Sani Umar
Data Poisoning Attacks on EEG Signal-based Risk Assessment Systems
Feb 08, 2023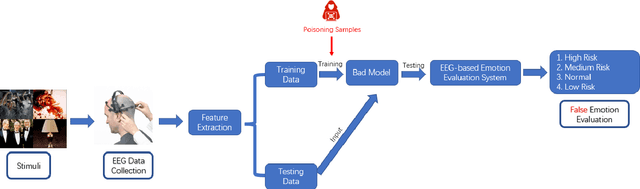
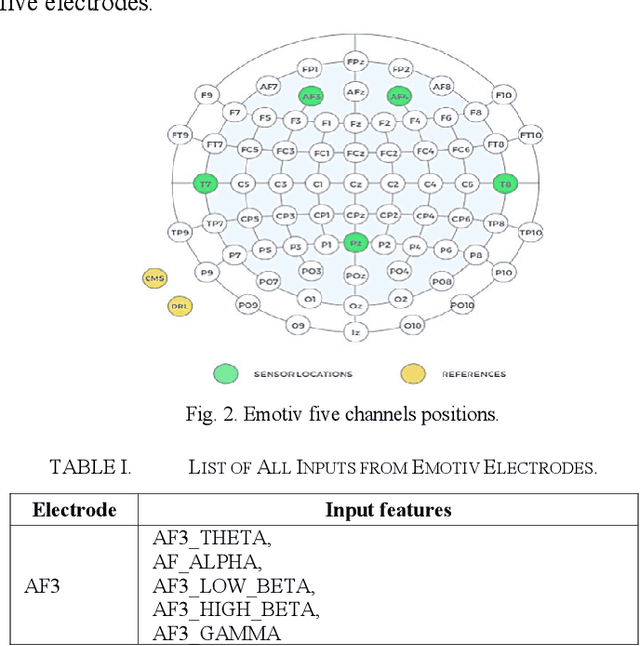
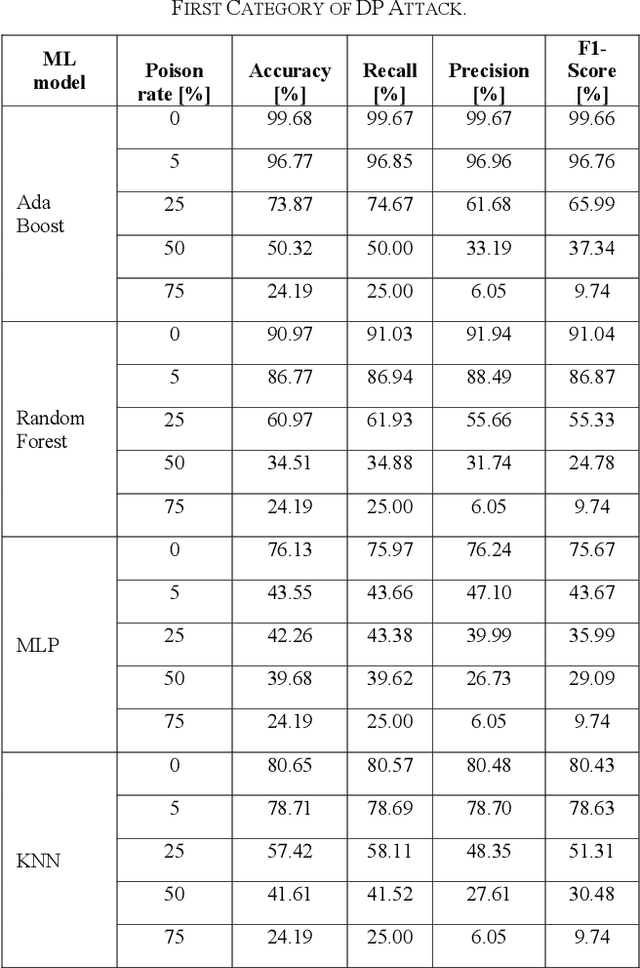
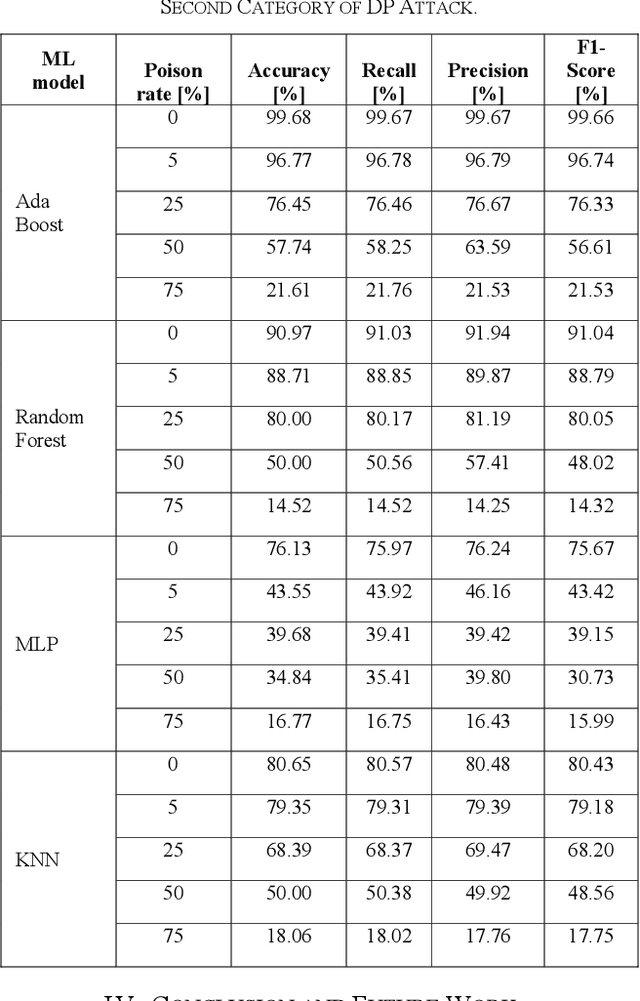
Abstract:Industrial insider risk assessment using electroencephalogram (EEG) signals has consistently attracted a lot of research attention. However, EEG signal-based risk assessment systems, which could evaluate the emotional states of humans, have shown several vulnerabilities to data poison attacks. In this paper, from the attackers' perspective, data poison attacks involving label-flipping occurring in the training stages of different machine learning models intrude on the EEG signal-based risk assessment systems using these machine learning models. This paper aims to propose two categories of label-flipping methods to attack different machine learning classifiers including Adaptive Boosting (AdaBoost), Multilayer Perceptron (MLP), Random Forest, and K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) dedicated to the classification of 4 different human emotions using EEG signals. This aims to degrade the performance of the aforementioned machine learning models concerning the classification task. The experimental results show that the proposed data poison attacks are model-agnostically effective whereas different models have different resilience to the data poison attacks.
Explainable Data Poison Attacks on Human Emotion Evaluation Systems based on EEG Signals
Jan 17, 2023



Abstract:The major aim of this paper is to explain the data poisoning attacks using label-flipping during the training stage of the electroencephalogram (EEG) signal-based human emotion evaluation systems deploying Machine Learning models from the attackers' perspective. Human emotion evaluation using EEG signals has consistently attracted a lot of research attention. The identification of human emotional states based on EEG signals is effective to detect potential internal threats caused by insider individuals. Nevertheless, EEG signal-based human emotion evaluation systems have shown several vulnerabilities to data poison attacks. The findings of the experiments demonstrate that the suggested data poison assaults are model-independently successful, although various models exhibit varying levels of resilience to the attacks. In addition, the data poison attacks on the EEG signal-based human emotion evaluation systems are explained with several Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) methods, including Shapley Additive Explanation (SHAP) values, Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations (LIME), and Generated Decision Trees. And the codes of this paper are publicly available on GitHub.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge