Santiago de Leon-Martinez
From Latent to Observable Position-Based Click Models in Carousel Interfaces
Feb 18, 2026Abstract:Click models are a central component of learning and evaluation in recommender systems, yet most existing models are designed for single ranked-list interfaces. In contrast, modern recommender platforms increasingly use complex interfaces such as carousels, which consist of multiple swipeable lists that enable complex user browsing behaviors. In this paper, we study position-based click models in carousel interfaces and examine optimization methods, model structure, and alignment with user behavior. We propose three novel position-based models tailored to carousels, including the first position-based model without latent variables that incorporates observed examination signals derived from eye tracking data, called the Observed Examination Position-Based Model (OEPBM). We develop a general implementation of these carousel click models, supporting multiple optimization techniques and conduct experiments comparing gradient-based methods with classical approaches, namely expectation-maximization and maximum likelihood estimation. Our results show that gradient-based optimization consistently achieve better click likelihoods. Among the evaluated models, the OEPBM achieves the strongest performance in click prediction and produces examination patterns that most closely align to user behavior. However, we also demonstrate that strong click fit does not imply realistic modeling of user examination and browsing patterns. This reveals a fundamental limitation of click-only models in complex interfaces and the need for incorporating additional behavioral signals when designing click models for carousel-based recommender systems.
Eye Movements as Indicators of Deception: A Machine Learning Approach
May 05, 2025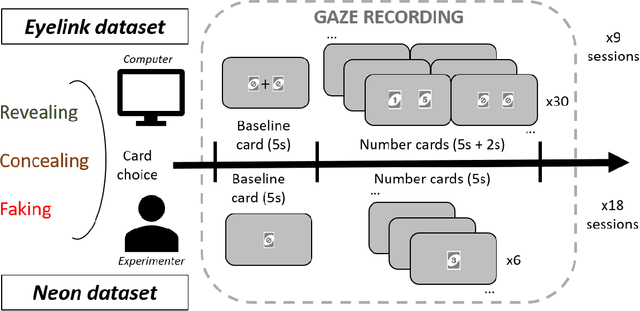
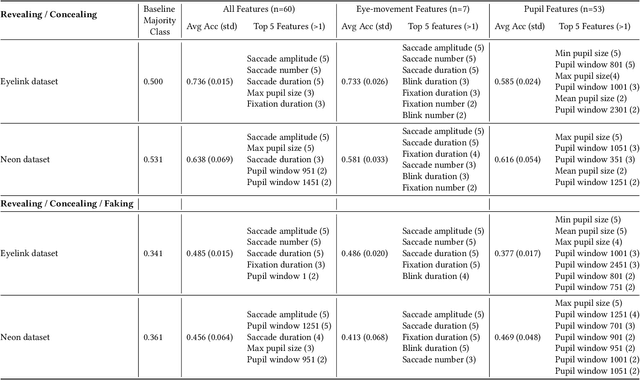
Abstract:Gaze may enhance the robustness of lie detectors but remains under-studied. This study evaluated the efficacy of AI models (using fixations, saccades, blinks, and pupil size) for detecting deception in Concealed Information Tests across two datasets. The first, collected with Eyelink 1000, contains gaze data from a computerized experiment where 87 participants revealed, concealed, or faked the value of a previously selected card. The second, collected with Pupil Neon, involved 36 participants performing a similar task but facing an experimenter. XGBoost achieved accuracies up to 74% in a binary classification task (Revealing vs. Concealing) and 49% in a more challenging three-classification task (Revealing vs. Concealing vs. Faking). Feature analysis identified saccade number, duration, amplitude, and maximum pupil size as the most important for deception prediction. These results demonstrate the feasibility of using gaze and AI to enhance lie detectors and encourage future research that may improve on this.
RecGaze: The First Eye Tracking and User Interaction Dataset for Carousel Interfaces
Apr 29, 2025Abstract:Carousel interfaces are widely used in e-commerce and streaming services, but little research has been devoted to them. Previous studies of interfaces for presenting search and recommendation results have focused on single ranked lists, but it appears their results cannot be extrapolated to carousels due to the added complexity. Eye tracking is a highly informative approach to understanding how users click, yet there are no eye tracking studies concerning carousels. There are very few interaction datasets on recommenders with carousel interfaces and none that contain gaze data. We introduce the RecGaze dataset: the first comprehensive feedback dataset on carousels that includes eye tracking results, clicks, cursor movements, and selection explanations. The dataset comprises of interactions from 3 movie selection tasks with 40 different carousel interfaces per user. In total, 87 users and 3,477 interactions are logged. In addition to the dataset, its description and possible use cases, we provide results of a survey on carousel design and the first analysis of gaze data on carousels, which reveals a golden triangle or F-pattern browsing behavior. Our work seeks to advance the field of carousel interfaces by providing the first dataset with eye tracking results on carousels. In this manner, we provide and encourage an empirical understanding of interactions with carousel interfaces, for building better recommender systems through gaze information, and also encourage the development of gaze-based recommenders.
Overshoot: Taking advantage of future gradients in momentum-based stochastic optimization
Jan 16, 2025Abstract:Overshoot is a novel, momentum-based stochastic gradient descent optimization method designed to enhance performance beyond standard and Nesterov's momentum. In conventional momentum methods, gradients from previous steps are aggregated with the gradient at current model weights before taking a step and updating the model. Rather than calculating gradient at the current model weights, Overshoot calculates the gradient at model weights shifted in the direction of the current momentum. This sacrifices the immediate benefit of using the gradient w.r.t. the exact model weights now, in favor of evaluating at a point, which will likely be more relevant for future updates. We show that incorporating this principle into momentum-based optimizers (SGD with momentum and Adam) results in faster convergence (saving on average at least 15% of steps). Overshoot consistently outperforms both standard and Nesterov's momentum across a wide range of tasks and integrates into popular momentum-based optimizers with zero memory and small computational overhead.
Understanding User Behavior in Carousel Recommendation Systems for Click Modeling and Learning to Rank
Jul 04, 2023Abstract:Carousels (also-known as multilists) have become the standard user interface for e-commerce platforms replacing the ranked list, the previous standard for recommender systems. While the research community has begun to focus on carousels, there are many unanswered questions and undeveloped areas when compared to the literature for ranked lists, which includes information retrieval research on the presentation of web search results. This work is an extended abstract for the RecSys 2023 Doctoral Symposium outlining a PhD project, with the main contribution of addressing the undeveloped areas in carousel recommenders: 1) the formulation of new click models and 2) learning to rank with click data. We present two significant barriers for this contribution and the field: lack of public datasets and lack of eye tracking user studies of browsing behavior. Clicks, the standard feedback collected by recommender systems, are insufficient to understand the whole interaction process of a user with a recommender requiring system designers to make assumptions, especially on browsing behavior. Eye tracking provides a means to elucidate the process and test these assumptions. Thus, to address these barriers and encourage future work, we will conduct an eye tracking user study within a carousel movie recommendation setting and make the dataset publicly available. Moreover, the insights learned on browsing behavior will help motivate the formulation of new click models and learning to rank.
Eye Tracking as a Source of Implicit Feedback in Recommender Systems: A Preliminary Analysis
May 12, 2023Abstract:Eye tracking in recommender systems can provide an additional source of implicit feedback, while helping to evaluate other sources of feedback. In this study, we use eye tracking data to inform a collaborative filtering model for movie recommendation providing an improvement over the click-based implementations and additionally analyze the area of interest (AOI) duration as related to the known information of click data and movies seen previously, showing AOI information consistently coincides with these items of interest.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge