representing normative directives, therefore it is plausible that there may be a representational model encompassing all of them. This presentation will introduce DPCL, a domain-specific language (DSL) for specifying higher-level policies (including norms, contracts, etc.), centred on Hohfeld's framework of fundamental legal concepts. DPCL has to be seen primarily as a "template", i.e. as an informational model for architectural reference, rather than a fully-fledged formal language; it aims to make explicit the general requirements that should be expected in a language for norm specification. In this respect, it goes rather in the direction of legal core ontologies, but differently from those, our proposal aims to keep the character of a DSL, rather than a set of axioms in a logical framework: it is meant to be cross-compiled to underlying languages/tools adequate to the type of target application. We provide here an overview of some of the language features.
Logic Conditionals, Supervenience, and Selection Tasks
Aug 11, 2019Abstract:Principles of cognitive economy would require that concepts about objects, properties and relations should be introduced only if they simplify the conceptualisation of a domain. Unexpectedly, classic logic conditionals, specifying structures holding within elements of a formal conceptualisation, do not always satisfy this crucial principle. The paper argues that this requirement is captured by supervenience, hereby further identified as a property necessary for compression. The resulting theory suggests an alternative explanation of the empirical experiences observable in Wason's selection tasks, associating human performance with conditionals on the ability of dealing with compression, rather than with logic necessity.
The Role of Normware in Trustworthy and Explainable AI
Dec 06, 2018
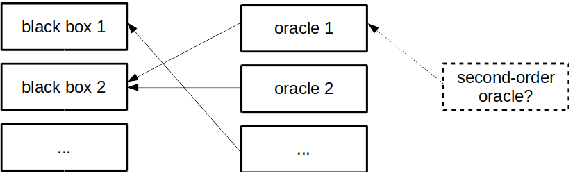

Abstract:For being potentially destructive, in practice incomprehensible and for the most unintelligible, contemporary technology is setting high challenges on our society. New conception methods are urgently required. Reorganizing ideas and discussions presented in AI and related fields, this position paper aims to highlight the importance of normware--that is, computational artifacts specifying norms--with respect to these issues, and argues for its irreducibility with respect to software by making explicit its neglected ecological dimension in the decision-making cycle.
Institutional Metaphors for Designing Large-Scale Distributed AI versus AI Techniques for Running Institutions
Mar 09, 2018Abstract:Artificial Intelligence (AI) started out with an ambition to reproduce the human mind, but, as the sheer scale of that ambition became apparent, quickly retreated into either studying specialized intelligent behaviours, or proposing overarching architectural concepts for interfacing specialized intelligent behaviour components, conceived of as agents in a kind of organization. This agent-based modeling paradigm, in turn, proves to have interesting applications in understanding, simulating, and predicting the behaviour of social and legal structures on an aggregate level. This chapter examines a number of relevant cross-cutting concerns, conceptualizations, modeling problems and design challenges in large-scale distributed Artificial Intelligence, as well as in institutional systems, and identifies potential grounds for novel advances.
Logic Programming Petri Nets
Jan 26, 2017



Abstract:With the purpose of modeling, specifying and reasoning in an integrated fashion with procedural and declarative aspects (both commonly present in cases or scenarios), the paper introduces Logic Programming Petri Nets (LPPN), an extension to the Petri Net notation providing an interface to logic programming constructs. Two semantics are presented. First, a hybrid operational semantics that separates the process component, treated with Petri nets, from the constraint/terminological component, treated with Answer Set Programming (ASP). Second, a denotational semantics maps the notation to ASP fully, via Event Calculus. These two alternative specifications enable a preliminary evaluation in terms of reasoning efficiency.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge