Sanjay Modgil
Understanding the Skills Gap between Higher Education and Industry in the UK in Artificial Intelligence Sector
Aug 20, 2024Abstract:As Artificial Intelligence (AI) changes how businesses work, there is a growing need for people who can work in this sector. This paper investigates how well universities in United Kingdom offering courses in AI, prepare students for jobs in the real world. To gain insight into the differences between university curricula and industry demands we review the contents of taught courses and job advertisement portals. By using custom data scraping tools to gather information from job advertisements and university curricula, and frequency and Naive Bayes classifier analysis, this study will show exactly what skills industry is looking for. In this study we identified 12 skill categories that were used for mapping. The study showed that the university curriculum in the AI domain is well balanced in most technical skills, including Programming and Machine learning subjects, but have a gap in Data Science and Maths and Statistics skill categories.
Towards Dialogues for Joint Human-AI Reasoning and Value Alignment
May 28, 2024Abstract:We argue that enabling human-AI dialogue, purposed to support joint reasoning (i.e., 'inquiry'), is important for ensuring that AI decision making is aligned with human values and preferences. In particular, we point to logic-based models of argumentation and dialogue, and suggest that the traditional focus on persuasion dialogues be replaced by a focus on inquiry dialogues, and the distinct challenges that joint inquiry raises. Given recent dramatic advances in the performance of large language models (LLMs), and the anticipated increase in their use for decision making, we provide a roadmap for research into inquiry dialogues for supporting joint human-LLM reasoning tasks that are ethically salient, and that thereby require that decisions are value aligned.
Moral Uncertainty and the Problem of Fanaticism
Dec 18, 2023Abstract:While there is universal agreement that agents ought to act ethically, there is no agreement as to what constitutes ethical behaviour. To address this problem, recent philosophical approaches to `moral uncertainty' propose aggregation of multiple ethical theories to guide agent behaviour. However, one of the foundational proposals for aggregation - Maximising Expected Choiceworthiness (MEC) - has been criticised as being vulnerable to fanaticism; the problem of an ethical theory dominating agent behaviour despite low credence (confidence) in said theory. Fanaticism thus undermines the `democratic' motivation for accommodating multiple ethical perspectives. The problem of fanaticism has not yet been mathematically defined. Representing moral uncertainty as an instance of social welfare aggregation, this paper contributes to the field of moral uncertainty by 1) formalising the problem of fanaticism as a property of social welfare functionals and 2) providing non-fanatical alternatives to MEC, i.e. Highest k-trimmed Mean and Highest Median.
On the Graded Acceptability of Arguments in Abstract and Instantiated Argumentation
Nov 08, 2018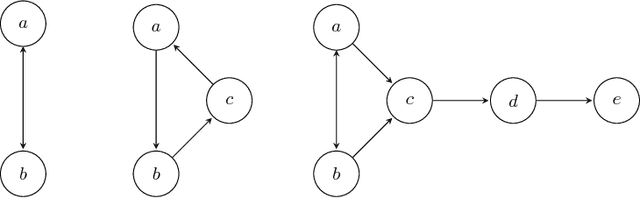
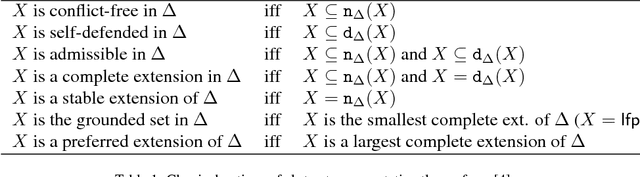

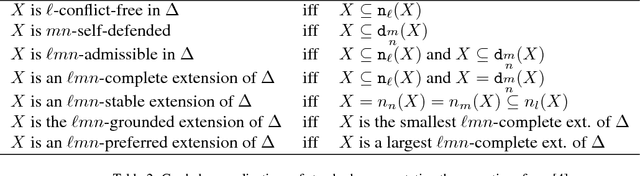
Abstract:The paper develops a formal theory of the degree of justification of arguments, which relies solely on the structure of an argumentation framework, and which can be successfully interfaced with approaches to instantiated argumentation. The theory is developed in three steps. First, the paper introduces a graded generalization of the two key notions underpinning Dung's semantics: self-defense and conflict-freeness. This leads to a natural generalization of Dung's semantics, whereby standard extensions are weakened or strengthened depending on the level of self-defense and conflict-freeness they meet. The paper investigates the fixpoint theory of these semantics, establishing existence results for them. Second, the paper shows how graded semantics readily provide an approach to argument rankings, offering a novel contribution to the recently growing research programme on ranking-based semantics. Third, this novel approach to argument ranking is applied and studied in the context of instantiated argumentation frameworks, and in so doing is shown to account for a simple form of accrual of arguments within the Dung paradigm. Finally, the theory is compared in detail with existing approaches.
A General Account of Argumentation with Preferences
Apr 18, 2018

Abstract:This paper builds on the recent ASPIC+ formalism, to develop a general framework for argumentation with preferences. We motivate a revised definition of conflict free sets of arguments, adapt ASPIC+ to accommodate a broader range of instantiating logics, and show that under some assumptions, the resulting framework satisfies key properties and rationality postulates. We then show that the generalised framework accommodates Tarskian logic instantiations extended with preferences, and then study instantiations of the framework by classical logic approaches to argumentation. We conclude by arguing that ASPIC+'s modelling of defeasible inference rules further testifies to the generality of the framework, and then examine and counter recent critiques of Dung's framework and its extensions to accommodate preferences.
* This paper contains correction to errors in the original paper which appears in the journal Artificial Intelligence
Prioritised Default Logic as Argumentation with Partial Order Default Priorities
Aug 25, 2016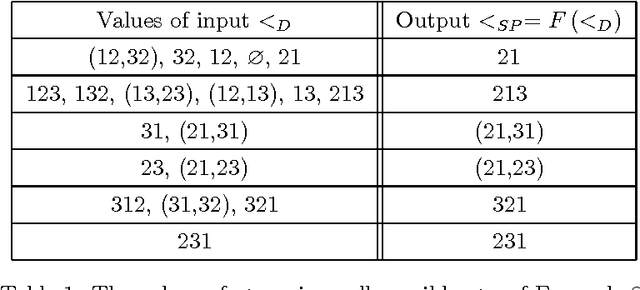
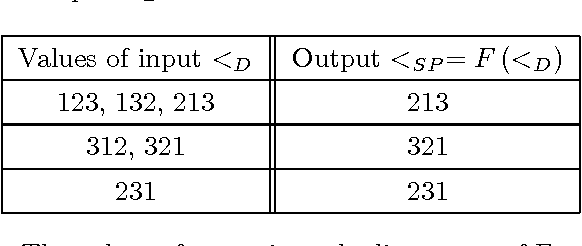
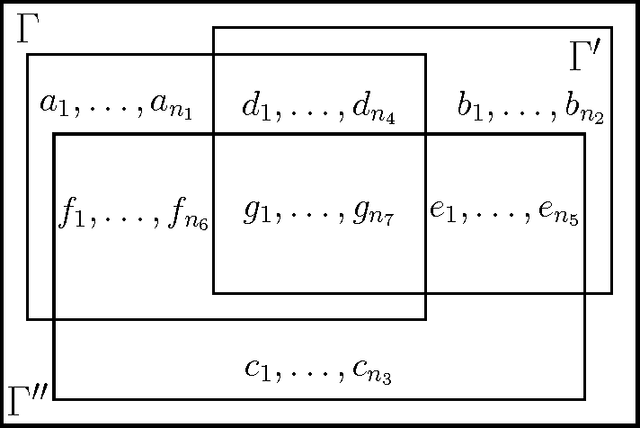
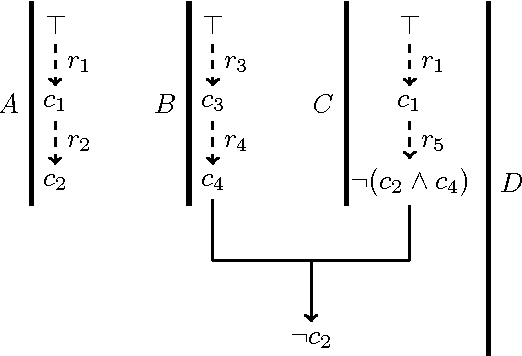
Abstract:We express Brewka's prioritised default logic (PDL) as argumentation using ASPIC+. By representing PDL as argumentation and designing an argument preference relation that takes the argument structure into account, we prove that the conclusions of the justified arguments correspond to the PDL extensions. We will first assume that the default priority is total, and then generalise to the case where it is a partial order. This provides a characterisation of non-monotonic inference in PDL as an exchange of argument and counter-argument, providing a basis for distributed non-monotonic reasoning in the form of dialogue.
Argumentation Semantics for Prioritised Default Logic
Jul 01, 2015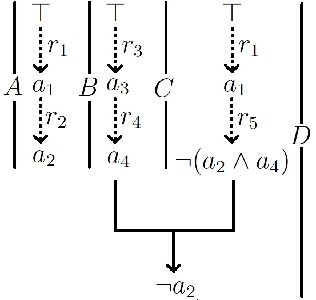



Abstract:We endow prioritised default logic (PDL) with argumentation semantics using the ASPIC+ framework for structured argumentation, and prove that the conclusions of the justified arguments are exactly the prioritised default extensions. Argumentation semantics for PDL will allow for the application of argument game proof theories to the process of inference in PDL, making the reasons for accepting a conclusion transparent and the inference process more intuitive. This also opens up the possibility for argumentation-based distributed reasoning and communication amongst agents with PDL representations of mental attitudes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge