Amir Mashmool
A Survey of Applications of Artificial Intelligence for Myocardial Infarction Disease Diagnosis
Jul 05, 2021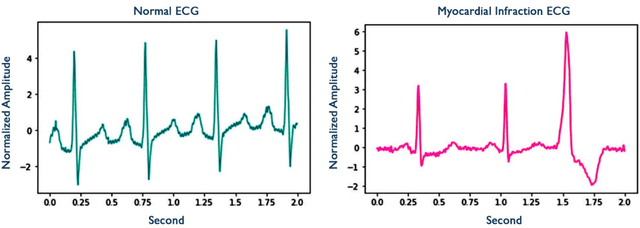


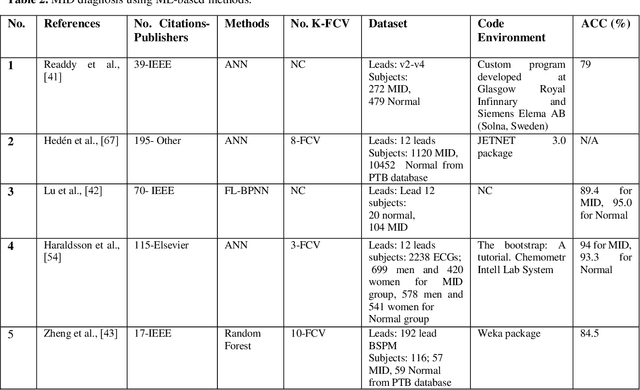
Abstract:Myocardial infarction disease (MID) is caused to the rapid progress of undiagnosed coronary artery disease (CAD) that indicates the injury of a heart cell by decreasing the blood flow to the cardiac muscles. MID is the leading cause of death in middle-aged and elderly subjects all over the world. In general, raw Electrocardiogram (ECG) signals are tested for MID identification by clinicians that is exhausting, time-consuming, and expensive. Artificial intelligence-based methods are proposed to handle the problems to diagnose MID on the ECG signals automatically. Hence, in this survey paper, artificial intelligence-based methods, including machine learning and deep learning, are review for MID diagnosis on the ECG signals. Using the methods demonstrate that the feature extraction and selection of ECG signals required to be handcrafted in the ML methods. In contrast, these tasks are explored automatically in the DL methods. Based on our best knowledge, Deep Convolutional Neural Network (DCNN) methods are highly required methods developed for the early diagnosis of MID on the ECG signals. Most researchers have tended to use DCNN methods, and no studies have surveyed using artificial intelligence methods for MID diagnosis on the ECG signals.
Early detection of the advanced persistent threat attack using performance analysis of deep learning
Sep 19, 2020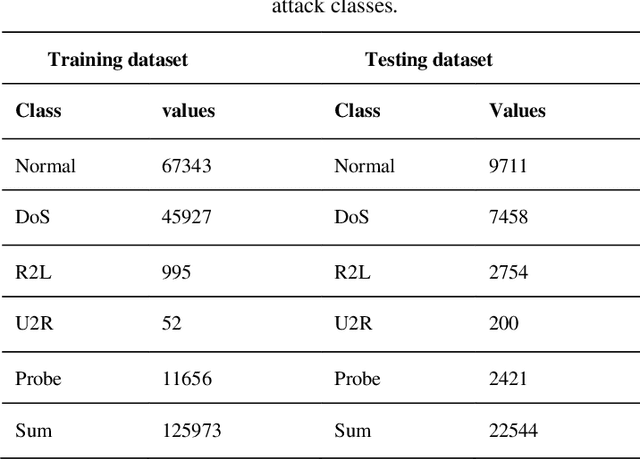

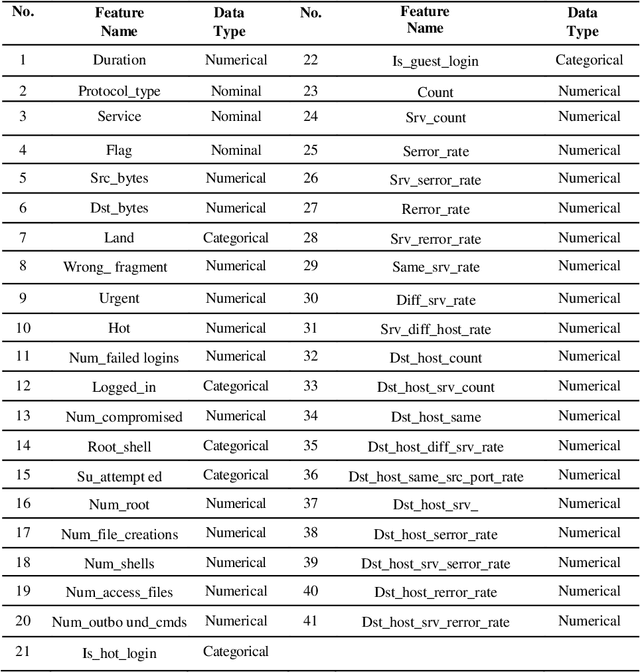
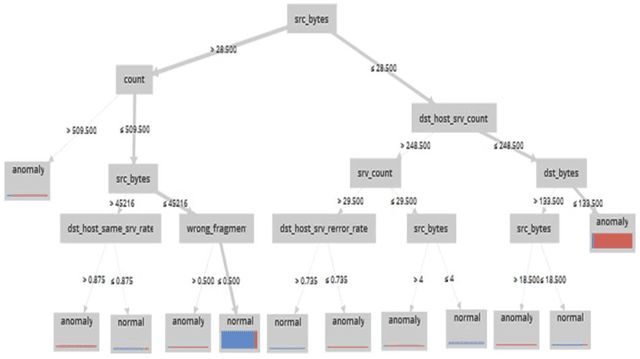
Abstract:One of the most common and important destructive attacks on the victim system is Advanced Persistent Threat (APT)-attack. The APT attacker can achieve his hostile goals by obtaining information and gaining financial benefits regarding the infrastructure of a network. One of the solutions to detect a secret APT attack is using network traffic. Due to the nature of the APT attack in terms of being on the network for a long time and the fact that the network may crash because of high traffic, it is difficult to detect this type of attack. Hence, in this study, machine learning methods such as C5.0 decision tree, Bayesian network and deep neural network are used for timely detection and classification of APT-attacks on the NSL-KDD dataset. Moreover, 10-fold cross validation method is used to experiment these models. As a result, the accuracy (ACC) of the C5.0 decision tree, Bayesian network and 6-layer deep learning models is obtained as 95.64%, 88.37% and 98.85%, respectively, and also, in terms of the important criterion of the false positive rate (FPR), the FPR value for the C5.0 decision tree, Bayesian network and 6-layer deep learning models is obtained as 2.56, 10.47 and 1.13, respectively. Other criterions such as sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, false negative rate and F-measure are also investigated for the models, and the experimental results show that the deep learning model with automatic multi-layered extraction of features has the best performance for timely detection of an APT-attack comparing to other classification models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge