Scott Powers
Some methods for heterogeneous treatment effect estimation in high-dimensions
Jul 01, 2017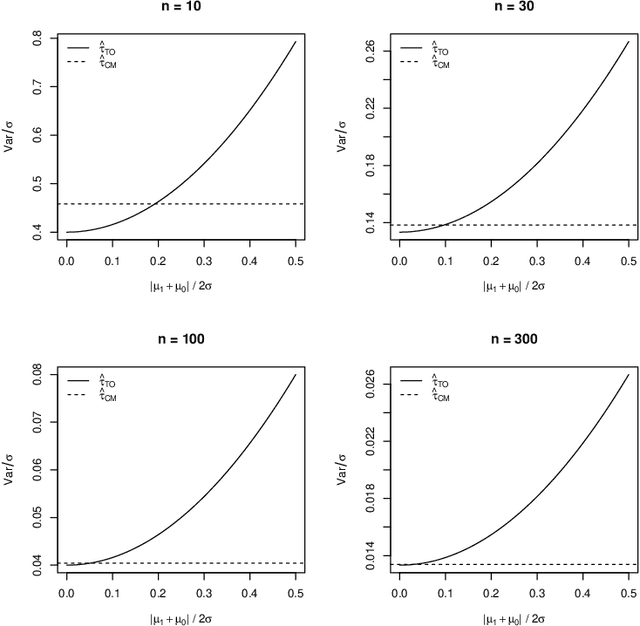
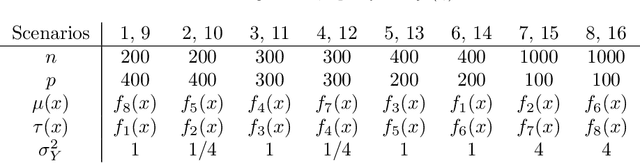
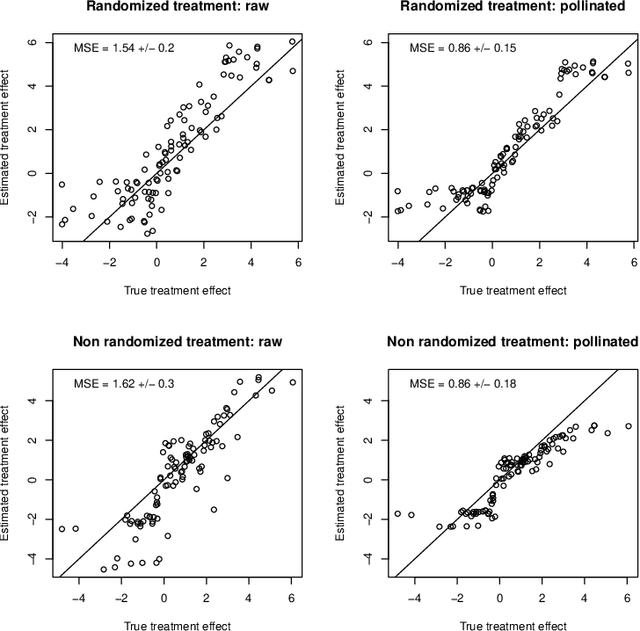
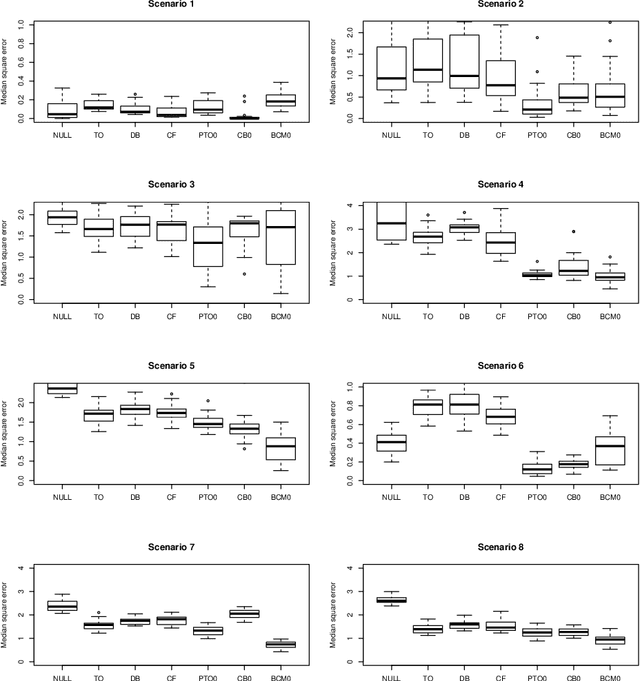
Abstract:When devising a course of treatment for a patient, doctors often have little quantitative evidence on which to base their decisions, beyond their medical education and published clinical trials. Stanford Health Care alone has millions of electronic medical records (EMRs) that are only just recently being leveraged to inform better treatment recommendations. These data present a unique challenge because they are high-dimensional and observational. Our goal is to make personalized treatment recommendations based on the outcomes for past patients similar to a new patient. We propose and analyze three methods for estimating heterogeneous treatment effects using observational data. Our methods perform well in simulations using a wide variety of treatment effect functions, and we present results of applying the two most promising methods to data from The SPRINT Data Analysis Challenge, from a large randomized trial of a treatment for high blood pressure.
Nuclear penalized multinomial regression with an application to predicting at bat outcomes in baseball
Jun 30, 2017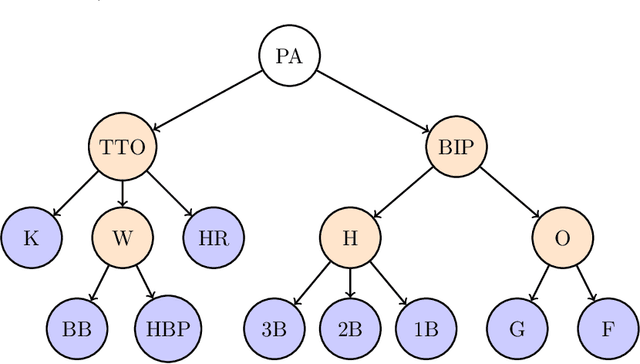
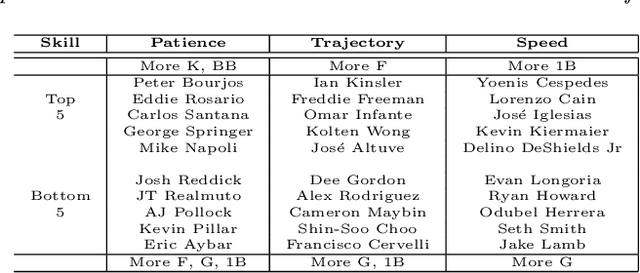
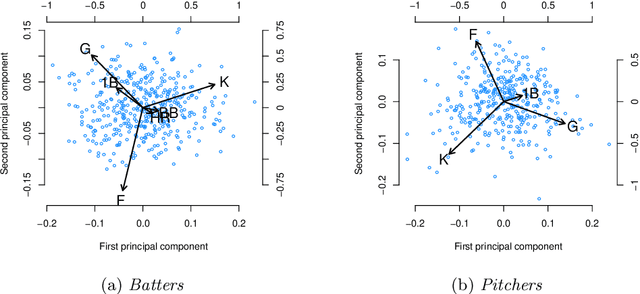
Abstract:We propose the nuclear norm penalty as an alternative to the ridge penalty for regularized multinomial regression. This convex relaxation of reduced-rank multinomial regression has the advantage of leveraging underlying structure among the response categories to make better predictions. We apply our method, nuclear penalized multinomial regression (NPMR), to Major League Baseball play-by-play data to predict outcome probabilities based on batter-pitcher matchups. The interpretation of the results meshes well with subject-area expertise and also suggests a novel understanding of what differentiates players.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge