Salsabila Zahirah Pranida
A Parallel Cross-Lingual Benchmark for Multimodal Idiomaticity Understanding
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Potentially idiomatic expressions (PIEs) construe meanings inherently tied to the everyday experience of a given language community. As such, they constitute an interesting challenge for assessing the linguistic (and to some extent cultural) capabilities of NLP systems. In this paper, we present XMPIE, a parallel multilingual and multimodal dataset of potentially idiomatic expressions. The dataset, containing 34 languages and over ten thousand items, allows comparative analyses of idiomatic patterns among language-specific realisations and preferences in order to gather insights about shared cultural aspects. This parallel dataset allows to evaluate model performance for a given PIE in different languages and whether idiomatic understanding in one language can be transferred to another. Moreover, the dataset supports the study of PIEs across textual and visual modalities, to measure to what extent PIE understanding in one modality transfers or implies in understanding in another modality (text vs. image). The data was created by language experts, with both textual and visual components crafted under multilingual guidelines, and each PIE is accompanied by five images representing a spectrum from idiomatic to literal meanings, including semantically related and random distractors. The result is a high-quality benchmark for evaluating multilingual and multimodal idiomatic language understanding.
Crowdsource, Crawl, or Generate? Creating SEA-VL, a Multicultural Vision-Language Dataset for Southeast Asia
Mar 10, 2025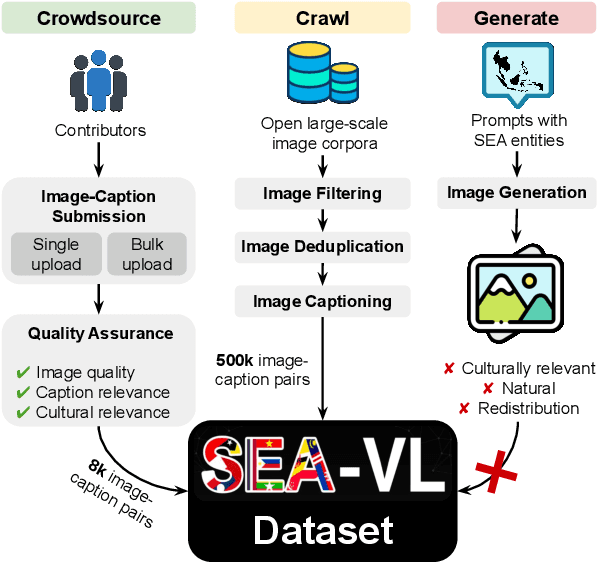
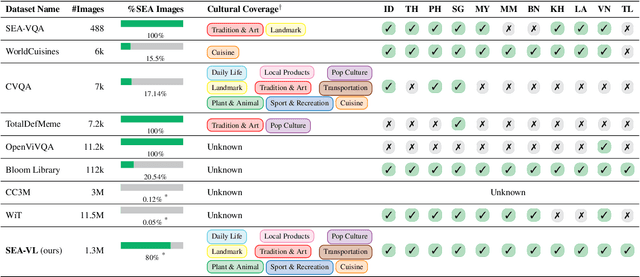
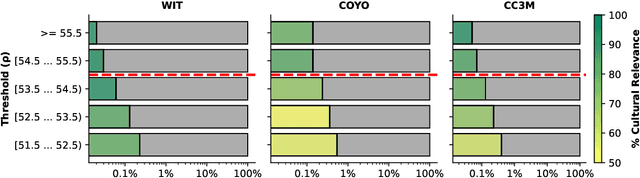

Abstract:Southeast Asia (SEA) is a region of extraordinary linguistic and cultural diversity, yet it remains significantly underrepresented in vision-language (VL) research. This often results in artificial intelligence (AI) models that fail to capture SEA cultural nuances. To fill this gap, we present SEA-VL, an open-source initiative dedicated to developing high-quality, culturally relevant data for SEA languages. By involving contributors from SEA countries, SEA-VL aims to ensure better cultural relevance and diversity, fostering greater inclusivity of underrepresented languages in VL research. Beyond crowdsourcing, our initiative goes one step further in the exploration of the automatic collection of culturally relevant images through crawling and image generation. First, we find that image crawling achieves approximately ~85% cultural relevance while being more cost- and time-efficient than crowdsourcing. Second, despite the substantial progress in generative vision models, synthetic images remain unreliable in accurately reflecting SEA cultures. The generated images often fail to reflect the nuanced traditions and cultural contexts of the region. Collectively, we gather 1.28M SEA culturally-relevant images, more than 50 times larger than other existing datasets. Through SEA-VL, we aim to bridge the representation gap in SEA, fostering the development of more inclusive AI systems that authentically represent diverse cultures across SEA.
Synthetic Data Generation for Culturally Nuanced Commonsense Reasoning in Low-Resource Languages
Feb 18, 2025

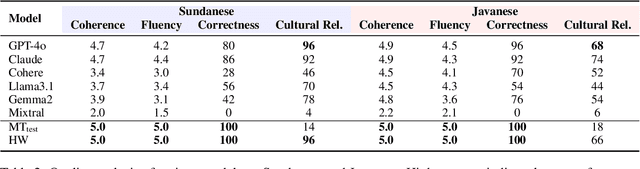

Abstract:Quantifying reasoning capability in low-resource languages remains a challenge in NLP due to data scarcity and limited access to annotators. While LLM-assisted dataset construction has proven useful for medium- and high-resource languages, its effectiveness in low-resource languages, particularly for commonsense reasoning, is still unclear. In this paper, we compare three dataset creation strategies: (1) LLM-assisted dataset generation, (2) machine translation, and (3) human-written data by native speakers, to build a culturally nuanced story comprehension dataset. We focus on Javanese and Sundanese, two major local languages in Indonesia, and evaluate the effectiveness of open-weight and closed-weight LLMs in assisting dataset creation through extensive manual validation. To assess the utility of synthetic data, we fine-tune language models on classification and generation tasks using this data and evaluate performance on a human-written test set. Our findings indicate that LLM-assisted data creation outperforms machine translation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge