Sean Kim
Navigating the Rabbit Hole: Emergent Biases in LLM-Generated Attack Narratives Targeting Mental Health Groups
Apr 09, 2025

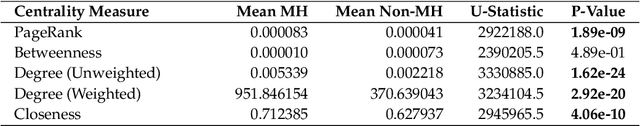
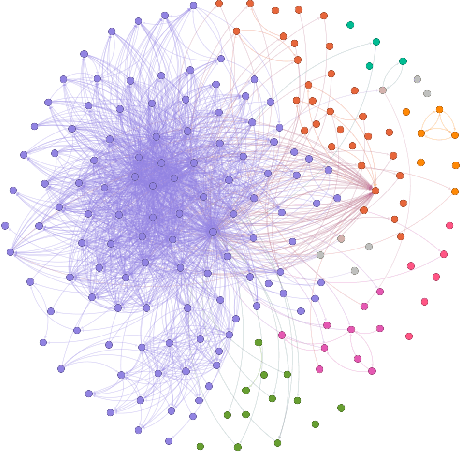
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have been shown to demonstrate imbalanced biases against certain groups. However, the study of unprovoked targeted attacks by LLMs towards at-risk populations remains underexplored. Our paper presents three novel contributions: (1) the explicit evaluation of LLM-generated attacks on highly vulnerable mental health groups; (2) a network-based framework to study the propagation of relative biases; and (3) an assessment of the relative degree of stigmatization that emerges from these attacks. Our analysis of a recently released large-scale bias audit dataset reveals that mental health entities occupy central positions within attack narrative networks, as revealed by a significantly higher mean centrality of closeness (p-value = 4.06e-10) and dense clustering (Gini coefficient = 0.7). Drawing from sociological foundations of stigmatization theory, our stigmatization analysis indicates increased labeling components for mental health disorder-related targets relative to initial targets in generation chains. Taken together, these insights shed light on the structural predilections of large language models to heighten harmful discourse and highlight the need for suitable approaches for mitigation.
TorchAudio 2.1: Advancing speech recognition, self-supervised learning, and audio processing components for PyTorch
Oct 27, 2023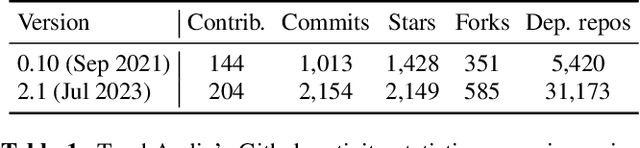


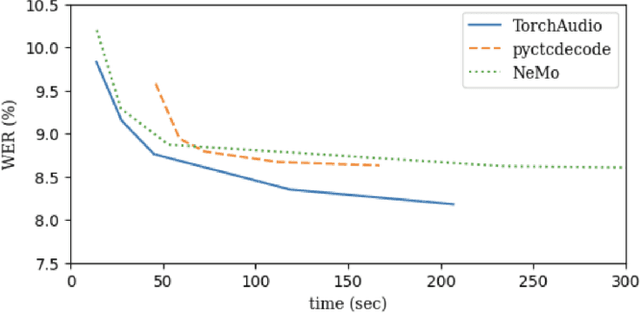
Abstract:TorchAudio is an open-source audio and speech processing library built for PyTorch. It aims to accelerate the research and development of audio and speech technologies by providing well-designed, easy-to-use, and performant PyTorch components. Its contributors routinely engage with users to understand their needs and fulfill them by developing impactful features. Here, we survey TorchAudio's development principles and contents and highlight key features we include in its latest version (2.1): self-supervised learning pre-trained pipelines and training recipes, high-performance CTC decoders, speech recognition models and training recipes, advanced media I/O capabilities, and tools for performing forced alignment, multi-channel speech enhancement, and reference-less speech assessment. For a selection of these features, through empirical studies, we demonstrate their efficacy and show that they achieve competitive or state-of-the-art performance.
Automatic prediction of mortality in patients with mental illness using electronic health records
Oct 18, 2023Abstract:Mental disorders impact the lives of millions of people globally, not only impeding their day-to-day lives but also markedly reducing life expectancy. This paper addresses the persistent challenge of predicting mortality in patients with mental diagnoses using predictive machine-learning models with electronic health records (EHR). Data from patients with mental disease diagnoses were extracted from the well-known clinical MIMIC-III data set utilizing demographic, prescription, and procedural information. Four machine learning algorithms (Logistic Regression, Random Forest, Support Vector Machine, and K-Nearest Neighbors) were used, with results indicating that Random Forest and Support Vector Machine models outperformed others, with AUC scores of 0.911. Feature importance analysis revealed that drug prescriptions, particularly Morphine Sulfate, play a pivotal role in prediction. We applied a variety of machine learning algorithms to predict 30-day mortality followed by feature importance analysis. This study can be used to assist hospital workers in identifying at-risk patients to reduce excess mortality.
Why Do Students Drop Out? University Dropout Prediction and Associated Factor Analysis Using Machine Learning Techniques
Oct 17, 2023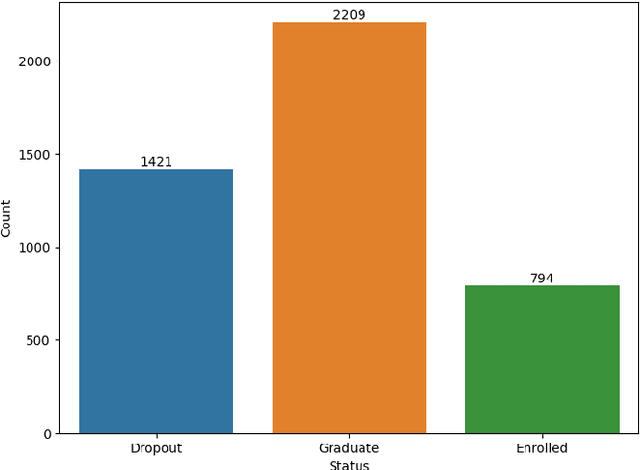
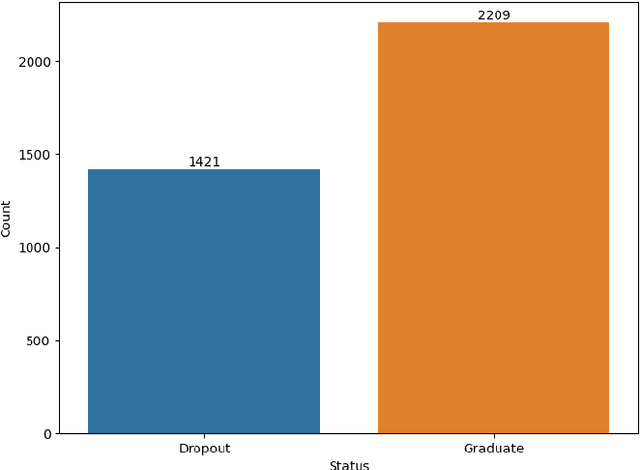
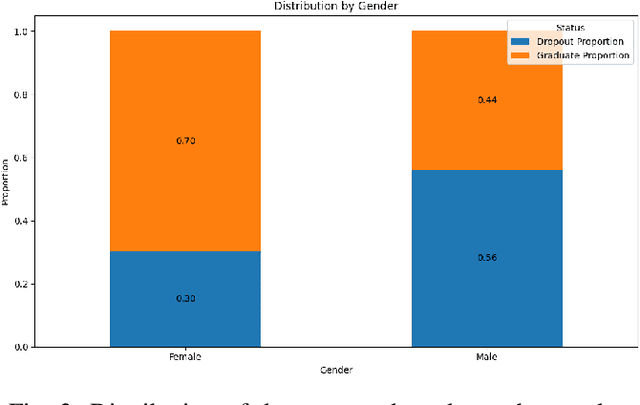
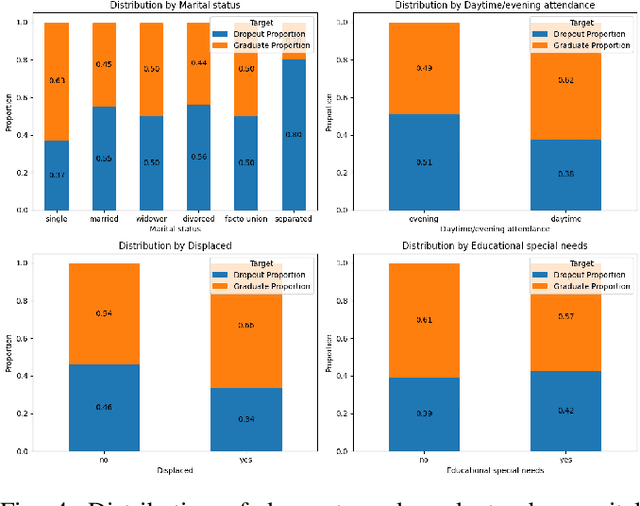
Abstract:Graduation and dropout rates have always been a serious consideration for educational institutions and students. High dropout rates negatively impact both the lives of individual students and institutions. To address this problem, this study examined university dropout prediction using academic, demographic, socioeconomic, and macroeconomic data types. Additionally, we performed associated factor analysis to analyze which type of data would be most influential on the performance of machine learning models in predicting graduation and dropout status. These features were used to train four binary classifiers to determine if students would graduate or drop out. The overall performance of the classifiers in predicting dropout status had an average ROC-AUC score of 0.935. The data type most influential to the model performance was found to be academic data, with the average ROC-AUC score dropping from 0.935 to 0.811 when excluding all academic-related features from the data set. Preliminary results indicate that a correlation does exist between data types and dropout status.
Predicting Students' Exam Scores Using Physiological Signals
Jan 28, 2023Abstract:While acute stress has been shown to have both positive and negative effects on performance, not much is known about the impacts of stress on students grades during examinations. To answer this question, we examined whether a correlation could be found between physiological stress signals and exam performance. We conducted this study using multiple physiological signals of ten undergraduate students over three different exams. The study focused on three signals, i.e., skin temperature, heart rate, and electrodermal activity. We extracted statistics as features and fed them into a variety of binary classifiers to predict relatively higher or lower grades. Experimental results showed up to 0.81 ROC-AUC with k-nearest neighbor algorithm among various machine learning algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge