Samuel Maddock
GEM+: Scalable State-of-the-Art Private Synthetic Data with Generator Networks
Nov 12, 2025
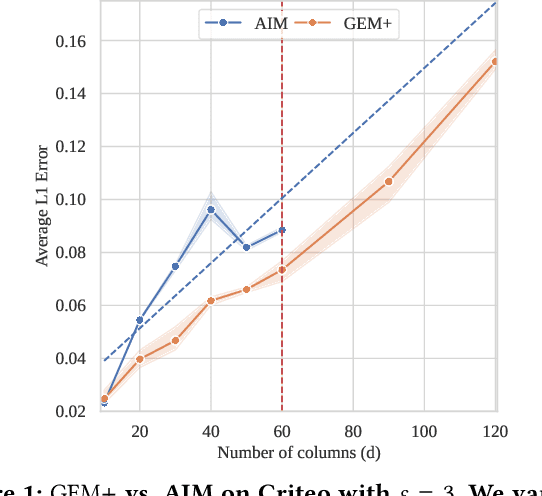
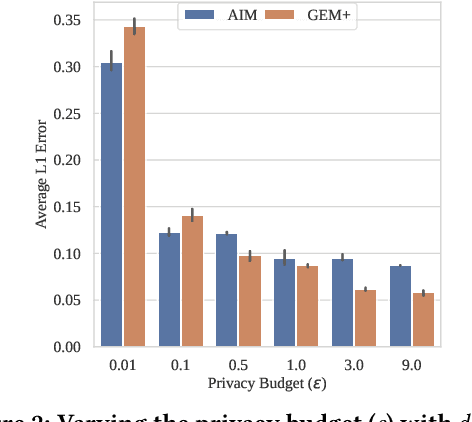
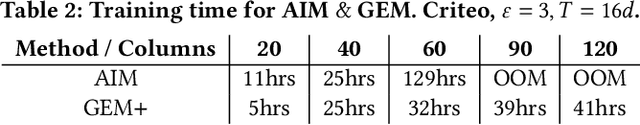
Abstract:State-of-the-art differentially private synthetic tabular data has been defined by adaptive 'select-measure-generate' frameworks, exemplified by methods like AIM. These approaches iteratively measure low-order noisy marginals and fit graphical models to produce synthetic data, enabling systematic optimisation of data quality under privacy constraints. Graphical models, however, are inefficient for high-dimensional data because they require substantial memory and must be retrained from scratch whenever the graph structure changes, leading to significant computational overhead. Recent methods, like GEM, overcome these limitations by using generator neural networks for improved scalability. However, empirical comparisons have mostly focused on small datasets, limiting real-world applicability. In this work, we introduce GEM+, which integrates AIM's adaptive measurement framework with GEM's scalable generator network. Our experiments show that GEM+ outperforms AIM in both utility and scalability, delivering state-of-the-art results while efficiently handling datasets with over a hundred columns, where AIM fails due to memory and computational overheads.
Private Federated Multiclass Post-hoc Calibration
Oct 02, 2025Abstract:Calibrating machine learning models so that predicted probabilities better reflect the true outcome frequencies is crucial for reliable decision-making across many applications. In Federated Learning (FL), the goal is to train a global model on data which is distributed across multiple clients and cannot be centralized due to privacy concerns. FL is applied in key areas such as healthcare and finance where calibration is strongly required, yet federated private calibration has been largely overlooked. This work introduces the integration of post-hoc model calibration techniques within FL. Specifically, we transfer traditional centralized calibration methods such as histogram binning and temperature scaling into federated environments and define new methods to operate them under strong client heterogeneity. We study (1) a federated setting and (2) a user-level Differential Privacy (DP) setting and demonstrate how both federation and DP impacts calibration accuracy. We propose strategies to mitigate degradation commonly observed under heterogeneity and our findings highlight that our federated temperature scaling works best for DP-FL whereas our weighted binning approach is best when DP is not required.
Synthetic Tabular Data: Methods, Attacks and Defenses
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:Synthetic data is often positioned as a solution to replace sensitive fixed-size datasets with a source of unlimited matching data, freed from privacy concerns. There has been much progress in synthetic data generation over the last decade, leveraging corresponding advances in machine learning and data analytics. In this survey, we cover the key developments and the main concepts in tabular synthetic data generation, including paradigms based on probabilistic graphical models and on deep learning. We provide background and motivation, before giving a technical deep-dive into the methodologies. We also address the limitations of synthetic data, by studying attacks that seek to retrieve information about the original sensitive data. Finally, we present extensions and open problems in this area.
Leveraging Vertical Public-Private Split for Improved Synthetic Data Generation
Apr 15, 2025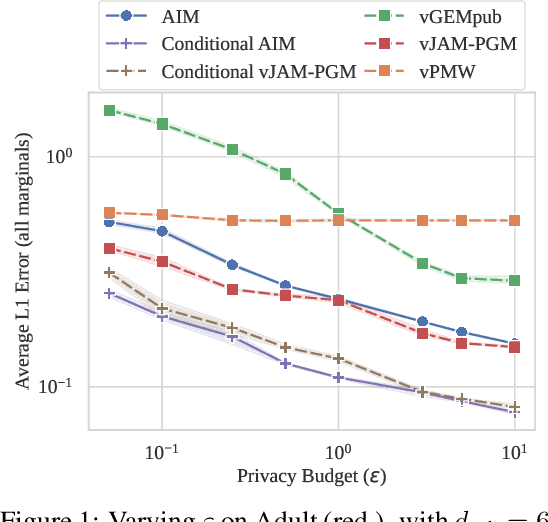


Abstract:Differentially Private Synthetic Data Generation (DP-SDG) is a key enabler of private and secure tabular-data sharing, producing artificial data that carries through the underlying statistical properties of the input data. This typically involves adding carefully calibrated statistical noise to guarantee individual privacy, at the cost of synthetic data quality. Recent literature has explored scenarios where a small amount of public data is used to help enhance the quality of synthetic data. These methods study a horizontal public-private partitioning which assumes access to a small number of public rows that can be used for model initialization, providing a small utility gain. However, realistic datasets often naturally consist of public and private attributes, making a vertical public-private partitioning relevant for practical synthetic data deployments. We propose a novel framework that adapts horizontal public-assisted methods into the vertical setting. We compare this framework against our alternative approach that uses conditional generation, highlighting initial limitations of public-data assisted methods and proposing future research directions to address these challenges.
FLAIM: AIM-based Synthetic Data Generation in the Federated Setting
Oct 05, 2023



Abstract:Preserving individual privacy while enabling collaborative data sharing is crucial for organizations. Synthetic data generation is one solution, producing artificial data that mirrors the statistical properties of private data. While numerous techniques have been devised under differential privacy, they predominantly assume data is centralized. However, data is often distributed across multiple clients in a federated manner. In this work, we initiate the study of federated synthetic tabular data generation. Building upon a SOTA central method known as AIM, we present DistAIM and FLAIM. We show it is straightforward to distribute AIM, extending a recent approach based on secure multi-party computation which necessitates additional overhead, making it less suited to federated scenarios. We then demonstrate that naively federating AIM can lead to substantial degradation in utility under the presence of heterogeneity. To mitigate both issues, we propose an augmented FLAIM approach that maintains a private proxy of heterogeneity. We simulate our methods across a range of benchmark datasets under different degrees of heterogeneity and show this can improve utility while reducing overhead.
CANIFE: Crafting Canaries for Empirical Privacy Measurement in Federated Learning
Oct 06, 2022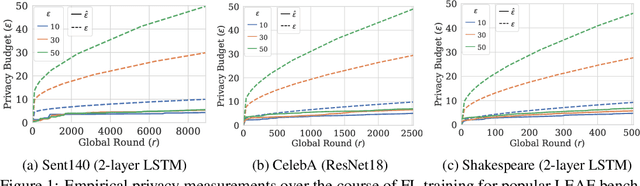

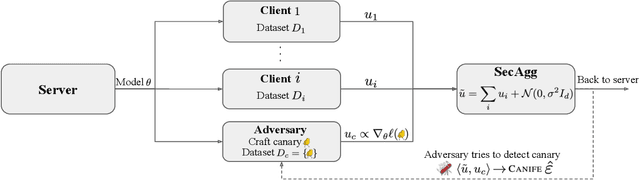
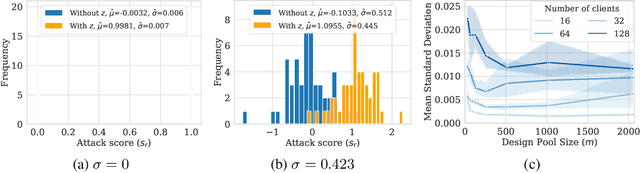
Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) is a setting for training machine learning models in distributed environments where the clients do not share their raw data but instead send model updates to a server. However, model updates can be subject to attacks and leak private information. Differential Privacy (DP) is a leading mitigation strategy which involves adding noise to clipped model updates, trading off performance for strong theoretical privacy guarantees. Previous work has shown that the threat model of DP is conservative and that the obtained guarantees may be vacuous or may not directly translate to information leakage in practice. In this paper, we aim to achieve a tighter measurement of the model exposure by considering a realistic threat model. We propose a novel method, CANIFE, that uses canaries - carefully crafted samples by a strong adversary to evaluate the empirical privacy of a training round. We apply this attack to vision models trained on CIFAR-10 and CelebA and to language models trained on Sent140 and Shakespeare. In particular, in realistic FL scenarios, we demonstrate that the empirical epsilon obtained with CANIFE is 2-7x lower than the theoretical bound.
Federated Boosted Decision Trees with Differential Privacy
Oct 06, 2022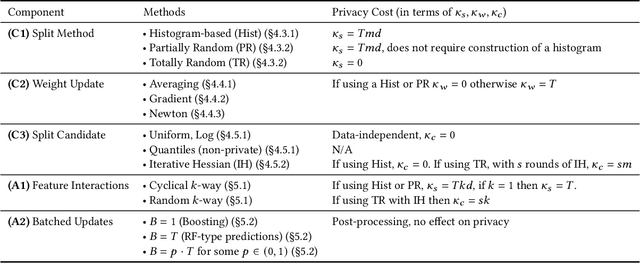
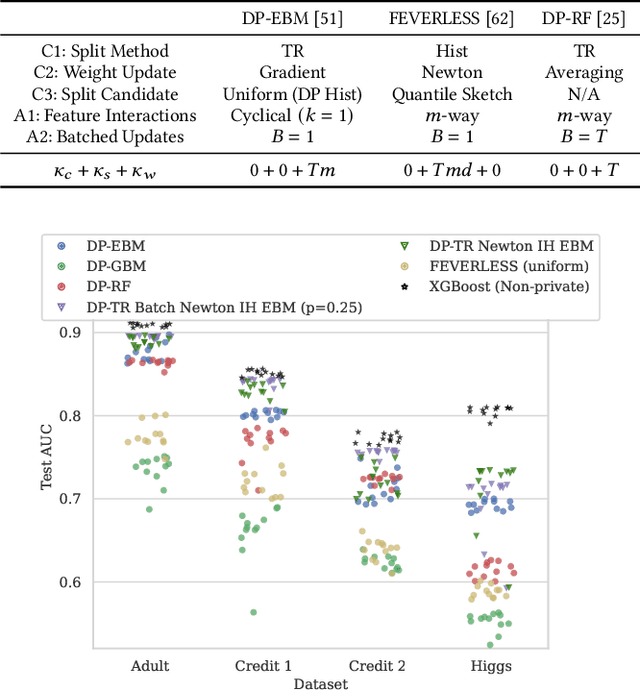


Abstract:There is great demand for scalable, secure, and efficient privacy-preserving machine learning models that can be trained over distributed data. While deep learning models typically achieve the best results in a centralized non-secure setting, different models can excel when privacy and communication constraints are imposed. Instead, tree-based approaches such as XGBoost have attracted much attention for their high performance and ease of use; in particular, they often achieve state-of-the-art results on tabular data. Consequently, several recent works have focused on translating Gradient Boosted Decision Tree (GBDT) models like XGBoost into federated settings, via cryptographic mechanisms such as Homomorphic Encryption (HE) and Secure Multi-Party Computation (MPC). However, these do not always provide formal privacy guarantees, or consider the full range of hyperparameters and implementation settings. In this work, we implement the GBDT model under Differential Privacy (DP). We propose a general framework that captures and extends existing approaches for differentially private decision trees. Our framework of methods is tailored to the federated setting, and we show that with a careful choice of techniques it is possible to achieve very high utility while maintaining strong levels of privacy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge