Sanaz Mojrian
Resource allocation optimization using artificial intelligence methods in various computing paradigms: A Review
Mar 23, 2022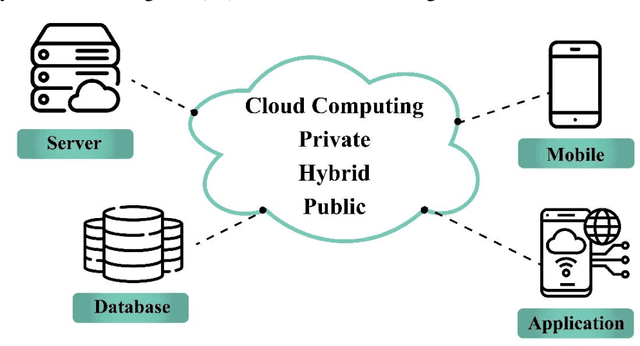
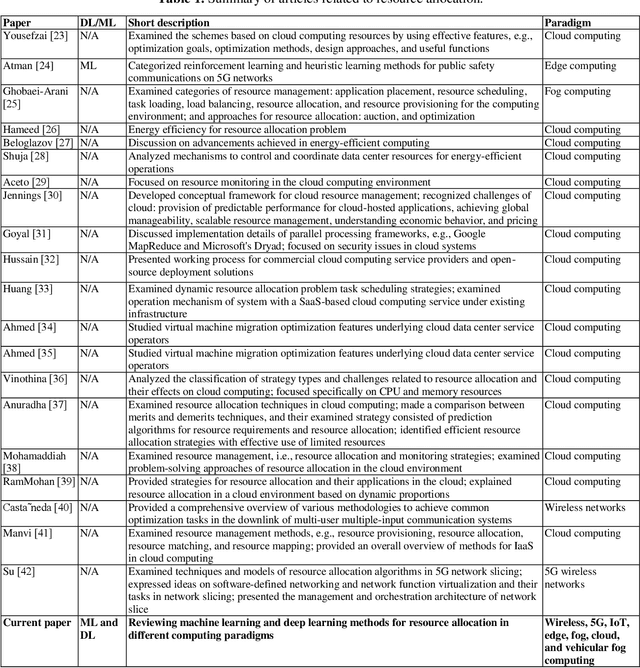
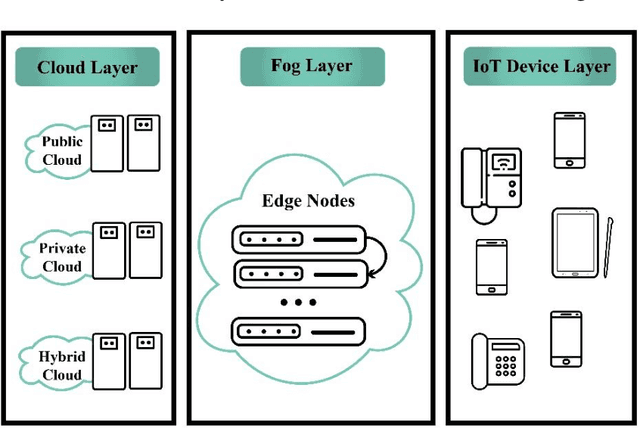
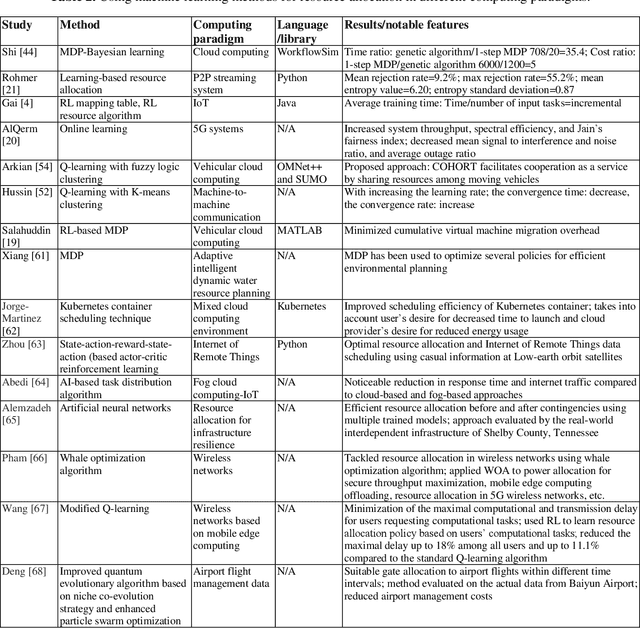
Abstract:With the advent of smart devices, the demand for various computational paradigms such as the Internet of Things, fog, and cloud computing has increased. However, effective resource allocation remains challenging in these paradigms. This paper presents a comprehensive literature review on the application of artificial intelligence (AI) methods such as deep learning (DL) and machine learning (ML) for resource allocation optimization in computational paradigms. To the best of our knowledge, there are no existing reviews on AI-based resource allocation approaches in different computational paradigms. The reviewed ML-based approaches are categorized as supervised and reinforcement learning (RL). Moreover, DL-based approaches and their combination with RL are surveyed. The review ends with a discussion on open research directions and a conclusion.
A Survey of Applications of Artificial Intelligence for Myocardial Infarction Disease Diagnosis
Jul 05, 2021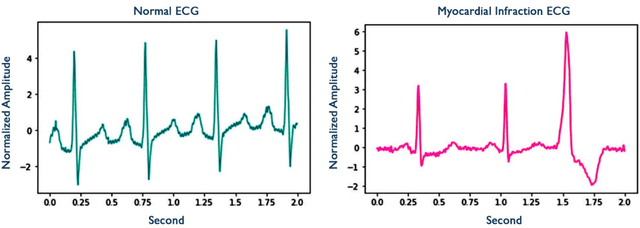


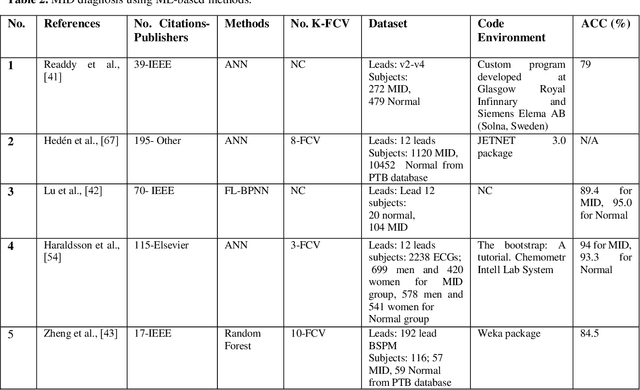
Abstract:Myocardial infarction disease (MID) is caused to the rapid progress of undiagnosed coronary artery disease (CAD) that indicates the injury of a heart cell by decreasing the blood flow to the cardiac muscles. MID is the leading cause of death in middle-aged and elderly subjects all over the world. In general, raw Electrocardiogram (ECG) signals are tested for MID identification by clinicians that is exhausting, time-consuming, and expensive. Artificial intelligence-based methods are proposed to handle the problems to diagnose MID on the ECG signals automatically. Hence, in this survey paper, artificial intelligence-based methods, including machine learning and deep learning, are review for MID diagnosis on the ECG signals. Using the methods demonstrate that the feature extraction and selection of ECG signals required to be handcrafted in the ML methods. In contrast, these tasks are explored automatically in the DL methods. Based on our best knowledge, Deep Convolutional Neural Network (DCNN) methods are highly required methods developed for the early diagnosis of MID on the ECG signals. Most researchers have tended to use DCNN methods, and no studies have surveyed using artificial intelligence methods for MID diagnosis on the ECG signals.
Hybrid Machine Learning Model of Extreme Learning Machine Radial basis function for Breast Cancer Detection and Diagnosis; a Multilayer Fuzzy Expert System
Oct 29, 2019
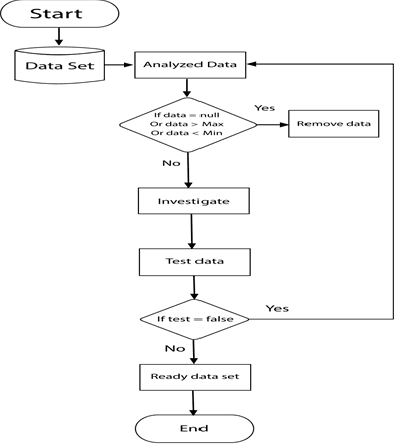
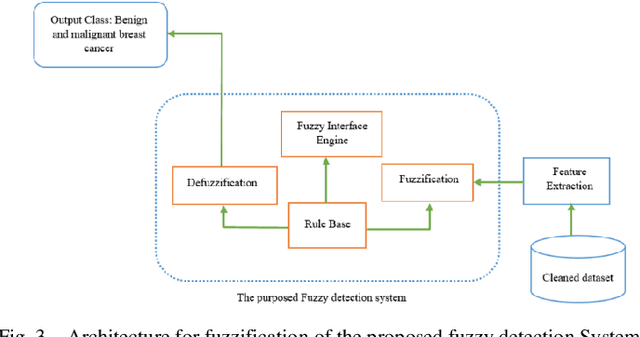
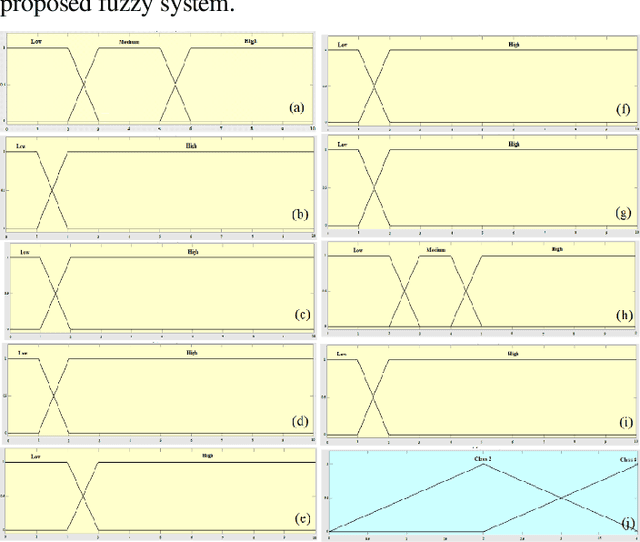
Abstract:Mammography is often used as the most common laboratory method for the detection of breast cancer, yet associated with the high cost and many side effects. Machine learning prediction as an alternative method has shown promising results. This paper presents a method based on a multilayer fuzzy expert system for the detection of breast cancer using an extreme learning machine (ELM) classification model integrated with radial basis function (RBF) kernel called ELM-RBF, considering the Wisconsin dataset. The performance of the proposed model is further compared with a linear-SVM model. The proposed model outperforms the linear-SVM model with RMSE, R2, MAPE equal to 0.1719, 0.9374 and 0.0539, respectively. Furthermore, both models are studied in terms of criteria of accuracy, precision, sensitivity, specificity, validation, true positive rate (TPR), and false-negative rate (FNR). The ELM-RBF model for these criteria presents better performance compared to the SVM model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge