Sehyung Kim
Super-class guided Transformer for Zero-Shot Attribute Classification
Jan 16, 2025



Abstract:Attribute classification is crucial for identifying specific characteristics within image regions. Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have been effective in zero-shot tasks by leveraging their general knowledge from large-scale datasets. Recent studies demonstrate that transformer-based models with class-wise queries can effectively address zero-shot multi-label classification. However, poor utilization of the relationship between seen and unseen attributes makes the model lack generalizability. Additionally, attribute classification generally involves many attributes, making maintaining the model's scalability difficult. To address these issues, we propose Super-class guided transFormer (SugaFormer), a novel framework that leverages super-classes to enhance scalability and generalizability for zero-shot attribute classification. SugaFormer employs Super-class Query Initialization (SQI) to reduce the number of queries, utilizing common semantic information from super-classes, and incorporates Multi-context Decoding (MD) to handle diverse visual cues. To strengthen generalizability, we introduce two knowledge transfer strategies that utilize VLMs. During training, Super-class guided Consistency Regularization (SCR) aligns model's features with VLMs using super-class guided prompts, and during inference, Zero-shot Retrieval-based Score Enhancement (ZRSE) refines predictions for unseen attributes. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SugaFormer achieves state-of-the-art performance across three widely-used attribute classification benchmarks under zero-shot, and cross-dataset transfer settings. Our code is available at https://github.com/mlvlab/SugaFormer.
SoccerNet 2024 Challenges Results
Sep 16, 2024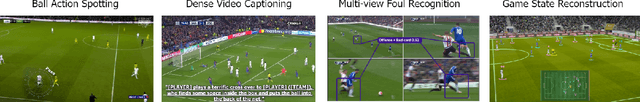
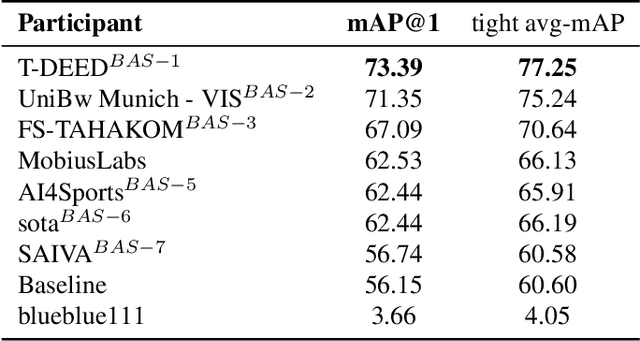
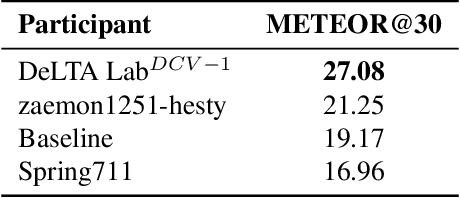
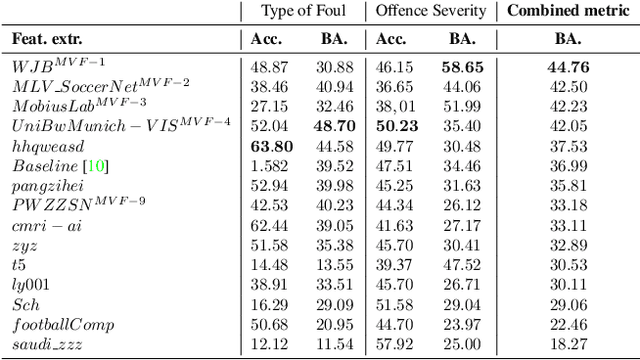
Abstract:The SoccerNet 2024 challenges represent the fourth annual video understanding challenges organized by the SoccerNet team. These challenges aim to advance research across multiple themes in football, including broadcast video understanding, field understanding, and player understanding. This year, the challenges encompass four vision-based tasks. (1) Ball Action Spotting, focusing on precisely localizing when and which soccer actions related to the ball occur, (2) Dense Video Captioning, focusing on describing the broadcast with natural language and anchored timestamps, (3) Multi-View Foul Recognition, a novel task focusing on analyzing multiple viewpoints of a potential foul incident to classify whether a foul occurred and assess its severity, (4) Game State Reconstruction, another novel task focusing on reconstructing the game state from broadcast videos onto a 2D top-view map of the field. Detailed information about the tasks, challenges, and leaderboards can be found at https://www.soccer-net.org, with baselines and development kits available at https://github.com/SoccerNet.
Retrieval-Augmented Open-Vocabulary Object Detection
Apr 08, 2024Abstract:Open-vocabulary object detection (OVD) has been studied with Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to detect novel objects beyond the pre-trained categories. Previous approaches improve the generalization ability to expand the knowledge of the detector, using 'positive' pseudo-labels with additional 'class' names, e.g., sock, iPod, and alligator. To extend the previous methods in two aspects, we propose Retrieval-Augmented Losses and visual Features (RALF). Our method retrieves related 'negative' classes and augments loss functions. Also, visual features are augmented with 'verbalized concepts' of classes, e.g., worn on the feet, handheld music player, and sharp teeth. Specifically, RALF consists of two modules: Retrieval Augmented Losses (RAL) and Retrieval-Augmented visual Features (RAF). RAL constitutes two losses reflecting the semantic similarity with negative vocabularies. In addition, RAF augments visual features with the verbalized concepts from a large language model (LLM). Our experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of RALF on COCO and LVIS benchmark datasets. We achieve improvement up to 3.4 box AP$_{50}^{\text{N}}$ on novel categories of the COCO dataset and 3.6 mask AP$_{\text{r}}$ gains on the LVIS dataset. Code is available at https://github.com/mlvlab/RALF .
Groupwise Query Specialization and Quality-Aware Multi-Assignment for Transformer-based Visual Relationship Detection
Mar 26, 2024Abstract:Visual Relationship Detection (VRD) has seen significant advancements with Transformer-based architectures recently. However, we identify two key limitations in a conventional label assignment for training Transformer-based VRD models, which is a process of mapping a ground-truth (GT) to a prediction. Under the conventional assignment, an unspecialized query is trained since a query is expected to detect every relation, which makes it difficult for a query to specialize in specific relations. Furthermore, a query is also insufficiently trained since a GT is assigned only to a single prediction, therefore near-correct or even correct predictions are suppressed by being assigned no relation as a GT. To address these issues, we propose Groupwise Query Specialization and Quality-Aware Multi-Assignment (SpeaQ). Groupwise Query Specialization trains a specialized query by dividing queries and relations into disjoint groups and directing a query in a specific query group solely toward relations in the corresponding relation group. Quality-Aware Multi-Assignment further facilitates the training by assigning a GT to multiple predictions that are significantly close to a GT in terms of a subject, an object, and the relation in between. Experimental results and analyses show that SpeaQ effectively trains specialized queries, which better utilize the capacity of a model, resulting in consistent performance gains with zero additional inference cost across multiple VRD models and benchmarks. Code is available at https://github.com/mlvlab/SpeaQ.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge