Sebastian Wagner-Carena
for the LSST Dark Energy Science Collaboration
Hierarchical Inference of the Lensing Convergence from Photometric Catalogs with Bayesian Graph Neural Networks
Nov 15, 2022Abstract:We present a Bayesian graph neural network (BGNN) that can estimate the weak lensing convergence ($\kappa$) from photometric measurements of galaxies along a given line of sight. The method is of particular interest in strong gravitational time delay cosmography (TDC), where characterizing the "external convergence" ($\kappa_{\rm ext}$) from the lens environment and line of sight is necessary for precise inference of the Hubble constant ($H_0$). Starting from a large-scale simulation with a $\kappa$ resolution of $\sim$1$'$, we introduce fluctuations on galaxy-galaxy lensing scales of $\sim$1$''$ and extract random sightlines to train our BGNN. We then evaluate the model on test sets with varying degrees of overlap with the training distribution. For each test set of 1,000 sightlines, the BGNN infers the individual $\kappa$ posteriors, which we combine in a hierarchical Bayesian model to yield constraints on the hyperparameters governing the population. For a test field well sampled by the training set, the BGNN recovers the population mean of $\kappa$ precisely and without bias, resulting in a contribution to the $H_0$ error budget well under 1\%. In the tails of the training set with sparse samples, the BGNN, which can ingest all available information about each sightline, extracts more $\kappa$ signal compared to a simplified version of the traditional method based on matching galaxy number counts, which is limited by sample variance. Our hierarchical inference pipeline using BGNNs promises to improve the $\kappa_{\rm ext}$ characterization for precision TDC. The implementation of our pipeline is available as a public Python package, Node to Joy.
Large-Scale Gravitational Lens Modeling with Bayesian Neural Networks for Accurate and Precise Inference of the Hubble Constant
Nov 30, 2020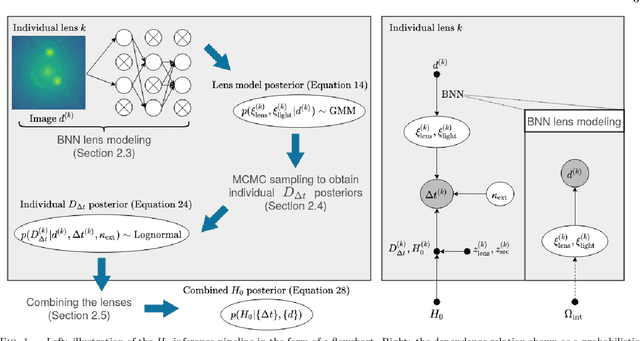
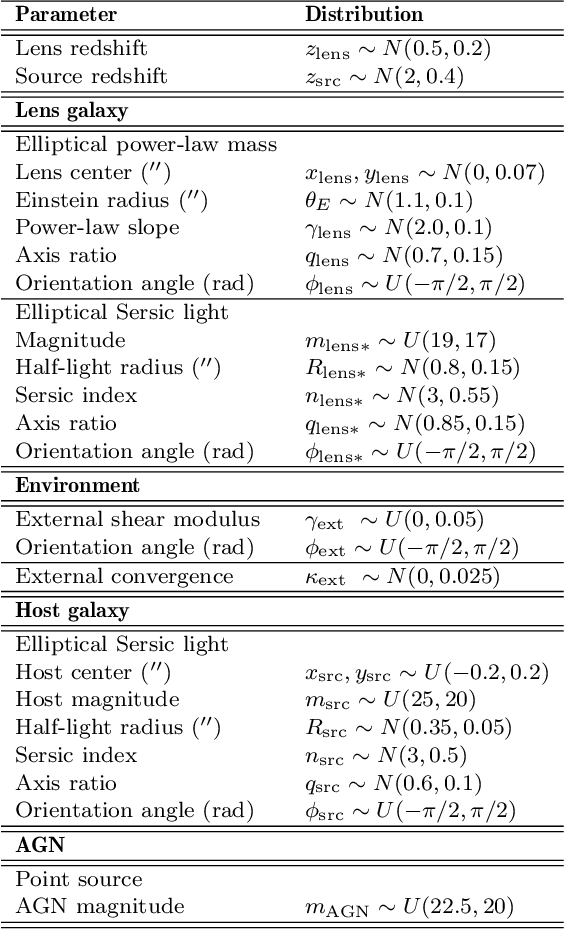
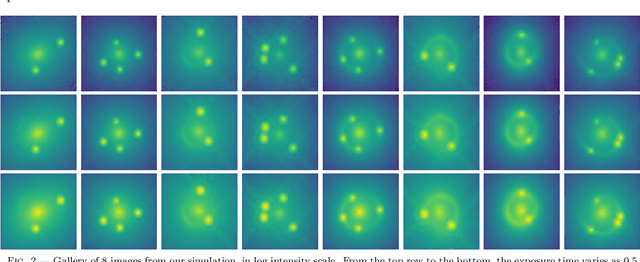
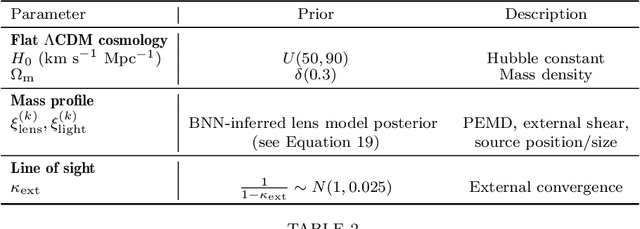
Abstract:We investigate the use of approximate Bayesian neural networks (BNNs) in modeling hundreds of time-delay gravitational lenses for Hubble constant ($H_0$) determination. Our BNN was trained on synthetic HST-quality images of strongly lensed active galactic nuclei (AGN) with lens galaxy light included. The BNN can accurately characterize the posterior PDFs of model parameters governing the elliptical power-law mass profile in an external shear field. We then propagate the BNN-inferred posterior PDFs into ensemble $H_0$ inference, using simulated time delay measurements from a plausible dedicated monitoring campaign. Assuming well-measured time delays and a reasonable set of priors on the environment of the lens, we achieve a median precision of $9.3$\% per lens in the inferred $H_0$. A simple combination of 200 test-set lenses results in a precision of 0.5 $\textrm{km s}^{-1} \textrm{ Mpc}^{-1}$ ($0.7\%$), with no detectable bias in this $H_0$ recovery test. The computation time for the entire pipeline -- including the training set generation, BNN training, and $H_0$ inference -- translates to 9 minutes per lens on average for 200 lenses and converges to 6 minutes per lens as the sample size is increased. Being fully automated and efficient, our pipeline is a promising tool for exploring ensemble-level systematics in lens modeling for $H_0$ inference.
Hierarchical Inference With Bayesian Neural Networks: An Application to Strong Gravitational Lensing
Oct 28, 2020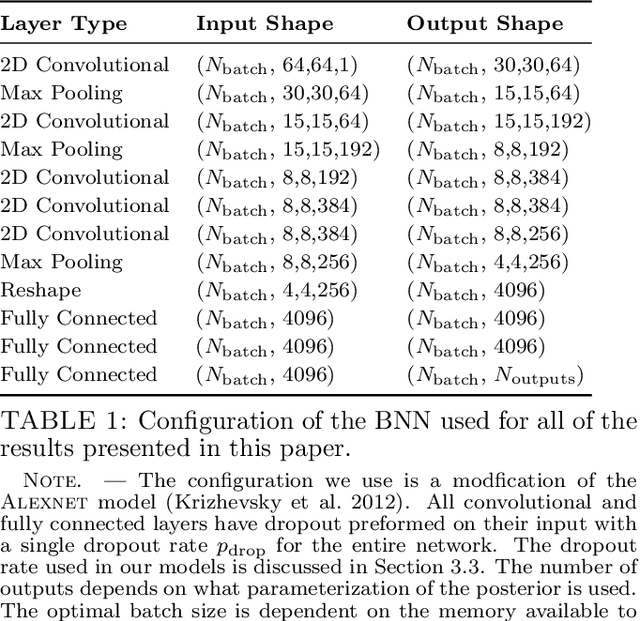
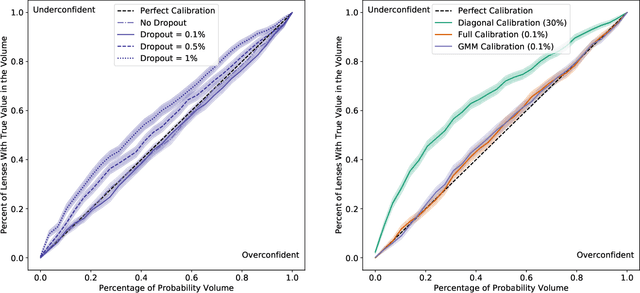
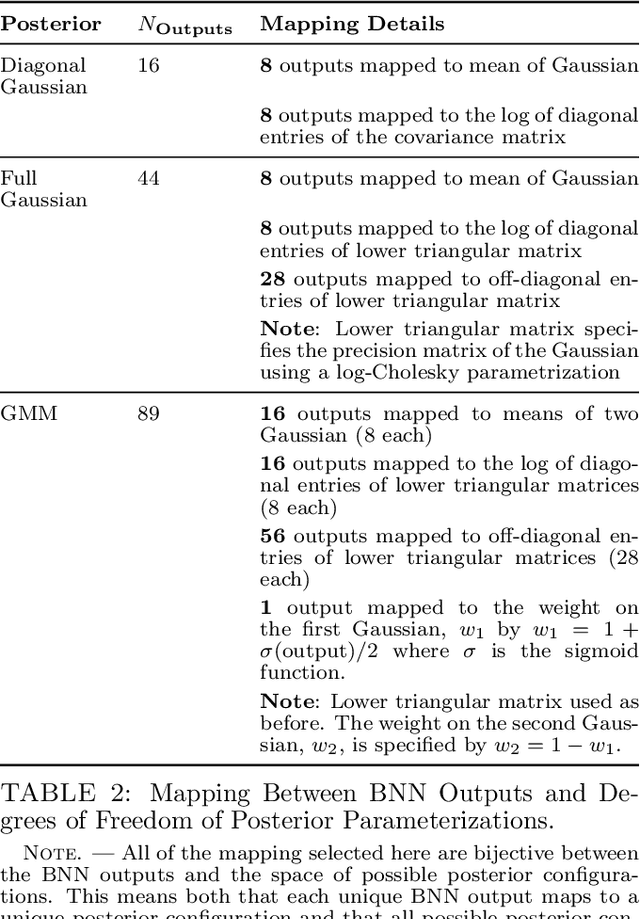
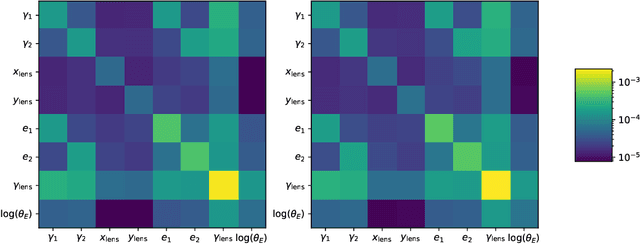
Abstract:In the past few years, approximate Bayesian Neural Networks (BNNs) have demonstrated the ability to produce statistically consistent posteriors on a wide range of inference problems at unprecedented speed and scale. However, any disconnect between training sets and the distribution of real-world objects can introduce bias when BNNs are applied to data. This is a common challenge in astrophysics and cosmology, where the unknown distribution of objects in our Universe is often the science goal. In this work, we incorporate BNNs with flexible posterior parameterizations into a hierarchical inference framework that allows for the reconstruction of population hyperparameters and removes the bias introduced by the training distribution. We focus on the challenge of producing posterior PDFs for strong gravitational lens mass model parameters given Hubble Space Telescope (HST) quality single-filter, lens-subtracted, synthetic imaging data. We show that the posterior PDFs are sufficiently accurate (i.e., statistically consistent with the truth) across a wide variety of power-law elliptical lens mass distributions. We then apply our approach to test data sets whose lens parameters are drawn from distributions that are drastically different from the training set. We show that our hierarchical inference framework mitigates the bias introduced by an unrepresentative training set's interim prior. Simultaneously, given a sufficiently broad training set, we can precisely reconstruct the population hyperparameters governing our test distributions. Our full pipeline, from training to hierarchical inference on thousands of lenses, can be run in a day. The framework presented here will allow us to efficiently exploit the full constraining power of future ground- and space-based surveys.
A Novel CMB Component Separation Method: Hierarchical Generalized Morphological Component Analysis
Oct 17, 2019



Abstract:We present a novel technique for Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) foreground subtraction based on the framework of blind source separation. Inspired by previous work incorporating local variation to Generalized Morphological Component Analysis (GMCA), we introduce Hierarchical GMCA (HGMCA), a Bayesian hierarchical framework for source separation. We test our method on $N_{\rm side}=256$ simulated sky maps that include dust, synchrotron, free-free and anomalous microwave emission, and show that HGMCA reduces foreground contamination by $25\%$ over GMCA in both the regions included and excluded by the Planck UT78 mask, decreases the error in the measurement of the CMB temperature power spectrum to the $0.02-0.03\%$ level at $\ell>200$ (and $<0.26\%$ for all $\ell$), and reduces correlation to all the foregrounds. We find equivalent or improved performance when compared to state-of-the-art Internal Linear Combination (ILC)-type algorithms on these simulations, suggesting that HGMCA may be a competitive alternative to foreground separation techniques previously applied to observed CMB data. Additionally, we show that our performance does not suffer when we perturb model parameters or alter the CMB realization, which suggests that our algorithm generalizes well beyond our simplified simulations. Our results open a new avenue for constructing CMB maps through Bayesian hierarchical analysis.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge