Sarath Bethapudi
MedNeRF: Medical Neural Radiance Fields for Reconstructing 3D-aware CT-Projections from a Single X-ray
Feb 02, 2022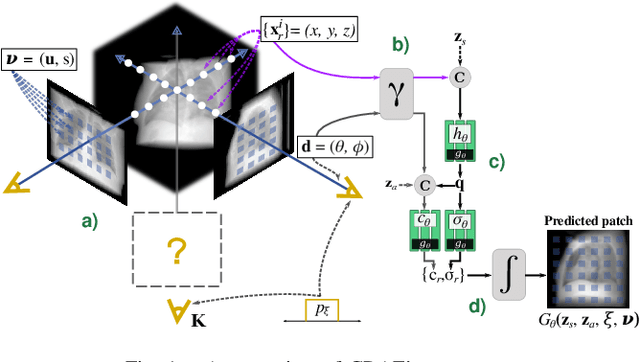
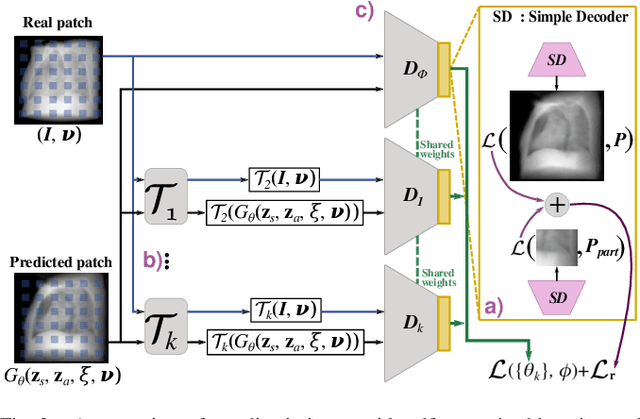
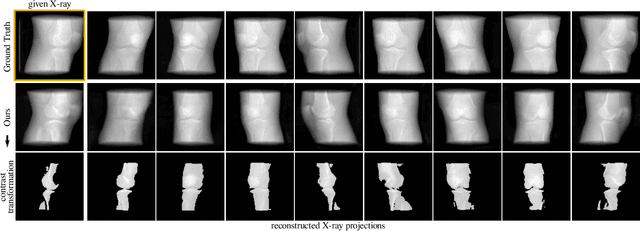
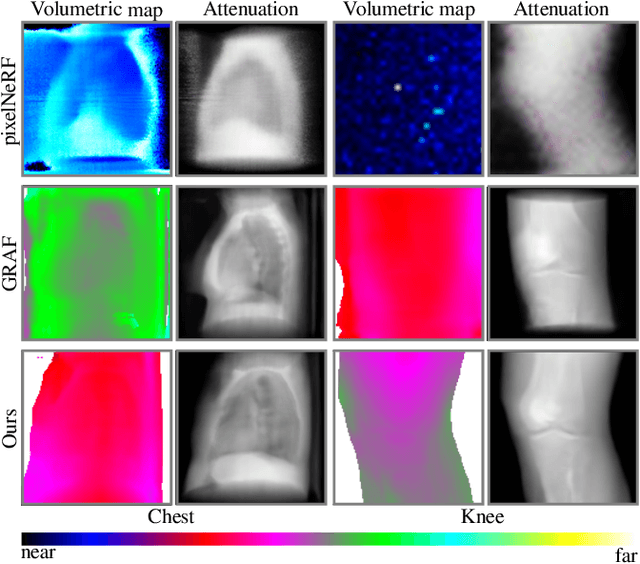
Abstract:Computed tomography (CT) is an effective medical imaging modality, widely used in the field of clinical medicine for the diagnosis of various pathologies. Advances in Multidetector CT imaging technology have enabled additional functionalities, including generation of thin slice multiplanar cross-sectional body imaging and 3D reconstructions. However, this involves patients being exposed to a considerable dose of ionising radiation. Excessive ionising radiation can lead to deterministic and harmful effects on the body. This paper proposes a Deep Learning model that learns to reconstruct CT projections from a few or even a single-view X-ray. This is based on a novel architecture that builds from neural radiance fields, which learns a continuous representation of CT scans by disentangling the shape and volumetric depth of surface and internal anatomical structures from 2D images. Our model is trained on chest and knee datasets, and we demonstrate qualitative and quantitative high-fidelity renderings and compare our approach to other recent radiance field-based methods. Our code and link to our datasets will be available at our GitHub.
Unsupervised Region-based Anomaly Detection in Brain MRI with Adversarial Image Inpainting
Oct 05, 2020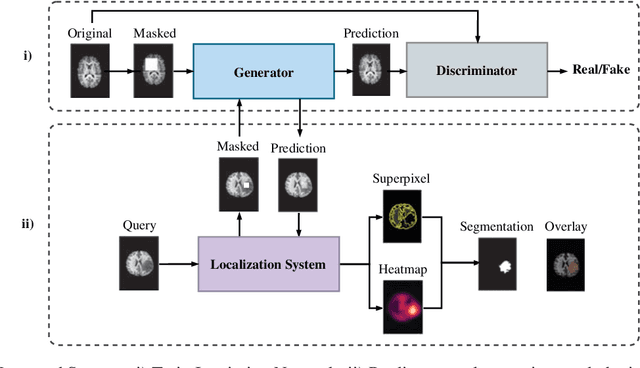
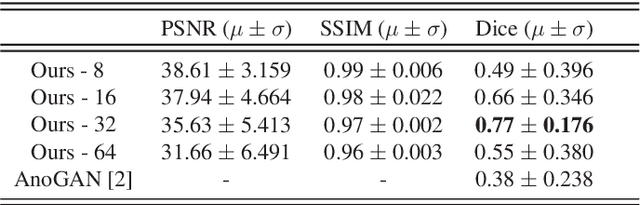
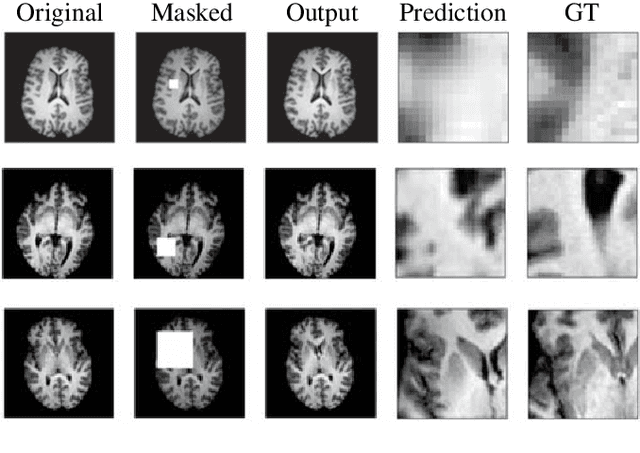
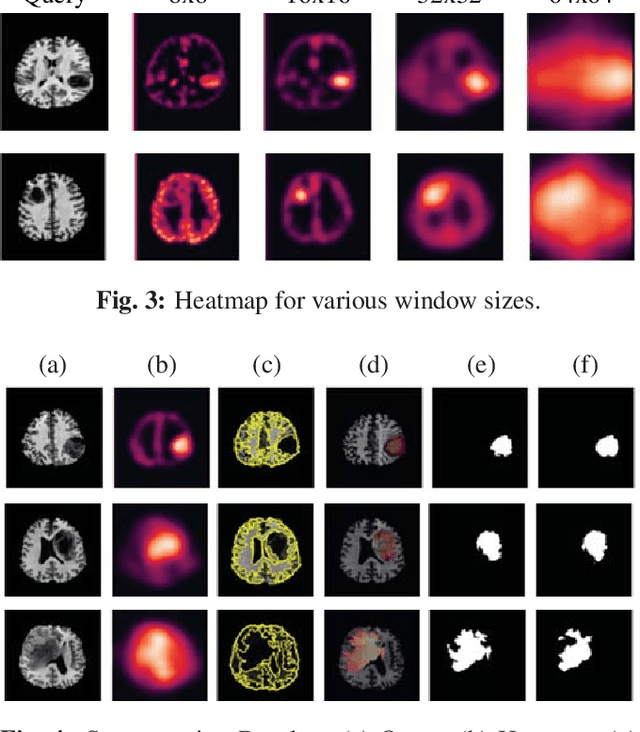
Abstract:Medical segmentation is performed to determine the bounds of regions of interest (ROI) prior to surgery. By allowing the study of growth, structure, and behaviour of the ROI in the planning phase, critical information can be obtained, increasing the likelihood of a successful operation. Usually, segmentations are performed manually or via machine learning methods trained on manual annotations. In contrast, this paper proposes a fully automatic, unsupervised inpainting-based brain tumour segmentation system for T1-weighted MRI. First, a deep convolutional neural network (DCNN) is trained to reconstruct missing healthy brain regions. Then, upon application, anomalous regions are determined by identifying areas of highest reconstruction loss. Finally, superpixel segmentation is performed to segment those regions. We show the proposed system is able to segment various sized and abstract tumours and achieves a mean and standard deviation Dice score of 0.771 and 0.176, respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge