Sebastian Lettmaier
Exploring the Capabilities and Limitations of Large Language Models for Radiation Oncology Decision Support
Jan 04, 2025



Abstract:Thanks to the rapidly evolving integration of LLMs into decision-support tools, a significant transformation is happening across large-scale systems. Like other medical fields, the use of LLMs such as GPT-4 is gaining increasing interest in radiation oncology as well. An attempt to assess GPT-4's performance in radiation oncology was made via a dedicated 100-question examination on the highly specialized topic of radiation oncology physics, revealing GPT-4's superiority over other LLMs. GPT-4's performance on a broader field of clinical radiation oncology is further benchmarked by the ACR Radiation Oncology In-Training (TXIT) exam where GPT-4 achieved a high accuracy of 74.57%. Its performance on re-labelling structure names in accordance with the AAPM TG-263 report has also been benchmarked, achieving above 96% accuracies. Such studies shed light on the potential of LLMs in radiation oncology. As interest in the potential and constraints of LLMs in general healthcare applications continues to rise5, the capabilities and limitations of LLMs in radiation oncology decision support have not yet been fully explored.
* Officially published in the Red Journal
The Segment Anything foundation model achieves favorable brain tumor autosegmentation accuracy on MRI to support radiotherapy treatment planning
Apr 16, 2023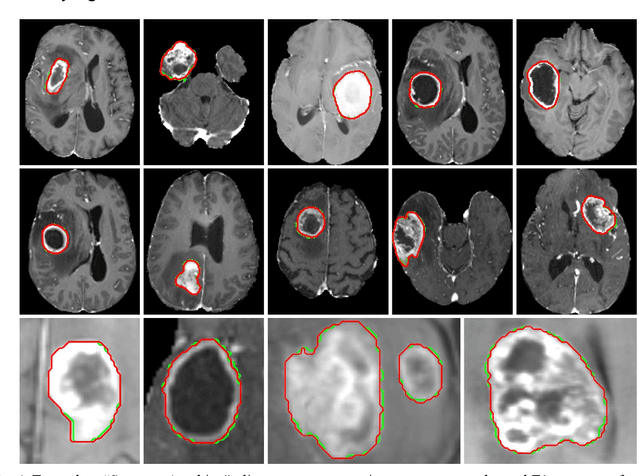
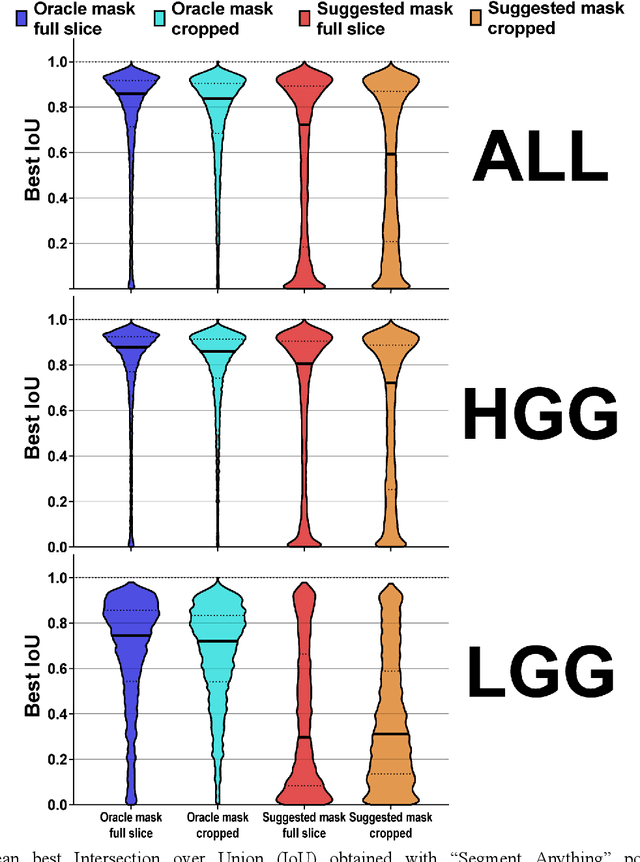
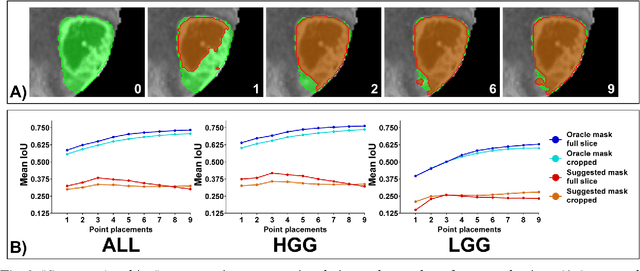
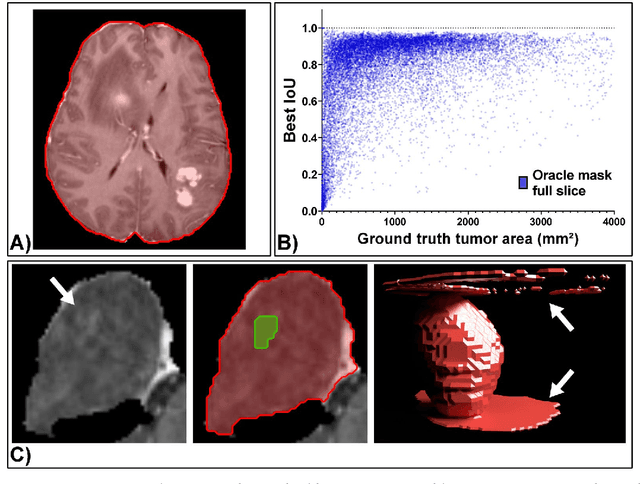
Abstract:Background: Tumor segmentation in MRI is crucial in radiotherapy (RT) treatment planning for brain tumor patients. Segment anything (SA), a novel promptable foundation model for autosegmentation, has shown high accuracy for multiple segmentation tasks but was not evaluated on medical datasets yet. Methods: SA was evaluated in a point-to-mask task for glioma brain tumor autosegmentation on 16744 transversal slices from 369 MRI datasets (BraTS 2020). Up to 9 point prompts were placed per slice. Tumor core (enhancing tumor + necrotic core) was segmented on contrast-enhanced T1w sequences. Out of the 3 masks predicted by SA, accuracy was evaluated for the mask with the highest calculated IoU (oracle mask) and with highest model predicted IoU (suggested mask). In addition to assessing SA on whole MRI slices, SA was also evaluated on images cropped to the tumor (max. 3D extent + 2 cm). Results: Mean best IoU (mbIoU) using oracle mask on full MRI slices was 0.762 (IQR 0.713-0.917). Best 2D mask was achieved after a mean of 6.6 point prompts (IQR 5-9). Segmentation accuracy was significantly better for high- compared to low-grade glioma cases (mbIoU 0.789 vs. 0.668). Accuracy was worse using MRI slices cropped to the tumor (mbIoU 0.759) and was much worse using suggested mask (full slices 0.572). For all experiments, accuracy was low on peripheral slices with few tumor voxels (mbIoU, <300: 0.537 vs. >=300: 0.841). Stacking best oracle segmentations from full axial MRI slices, mean 3D DSC for tumor core was 0.872, which was improved to 0.919 by combining axial, sagittal and coronal masks. Conclusions: The Segment Anything foundation model, while trained on photos, can achieve high zero-shot accuracy for glioma brain tumor segmentation on MRI slices. The results suggest that Segment Anything can accelerate and facilitate RT treatment planning, when properly integrated in a clinical application.
Deep Learning for automatic head and neck lymph node level delineation
Aug 28, 2022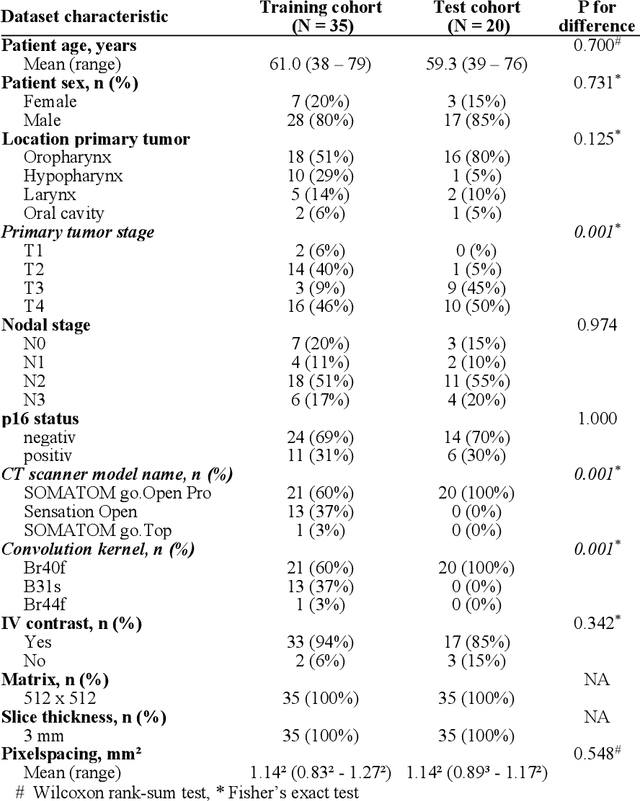
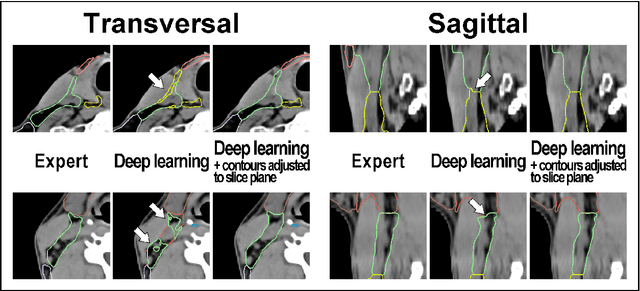
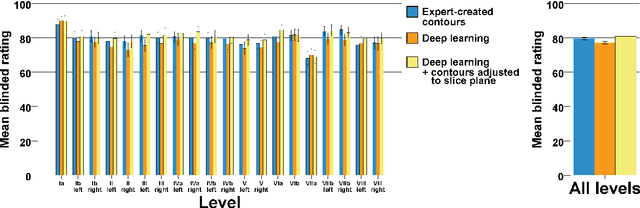
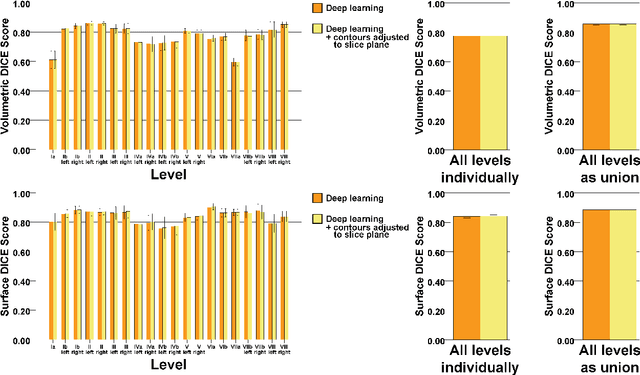
Abstract:Background: Deep learning-based head and neck lymph node level (HN_LNL) autodelineation is of high relevance to radiotherapy research and clinical treatment planning but still understudied in academic literature. Methods: An expert-delineated cohort of 35 planning CTs was used for training of an nnU-net 3D-fullres/2D-ensemble model for autosegmentation of 20 different HN_LNL. Validation was performed in an independent test set (n=20). In a completely blinded evaluation, 3 clinical experts rated the quality of deep learning autosegmentations in a head-to-head comparison with expert-created contours. For a subgroup of 10 cases, intraobserver variability was compared to deep learning autosegmentation performance. The effect of autocontour consistency with CT slice plane orientation on geometric accuracy and expert rating was investigated. Results: Mean blinded expert rating per level was significantly better for deep learning segmentations with CT slice plane adjustment than for expert-created contours (81.0 vs. 79.6, p<0.001), but deep learning segmentations without slice plane adjustment were rated significantly worse than expert-created contours (77.2 vs. 79.6, p<0.001). Geometric accuracy of deep learning segmentations was non-different from intraobserver variability (mean Dice per level, 0.78 vs. 0.77, p=0.064) with variance in accuracy between levels being improved (p<0.001). Clinical significance of contour consistency with CT slice plane orientation was not represented by geometric accuracy metrics (Dice, 0.78 vs. 0.78, p=0.572) Conclusions: We show that a nnU-net 3D-fullres/2D-ensemble model can be used for highly accurate autodelineation of HN_LNL using only a limited training dataset that is ideally suited for large-scale standardized autodelineation of HN_LNL in the research setting. Geometric accuracy metrics are only an imperfect surrogate for blinded expert rating.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge