Satoshi Tojo
Mitsubishi Research Institute, Inc
Anonymous Public Announcements
Apr 21, 2025



Abstract:We formalise the notion of an anonymous public announcement in the tradition of public announcement logic. Such announcements can be seen as in-between a public announcement from ``the outside" (an announcement of $\phi$) and a public announcement by one of the agents (an announcement of $K_a\phi$): we get more information than just $\phi$, but not (necessarily) about exactly who made it. Even if such an announcement is prima facie anonymous, depending on the background knowledge of the agents it might reveal the identity of the announcer: if I post something on a message board, the information might reveal who I am even if I don't sign my name. Furthermore, like in the Russian Cards puzzle, if we assume that the announcer's intention was to stay anonymous, that in fact might reveal more information. In this paper we first look at the case when no assumption about intentions are made, in which case the logic with an anonymous public announcement operator is reducible to epistemic logic. We then look at the case when we assume common knowledge of the intention to stay anonymous, which is both more complex and more interesting: in several ways it boils down to the notion of a ``safe" announcement (again, similarly to Russian Cards). Main results include formal expressivity results and axiomatic completeness for key logical languages.
8+8=4: Formalizing Time Units to Handle Symbolic Music Durations
Oct 23, 2023Abstract:This paper focuses on the nominal durations of musical events (notes and rests) in a symbolic musical score, and on how to conveniently handle these in computer applications. We propose the usage of a temporal unit that is directly related to the graphical symbols in musical scores and pair this with a set of operations that cover typical computations in music applications. We formalize this time unit and the more commonly used approach in a single mathematical framework, as semirings, algebraic structures that enable an abstract description of algorithms/processing pipelines. We then discuss some practical use cases and highlight when our system can improve such pipelines by making them more efficient in terms of data type used and the number of computations.
Encoded Summarization: Summarizing Documents into Continuous Vector Space for Legal Case Retrieval
Sep 15, 2023Abstract:We present our method for tackling a legal case retrieval task by introducing our method of encoding documents by summarizing them into continuous vector space via our phrase scoring framework utilizing deep neural networks. On the other hand, we explore the benefits from combining lexical features and latent features generated with neural networks. Our experiments show that lexical features and latent features generated with neural networks complement each other to improve the retrieval system performance. Furthermore, our experimental results suggest the importance of case summarization in different aspects: using provided summaries and performing encoded summarization. Our approach achieved F1 of 65.6% and 57.6% on the experimental datasets of legal case retrieval tasks.
Free-ordered CUG on Chemical Abstract Machine
Nov 16, 1994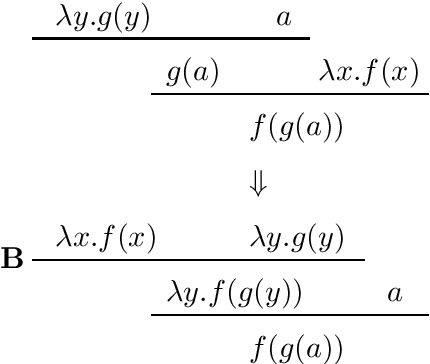

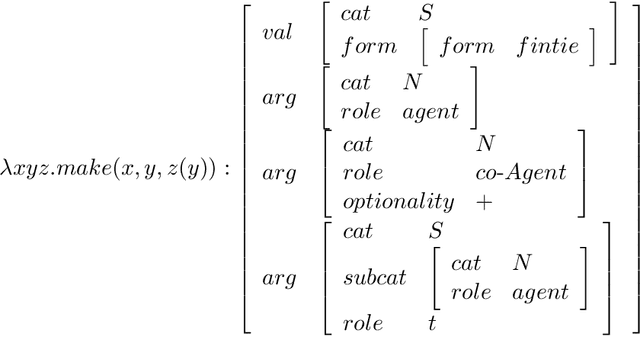
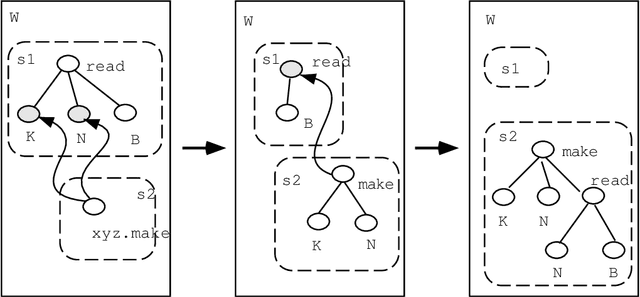
Abstract:We propose a paradigm for concurrent natural language generation. In order to represent grammar rules distributively, we adopt categorial unification grammar (CUG) where each category owns its functional type. We augment typed lambda calculus with several new combinators, to make the order of lambda-conversions free for partial / local processing. The concurrent calculus is modeled with Chemical Abstract Machine. We show an example of a Japanese causative auxiliary verb that requires a drastic rearrangement of case domination.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge